Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 6, 2019; 7(19): 3120-3125
Published online Oct 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.3120
Published online Oct 6, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.3120
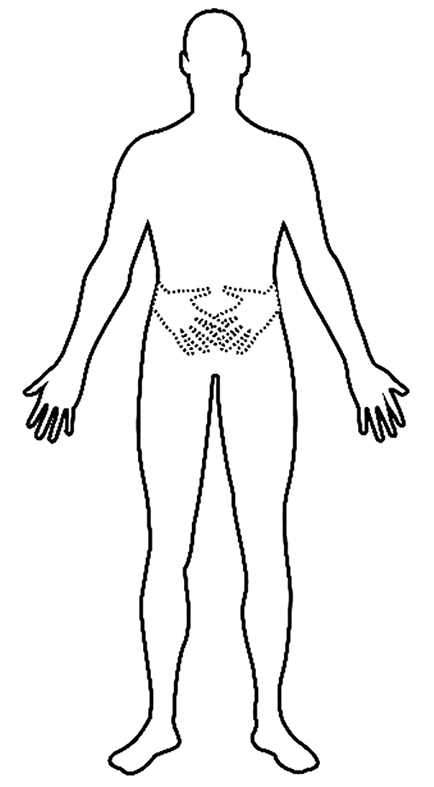
Figure 1 Schematic representation of the two supernumerary hands.
In addition to his actual limbs, two phantom hands were placed across the abdomen, which were not painful.
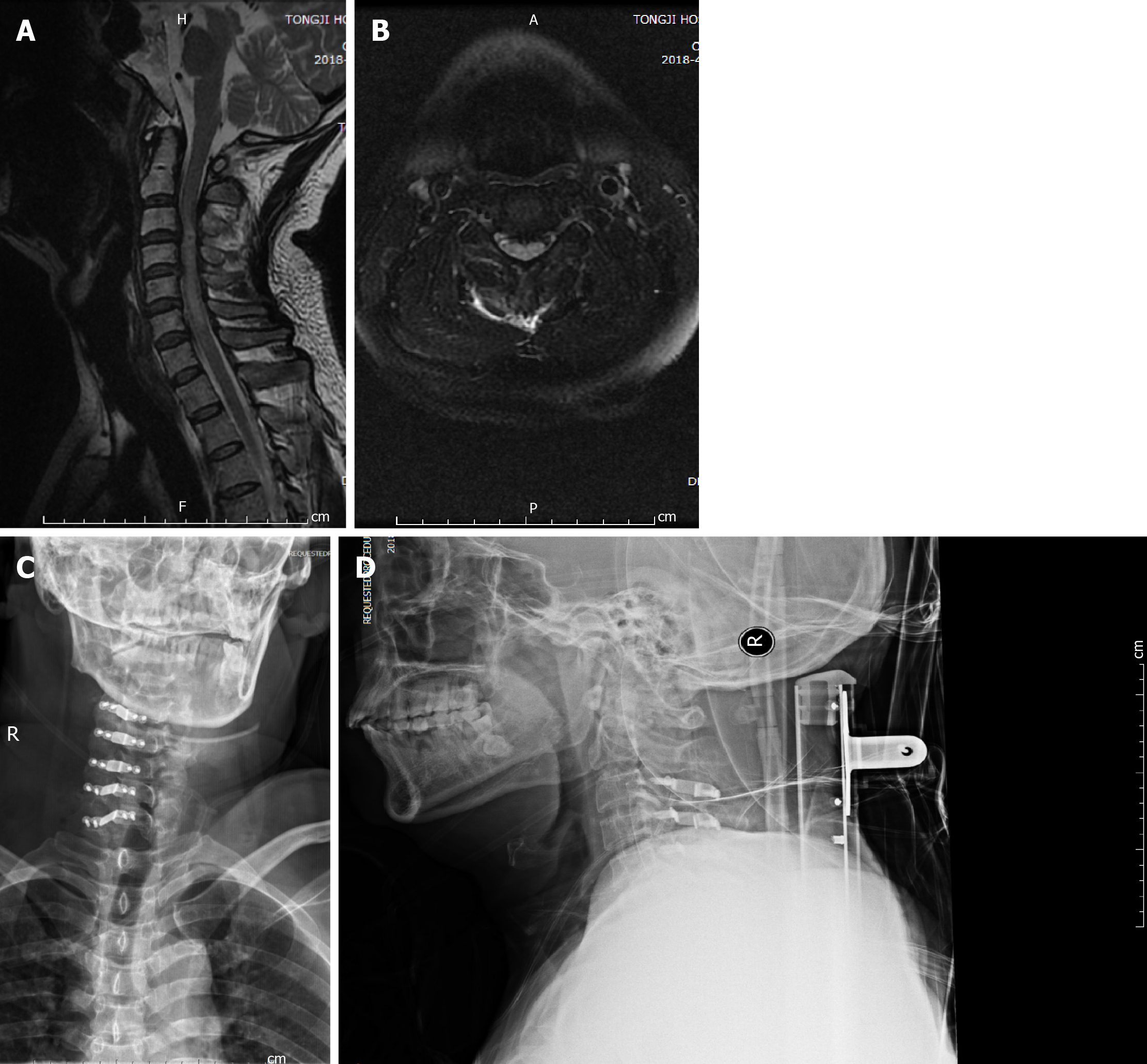
Figure 2 Neuroimaging of the spinal cord.
Magnetic resonance imaging T2-weighted sagittal view (A) and axial view (B) 3 d after injury, showing cervical cord signal change. Cervical spine X-ray anterior-posterior view (C) and lateral view (D) 3 d after surgery.
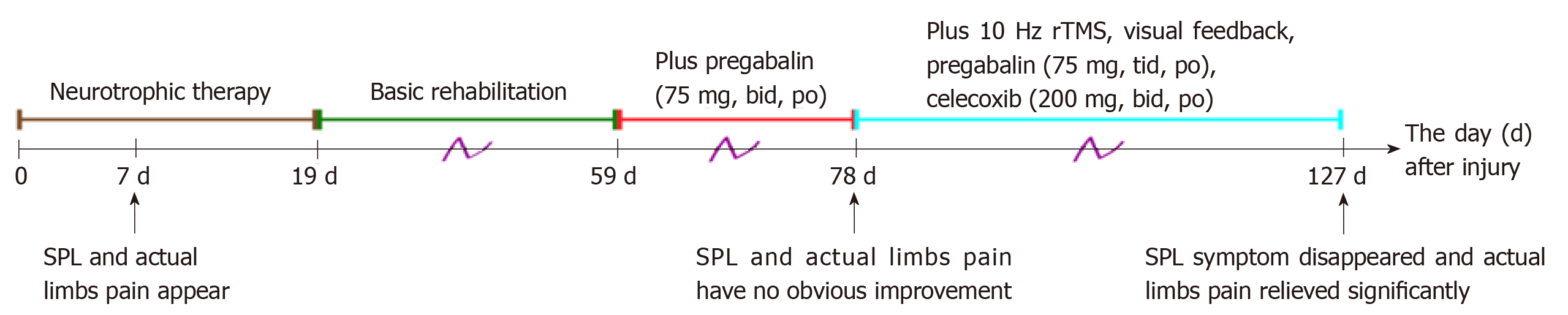
Figure 3 Rehabilitation process of supernumerary phantom limb and actual limb pain, showing the modification of treatment protocols.
rTMS: Repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation; SPL: Supernumerary phantom limb.
- Citation: Lu YS, Tong P, Guo TC, Ding XH, Zhang S, Zhang XJ. Effects of combined rTMS and visual feedback on the rehabilitation of supernumerary phantom limbs in a patient with spinal cord injury: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(19): 3120-3125
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i19/3120.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i19.3120