Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2019; 7(21): 3632-3638
Published online Nov 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3632
Published online Nov 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3632
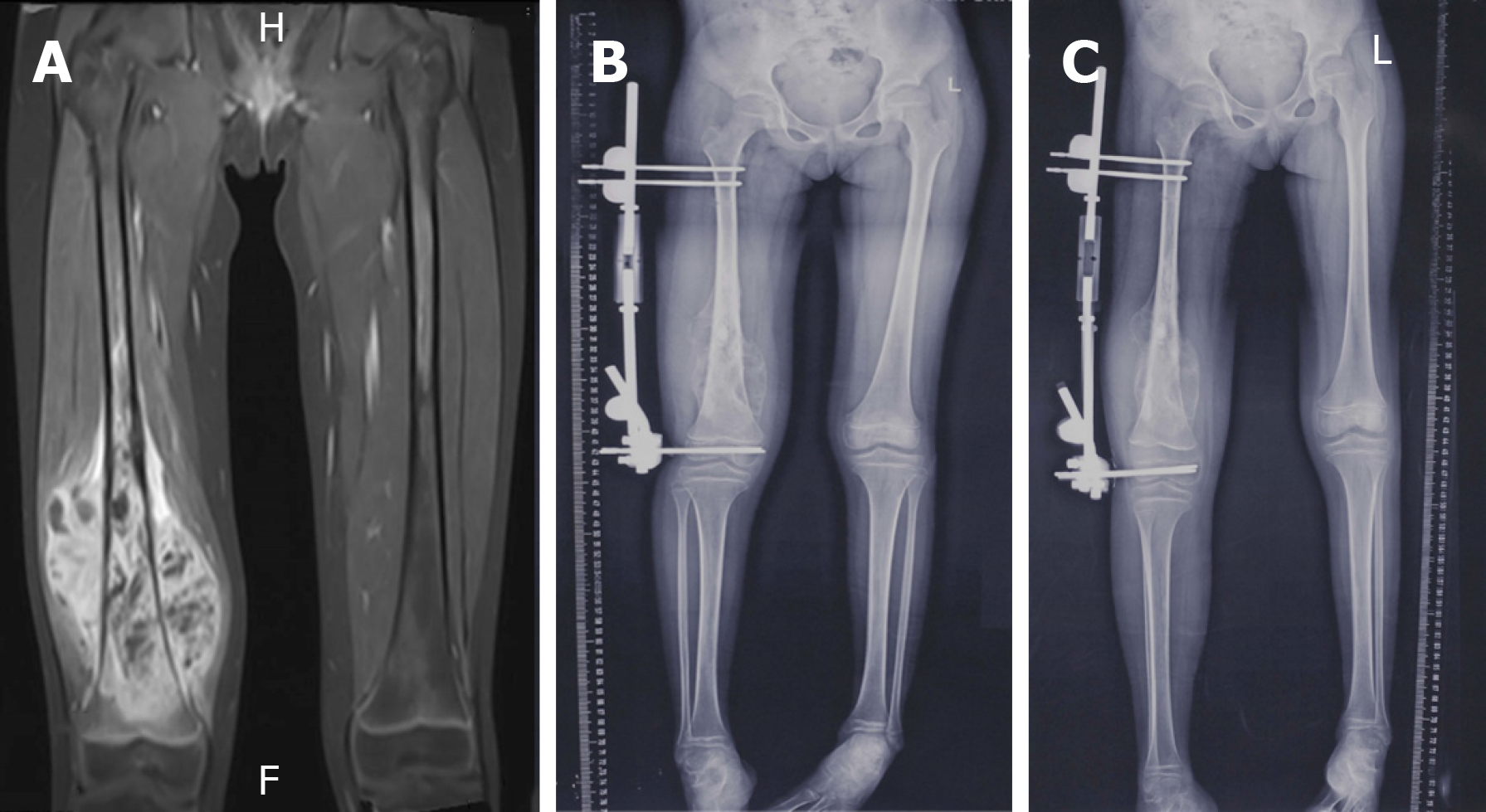
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging examinations.
A: T1WI of magnetic resonance imaging shows tumor does not involve the epiphysis; B: Epiphyseal distraction was performed to separate the epiphysis and diaphysis at a rate of 1 mm/d; C: The success of epiphysis separation was confirmed by plain x-ray 3 wk after distraction.
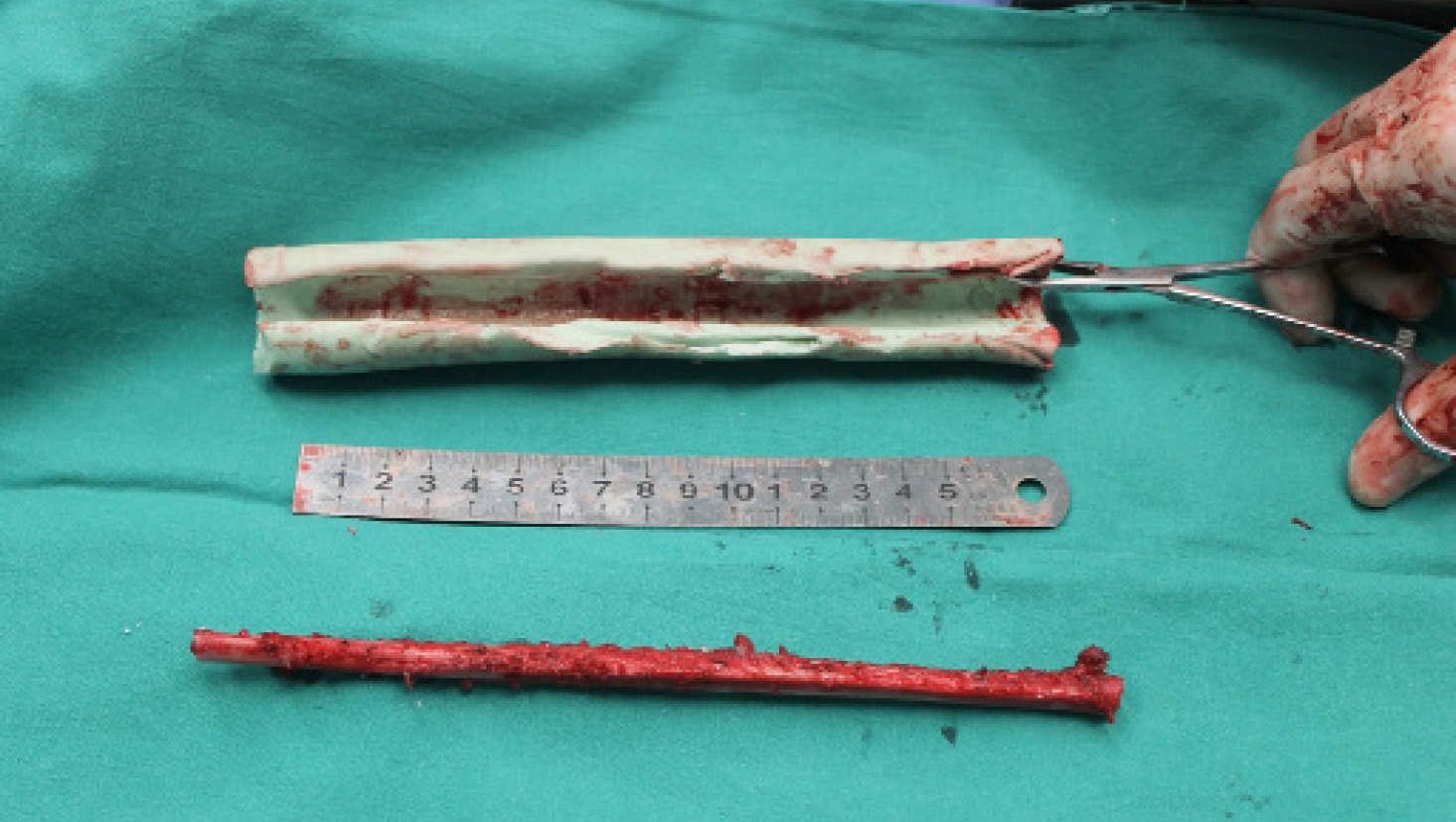
Figure 2 Free non-vascularized fibular graft was harvested and placed into the custom-made polymethyl methacrylate construct for reconstruction of 20 cm-long defect after tumor resection.
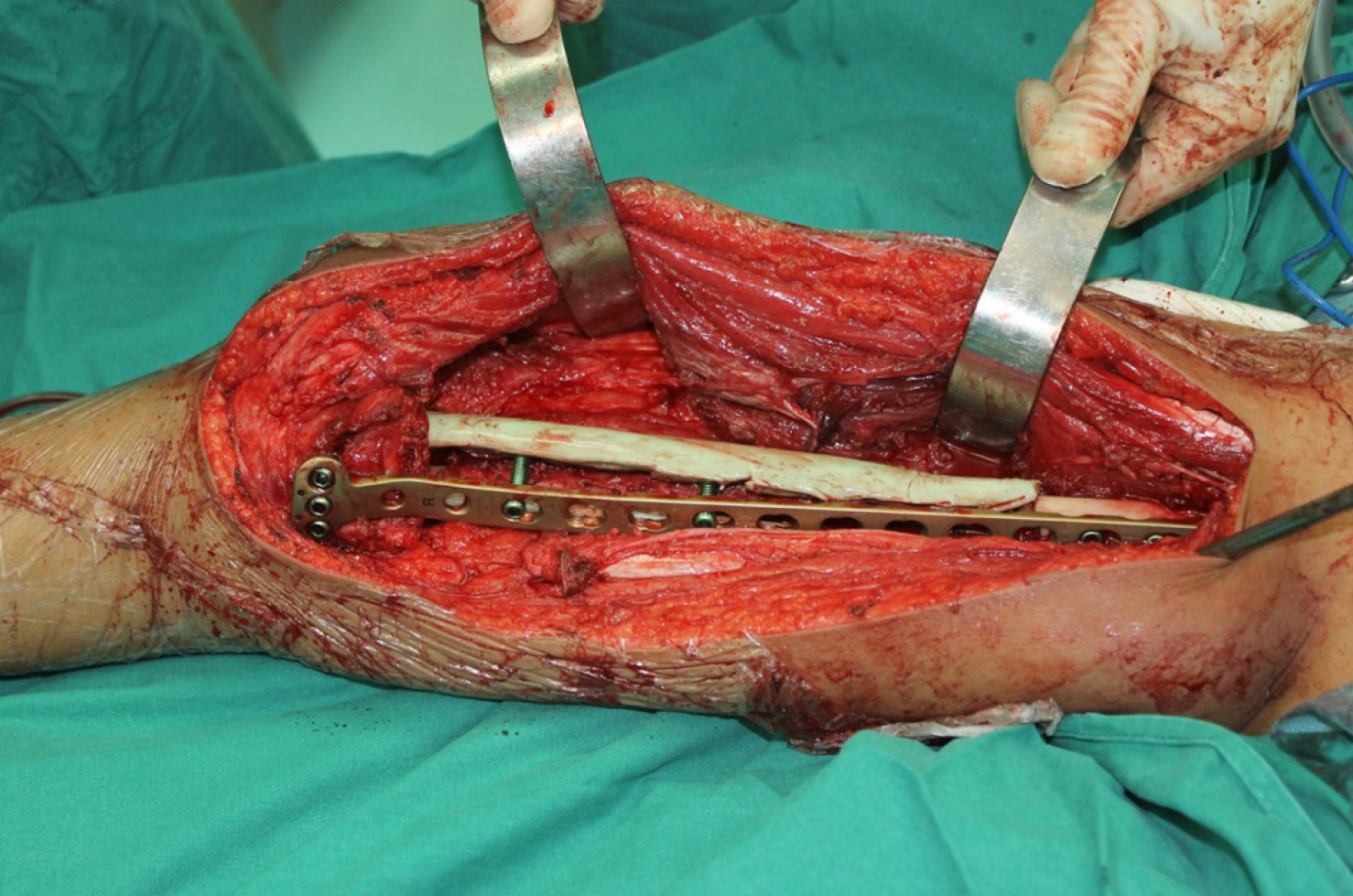
Figure 3 Direct view during the operation; for consideration of immediate stability, a locking compress plate was used medially for another inner support.
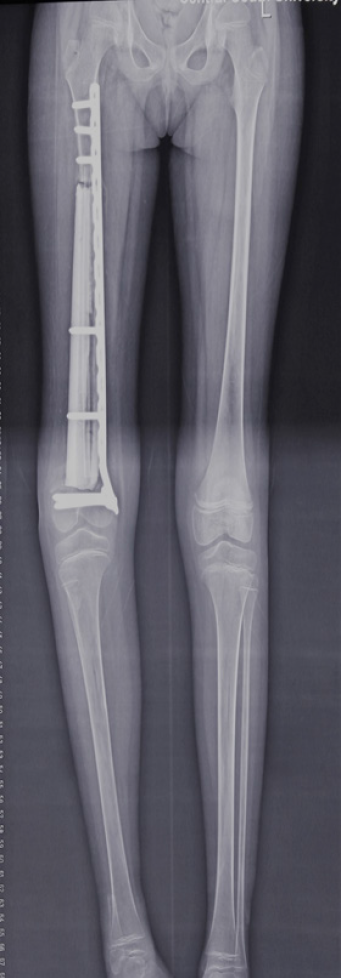
Figure 4 The plain x-ray examination shows that the 20 cm-long defect was successfully reconstructed by the hybrid complex, consisting of a custom-made polymethyl methacrylate construct and free non-vascularized fibular graft.
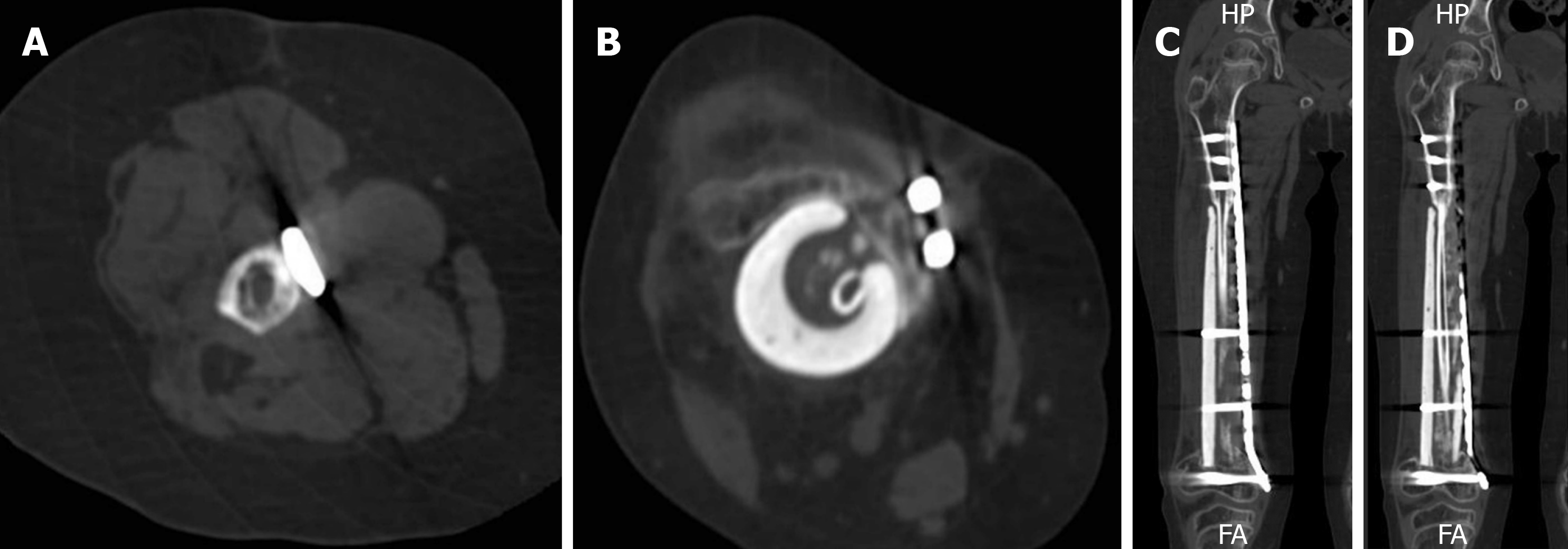
Figure 5 Bone union was achieved 6 mo after surgery in both proximal and distal, which was confirmed by CT.
A: Cross-section of proximal union side; B: Cross-section of distal union side; C: Coronal section of proximal union side; D: Coronal section of distal union side.
- Citation: Liang YH, He HB, Zhang C, Liu YP, Wan J. Epiphyseal distraction and hybrid reconstruction using polymethyl methacrylate construct combined with free non-vascularized fibular graft in pediatric patients with osteosarcoma around knee: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(21): 3632-3638
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i21/3632.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i21.3632