Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2019; 7(19): 3145-3152
Published online Oct 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.3145
Published online Oct 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.3145
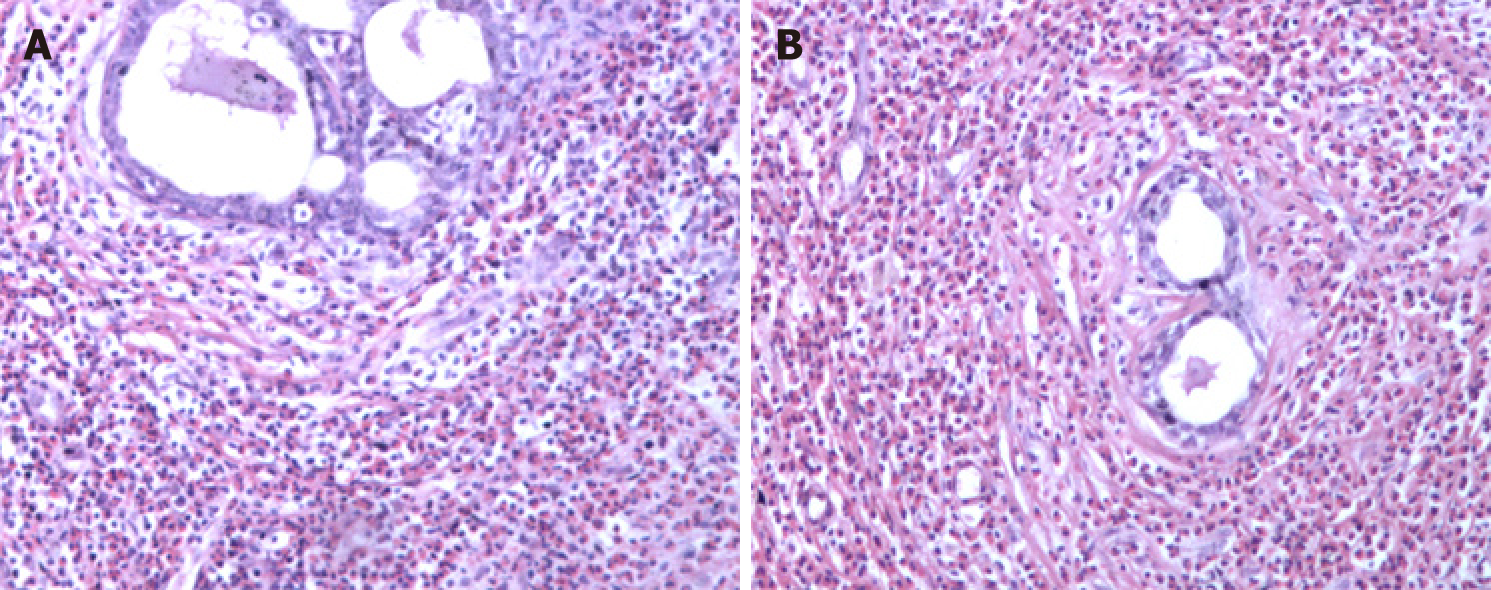
Figure 1 Breast pathology showing breast involvement by analysis of cell morphology (hematoxylin-eosin staining, ×100).
A and B: Intra-tissue ductal dilatation and interstitial eosinophil infiltration are shown.
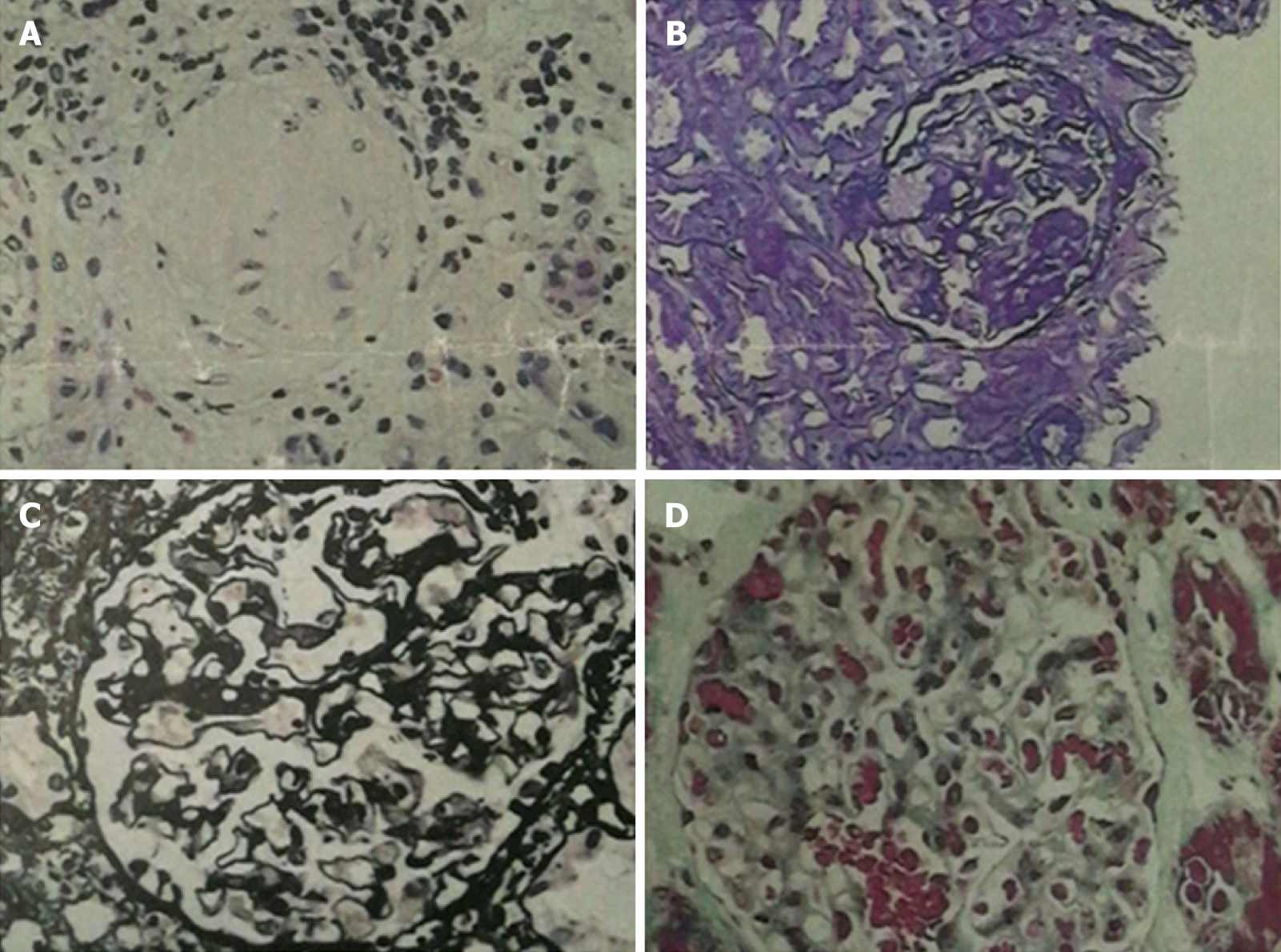
Figure 2 Renal pathology of nephrotic syndrome by analysis of morphological pattern using different staining methods.
The specimens were sliced at three layers, mainly in the renal cortex. The number of glomeruli at three layers was 23, 28, and 25, respectively. Glomerular sclerosis in four glomeruli, and glomerular segmental sclerosis and podocyte proliferation in one were found in 28 glomeruli of the second layer. The glomerular mesangial cells and matrix proliferated slightly, the capillary loops opened, and the basement membrane did not thicken. There was no obvious deposition of fumoglobin in the mesangium, subepithelium, or subendothelium, and no mesangial insertion or double track formation. No proliferation of parietal cells and no crescent formation were noted. The epithelial cells of renal tubules showed vacuolar degeneration, focal atrophy (about 5%), infiltration of small focal inflammatory cells in the renal interstitium, thickening of small arterial wall, and narrowing of lumen. Under fluorescence, IgM (+), IgA, IgG, C3, and C1q (-), and C3 (+) of arterioles were observed. The diagnosis was focal segmental glomerulosclerosis, non-specific type (FSGS, NOS). A: Hematoxylin-eosin stained (×400) histological image showing a sclerotic glomerulus; B: Periodic acid-Schiff stained (×400) histological image showing segmental glomerulosclerosis; C: Periodic acid-Schiff methenamine stained (×400) histological image showing open capillary loops and no significant thickening of basement membrane; D: Masson stained (×400) histological image showing no significant deposition of hemophilic protein.
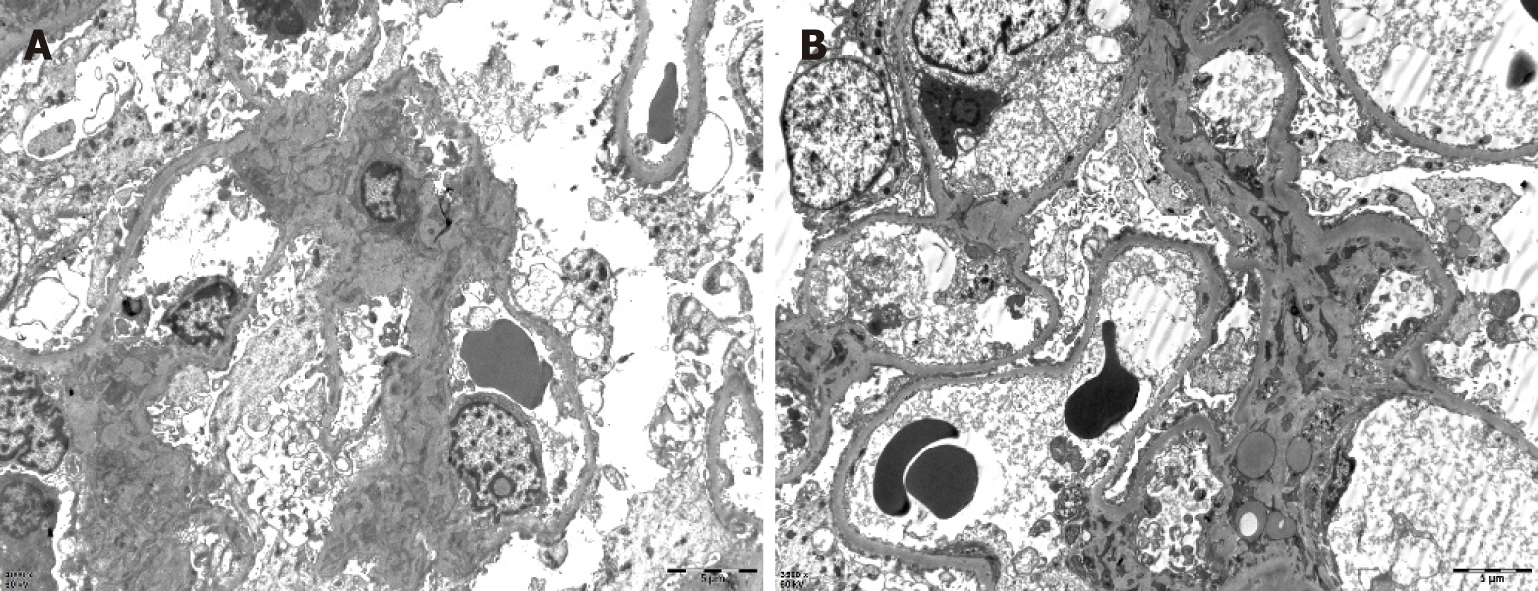
Figure 3 Renal pathology of nephrotic syndrome by electron microscopy.
After toluidine blue staining, two glomeruli were observed. One of them was observed by ultrathin section of glomerulus under an electron microscope. Erythrocytes aggregated in glomerular capillary lumen, capillary endothelial cells did not proliferate, and capillary loops were open. No obvious thickening of the wall of renal capsule, vacuolar degeneration of the wall cells, or proliferation of the wall cells was observed. Basement membrane showed no obvious thickening, with a thickness of about 300-450 nm. Visceral epithelial cells showed swelling, vacuolar degeneration, and diffuse fusion of foot processes. In the mesenchymal area, mesenchymal cells and matrix proliferated slightly, no exact electron dense deposits were found, and no electron dense deposits were found under the epithelium and endothelium. Vacuolar degeneration of renal tubular epithelial cells was noted, without special pathological changes in renal interstitium. Erythrocyte aggregation was seen in the lumen of individual renal interstitial capillaries. A diagnosis of focal segmental glomerulosclerosis was made (bar = 0.5 μm).
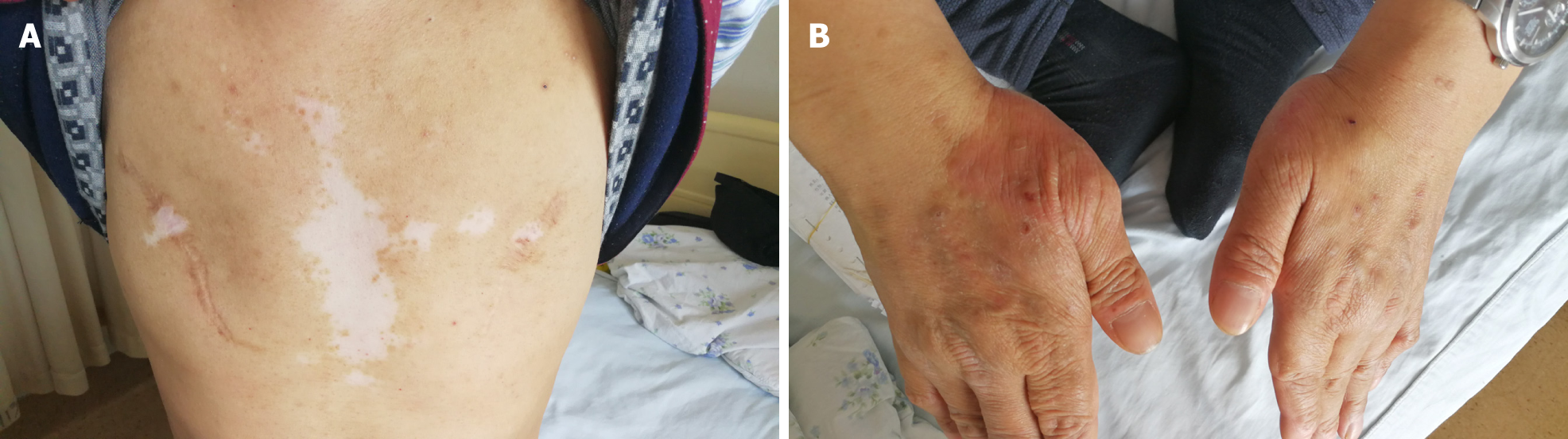
Figure 4 Skin changes of the patient.
A: Chest vitiligo and breast surgery: Irregular depigmentation areas in the middle of the patient's forechest and postoperative changes of bilateral mammary glands; B: Eczema on the back of both hands: Red rash on the back of the thumb root of the patient's hands, which fused into pieces.
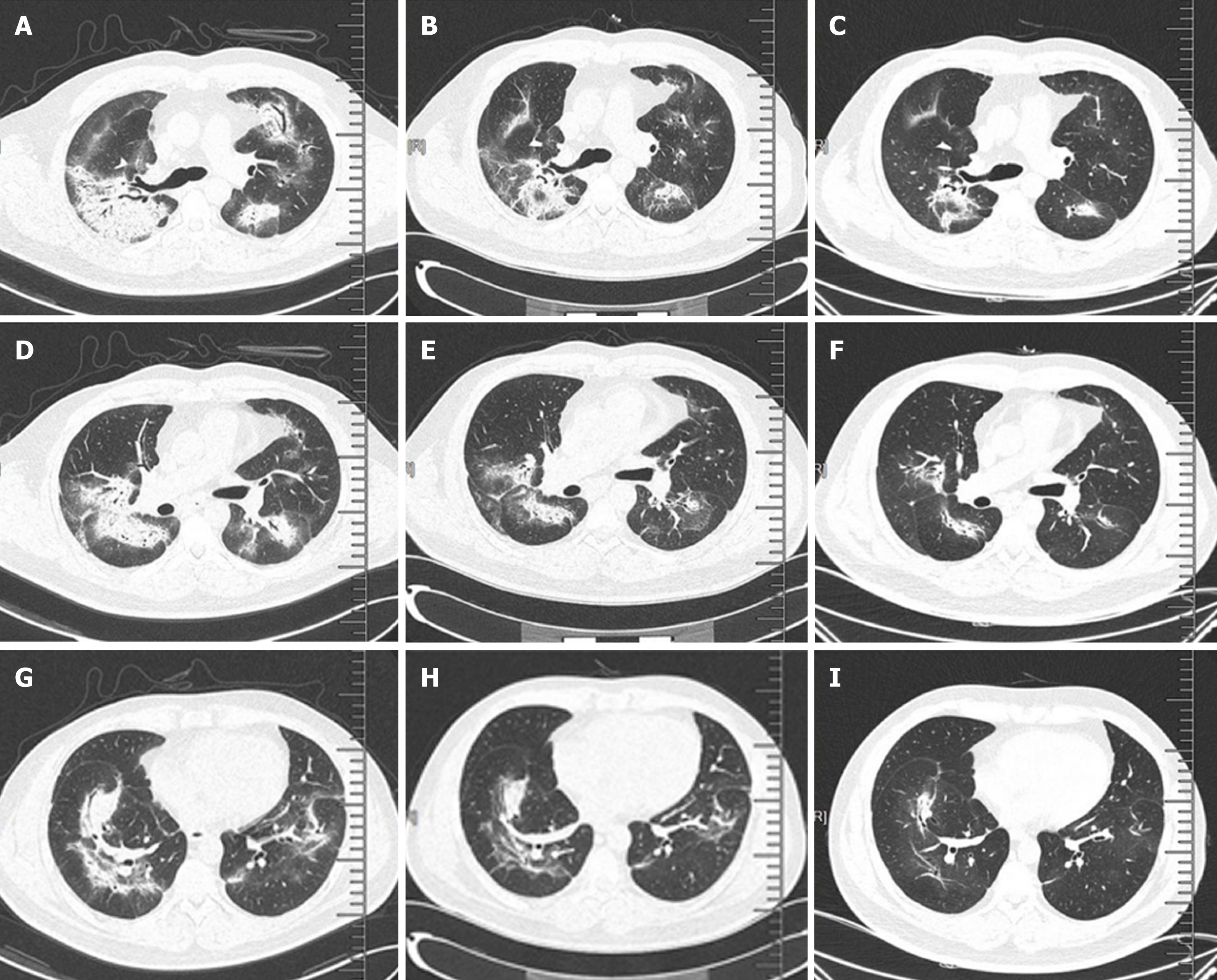
Figure 5 Pulmonary interstitial changes and review after hormone therapy.
A, D, and G: Chest computed tomography (CT) scan (lung window) showed scattered high-density patches in both lungs, some with soft tissue density, and bronchial shadow in them; B, E, and H: One month after admission (one week after hormone therapy), chest CT scan (lung window) showed that the range of scattered high-density patches in both lungs was less than before; C, F, and I: Four months after hormone therapy, chest CT scan (lung window) showed that the range of scattered high-density patches in both lungs was further reduced than before.
- Citation: Wu J, Li P, Chen Y, Yang XH, Lei MY, Zhao L. Hypereosinophilia, mastectomy, and nephrotic syndrome in a male patient: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(19): 3145-3152
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i19/3145.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.3145