Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2019; 7(22): 3851-3858
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3851
Published online Nov 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3851
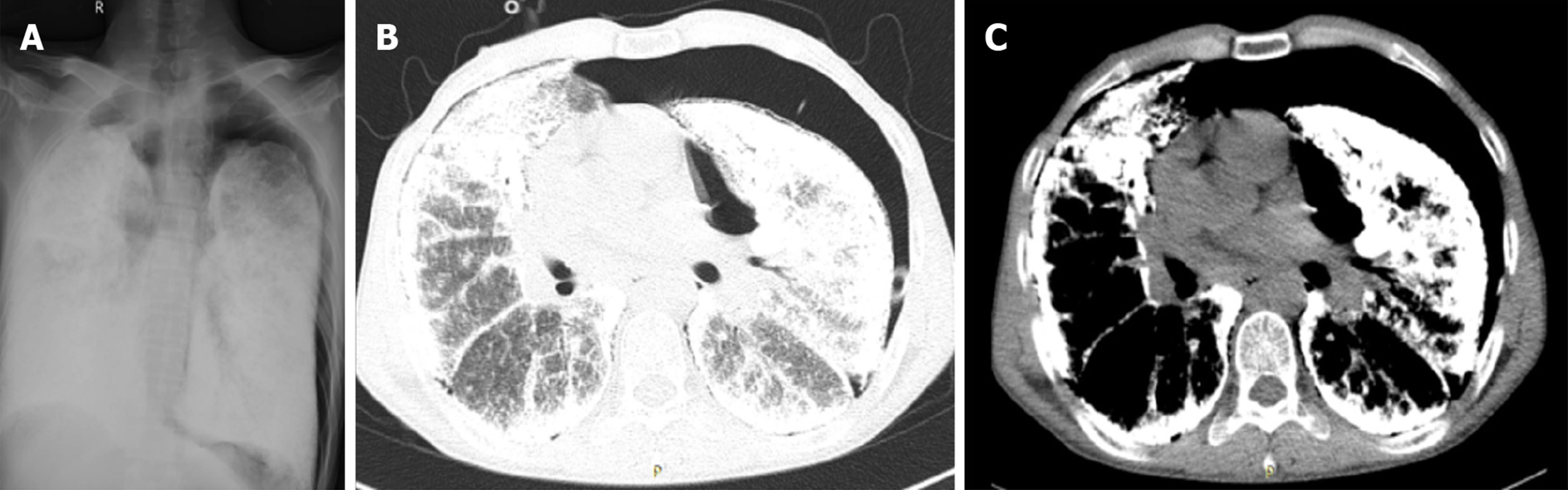
Figure 1 Preoperative imaging results suggestive of pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis.
A: Chest X-ray image showing bilateral, diffuse, symmetrical, sandstorm-like radiopaque micronodules and pneumothorax; B: Chest computed tomography (CT; pulmonary window) image showing decreased diffuse transmittance; C: Chest CT (mediastinal window) image showing calcified, minute miliary nodules in both lungs.
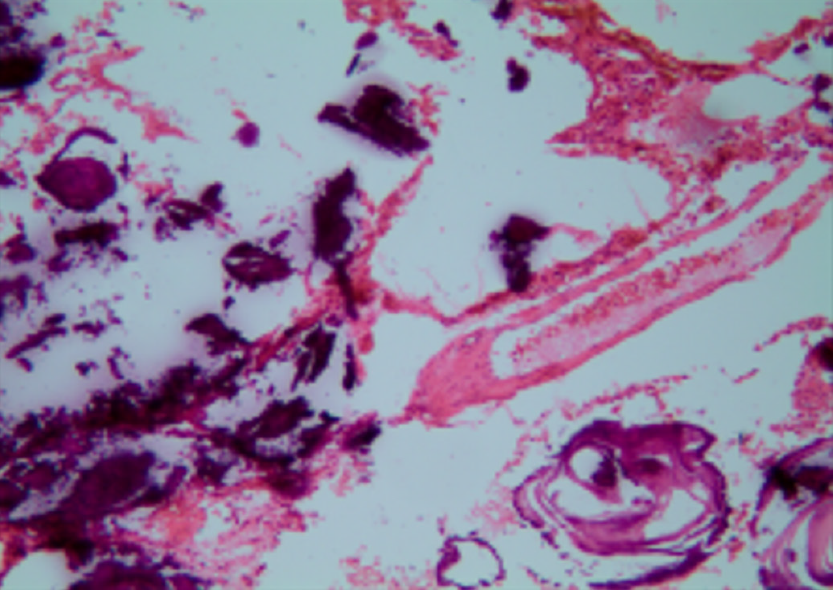
Figure 2 Intraoperative pathology showing large amounts of calcium salts in the alveoli (magnification, ×100).
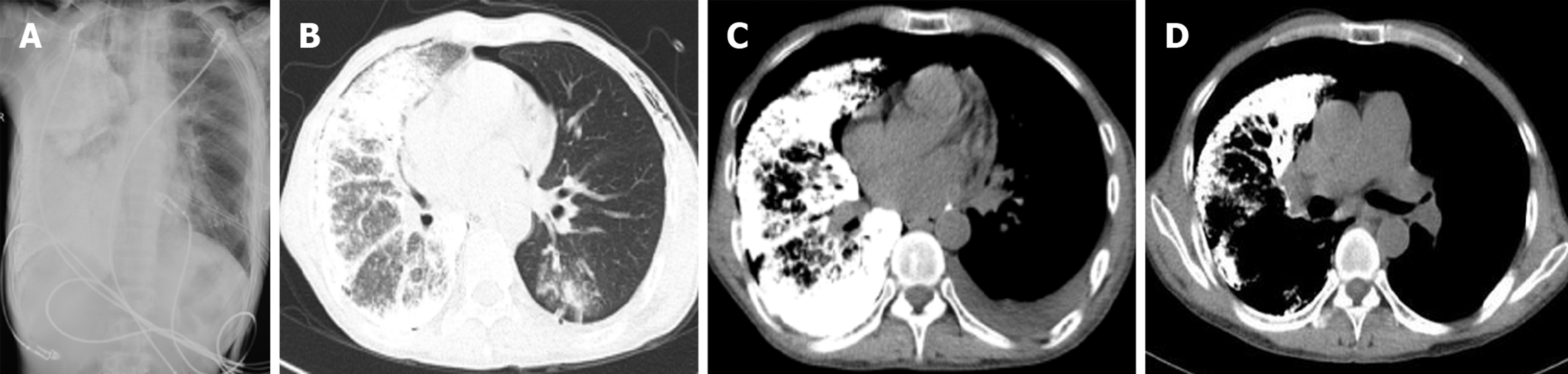
Figure 3 Postoperative imaging.
A: Postoperative chest radiograph (1 wk after surgery) revealing slight exudation in the left lung; B: High-resolution computed tomography (CT) image showing good dilation of the left transplanted lung, with mild pulmonary perfusion injury and local infection; C: CT image showing left-sided pleural effusion; D: CT image showing a left-sided main bronchial stricture.
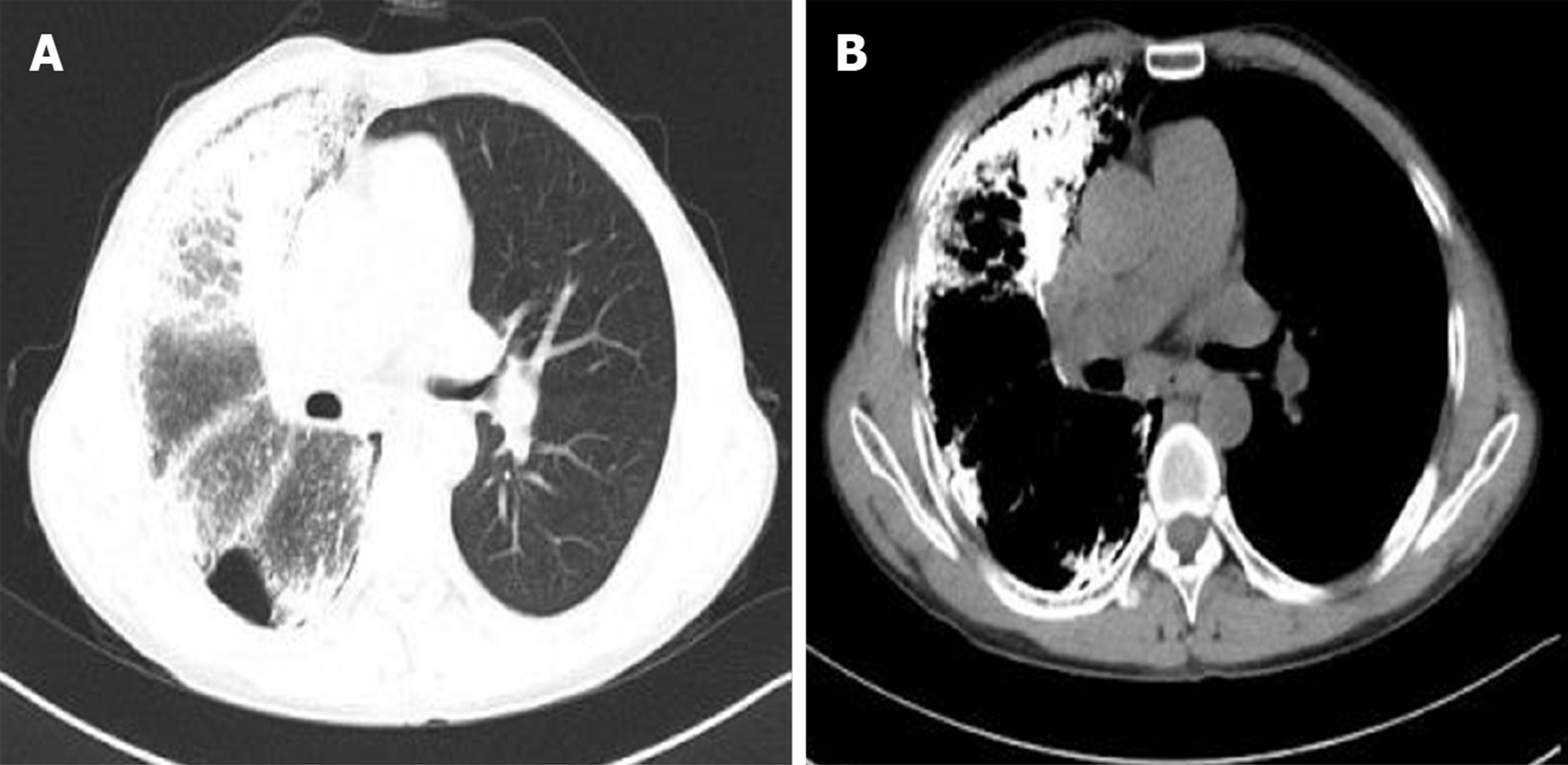
Figure 4 Postoperative imaging.
A and B: Chest computed tomography images acquired at the last follow-up visit in April 2019 indicate a good recovery.
- Citation: Ren XY, Fang XM, Chen JY, Ding H, Wang Y, Lu Q, Ming JL, Zhou LJ, Chen HW. Single-lung transplantation for pulmonary alveolar microlithiasis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(22): 3851-3858
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i22/3851.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i22.3851