Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 3990-4003
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3990
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3990
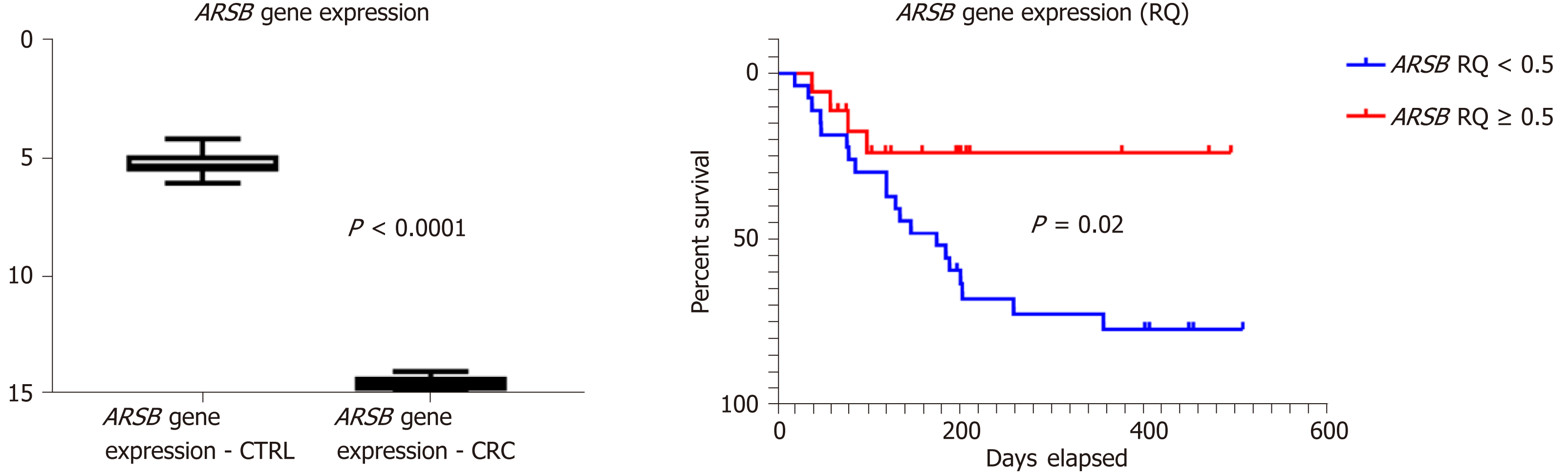
Figure 1 ARSB gene expression level is decreased in blood of patients with colorectal cancer, versus control group (left), the low level being a negative prognostic factor (right).
CRC: Colorectal cancer.
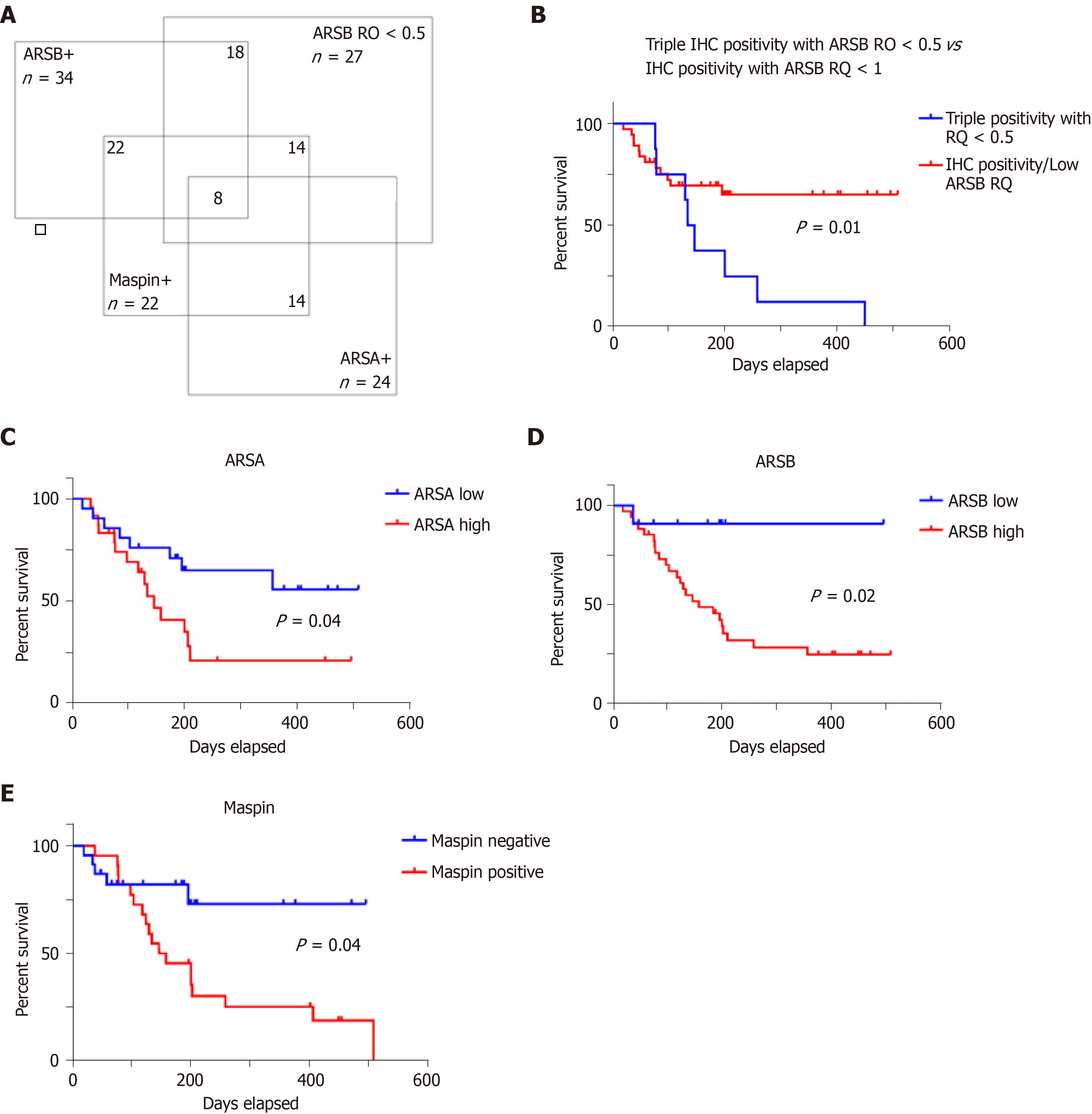
Figure 2 One third of colorectal cancer specimens (14/45 cases) show triple positivity for ARSA/ARSB/maspin and low circulating ARSB gene expression level (A), as independent negative prognostic factor (B); the overall survival also depends on independently evaluation of protein tissue level of ARSA (C), ARSB (D) and maspin (E).
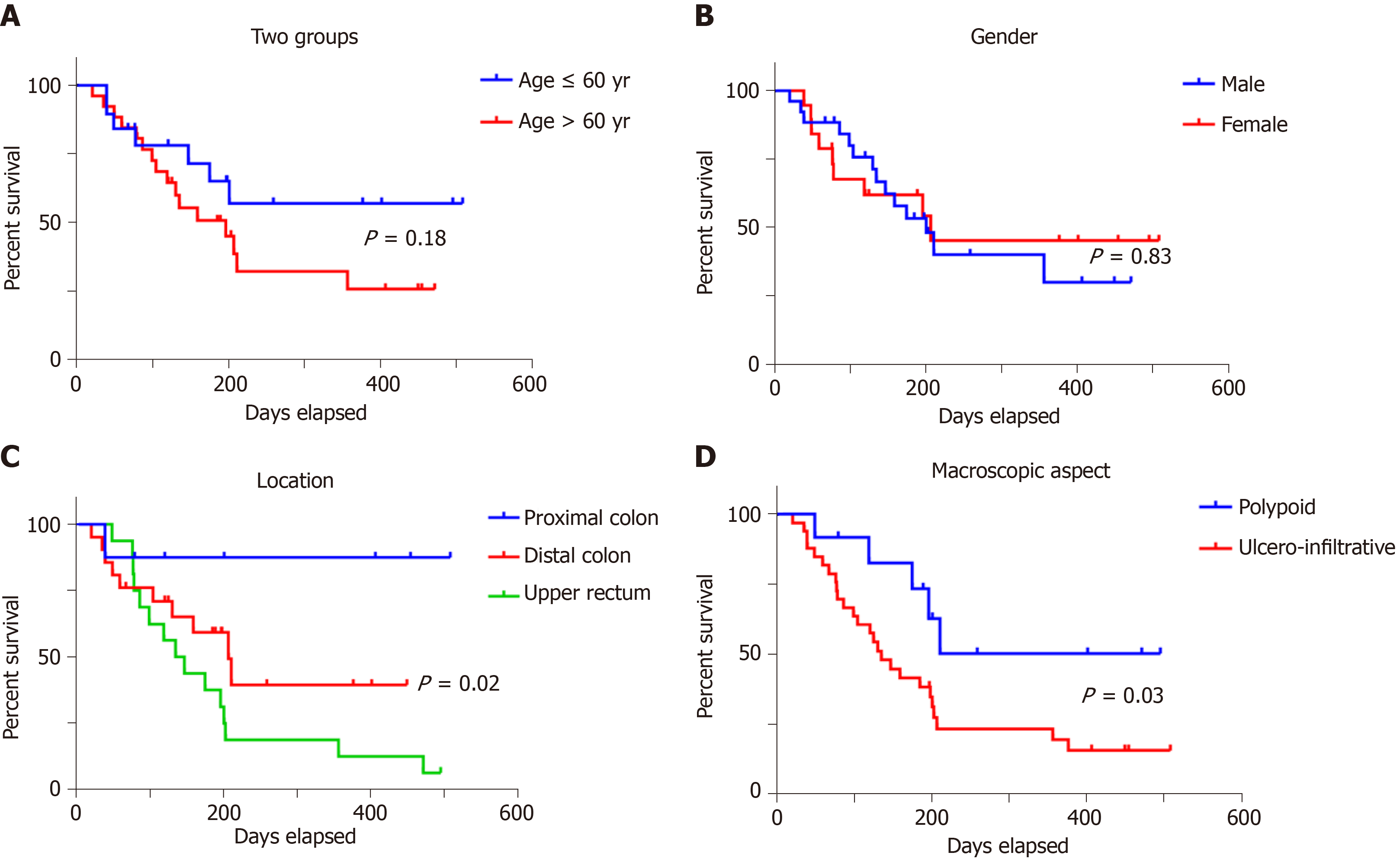
Figure 3 In colorectal cancer, overall survival rate is not influenced by patients’ age (A) or gender (B) but depends on tumor localization (C) and macroscopic aspect (D).
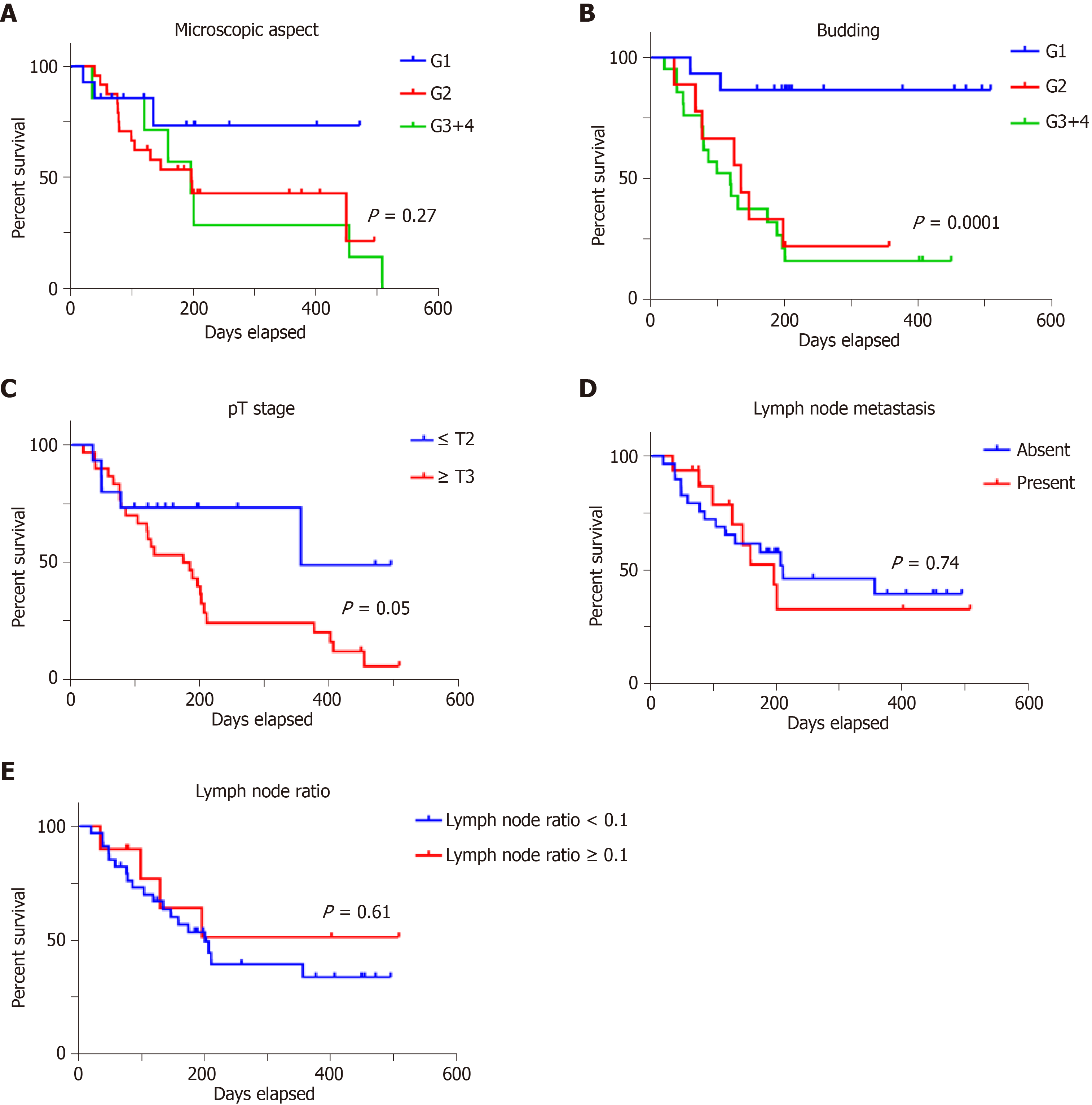
Figure 4 In colorectal adenocarcinomas, overall survival rate does not depend on grade of differentiation (A) but is strongly influenced by tumor budding degree (B); a slightly correlation is proved with depth of infiltration (C) but lymph node status is not an independent prognostic factor (D, E).
- Citation: Kovacs Z, Jung I, Szalman K, Banias L, Bara TJ, Gurzu S. Interaction of arylsulfatases A and B with maspin: A possible explanation for dysregulation of tumor cell metabolism and invasive potential of colorectal cancer. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 3990-4003
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/3990.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3990