Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 6, 2019; 7(23): 3934-3944
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3934
Published online Dec 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3934
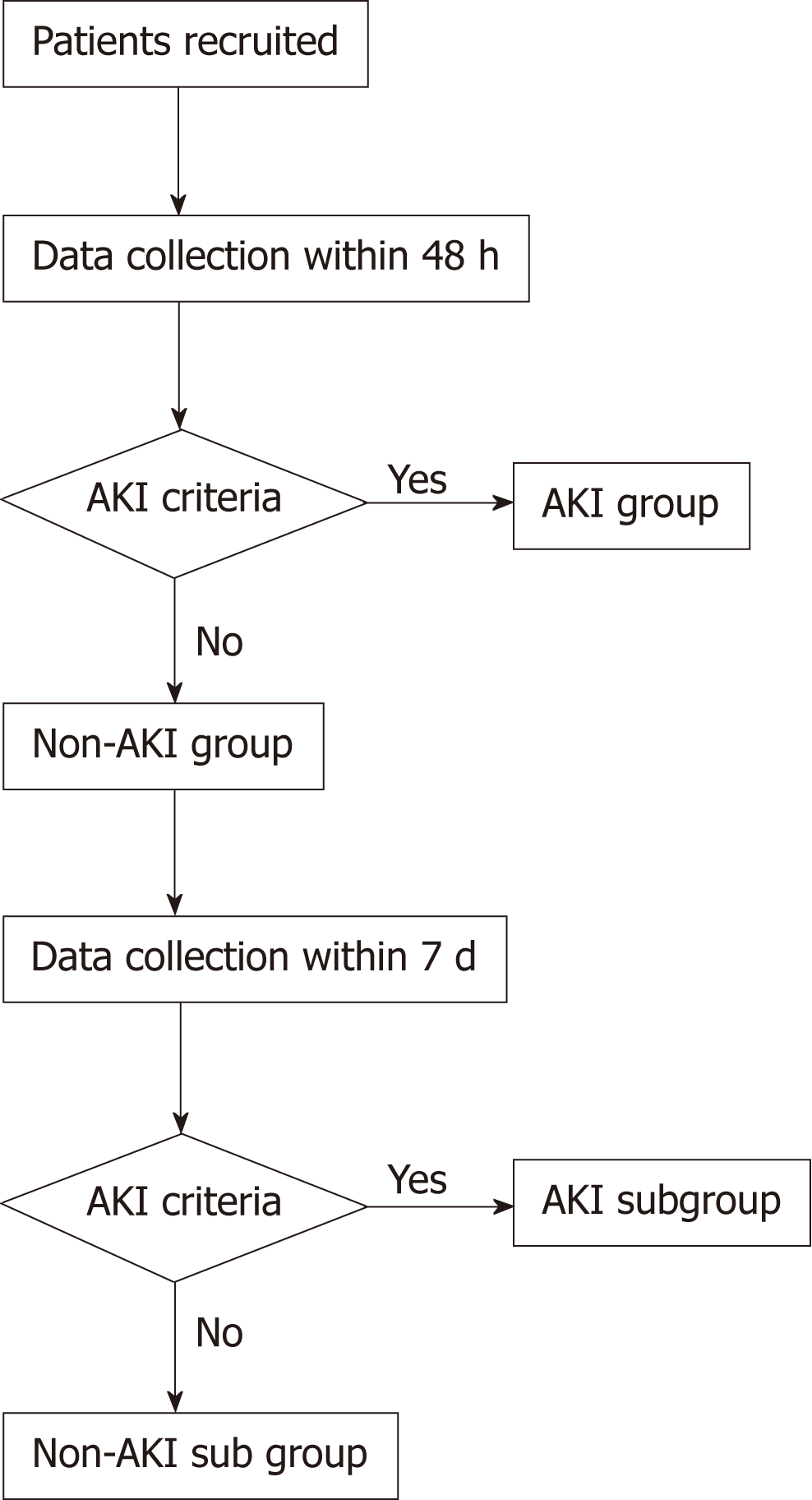
Figure 1 Grouping diagram of sepsis patients based on acute kidney injury diagnostic criteria.
AKI: Acute kidney injury.
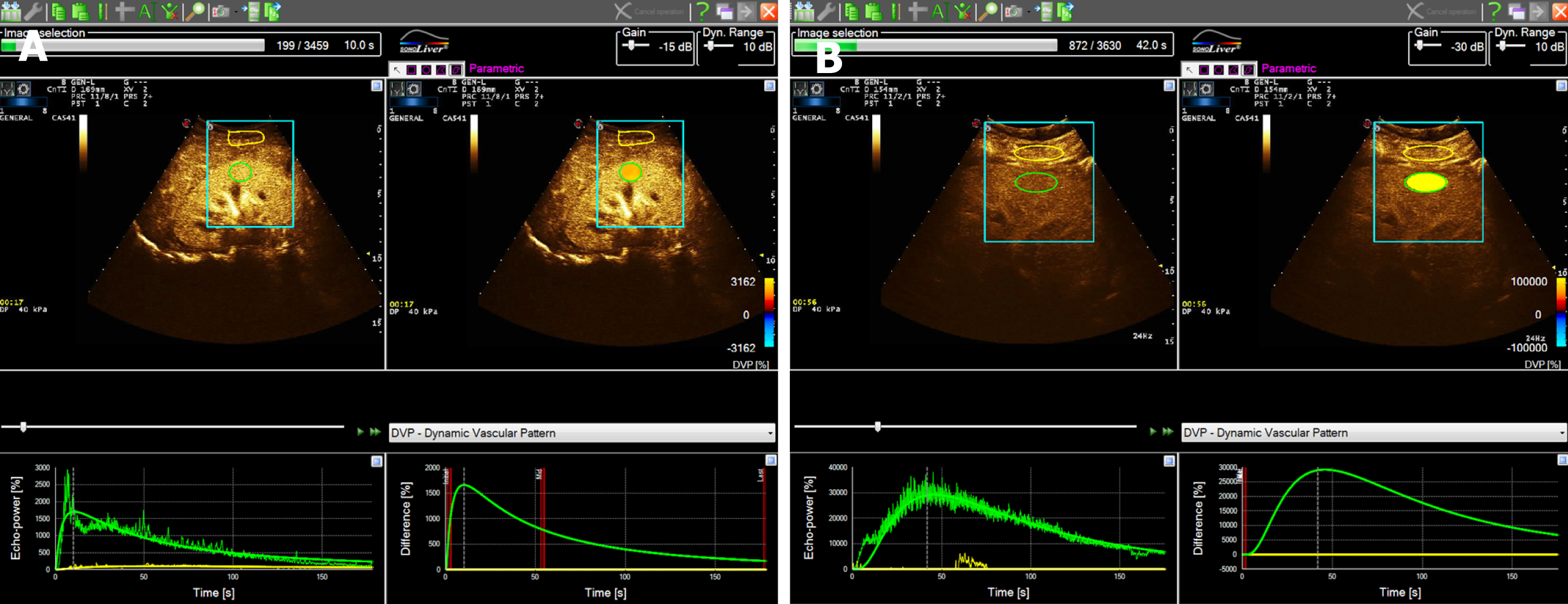
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced ultrasound in patients with septic acute kidney injury and non-acute kidney injury sepsis.
A: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound (CEUS) time-intensity curve (TIC) for patients with non-acute kidney injury (AKI) sepsis; B: CEUS TIC for patients with septic AKI.
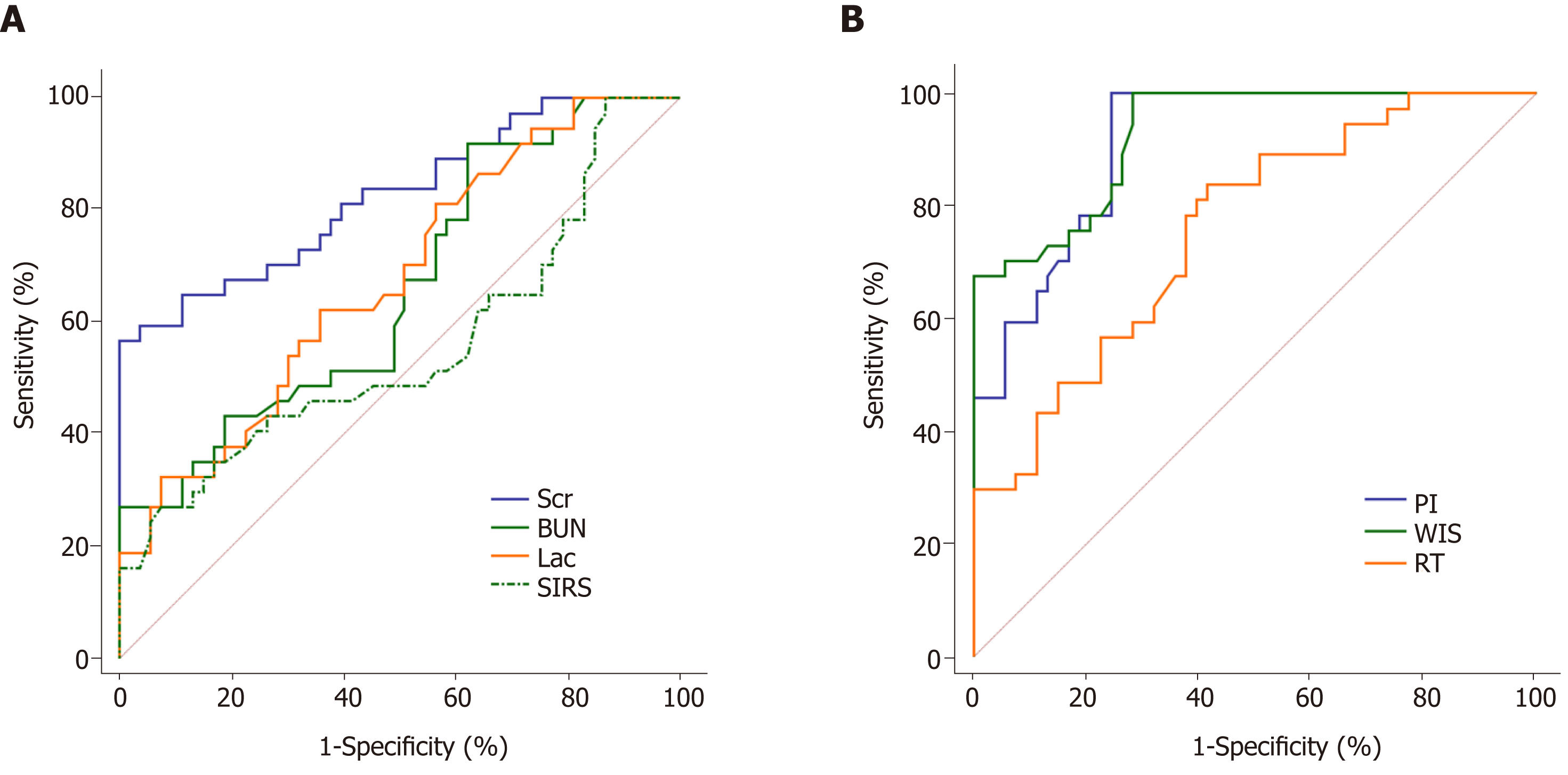
Figure 3 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of each potential indicator for the diagnosis of septic acute kidney injury.
A: Clinical indicators (Systemic inflammatory response score, blood lactic acid, serum creatinine, blood urea nitrogen) for the diagnosis of septic acute kidney injury (AKI); B: Contrast-enhanced ultrasound indicators (Peak intensity, wash in slope, rise time) for the diagnosis of sepsis AKI. SIRS: Systemic inflammatory response score; Lac: Blood lactic acid; Scr: Serum creatinine; BUN: Blood urea nitrogen; WIS: Wash in slope; PI: Peak intensity; RT: Rise time.
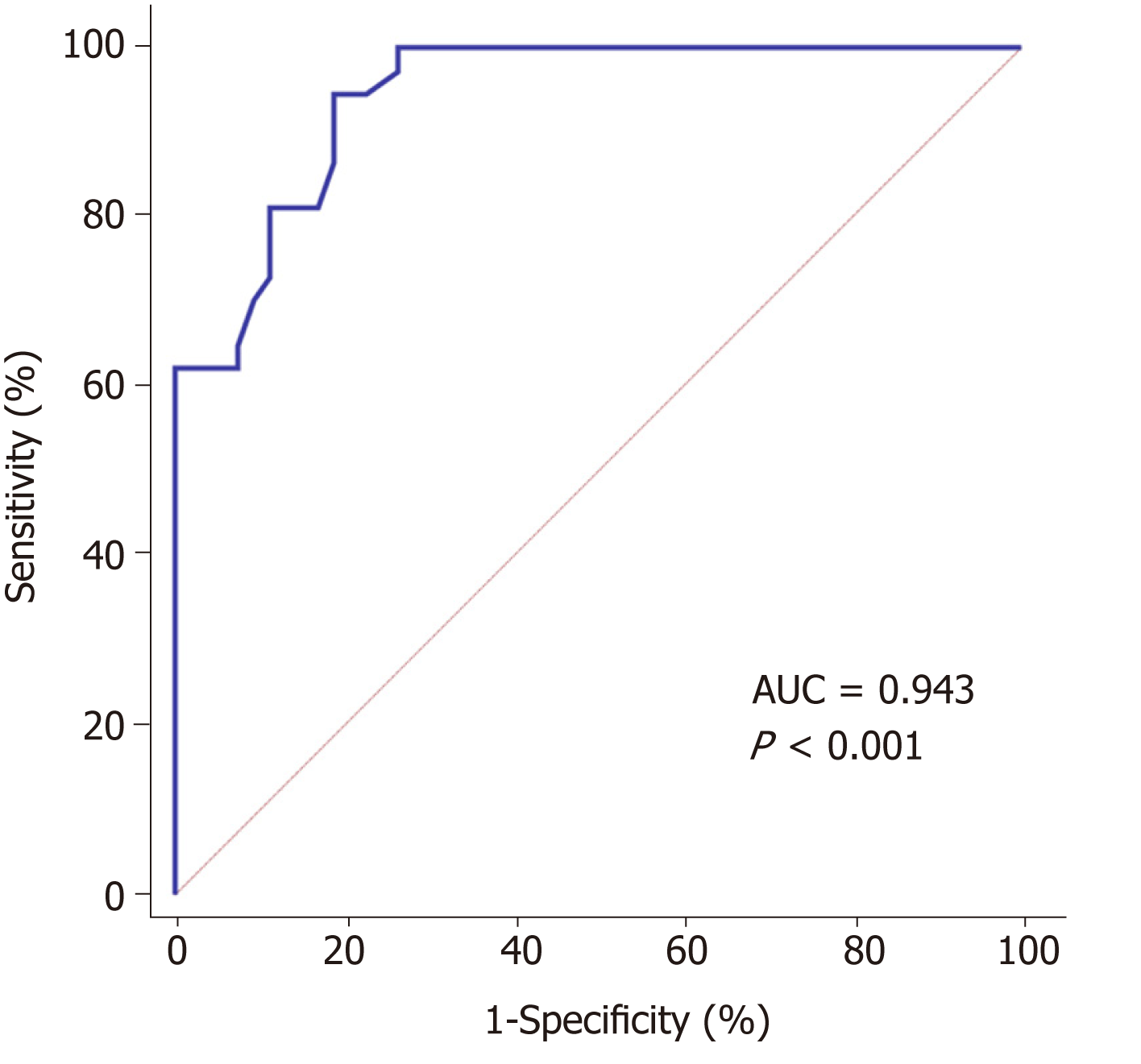
Figure 4 Receiver operating characteristic analysis of the combined diagnosis of serum creatinine, wash in slope, and peak intensity for septic acute kidney injury.
AUC: Area under curve.
- Citation: Wang XY, Pang YP, Jiang T, Wang S, Li JT, Shi BM, Yu C. Value of early diagnosis of sepsis complicated with acute kidney injury by renal contrast-enhanced ultrasound. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(23): 3934-3944
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i23/3934.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i23.3934