Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2019; 7(16): 2367-2373
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2367
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2367
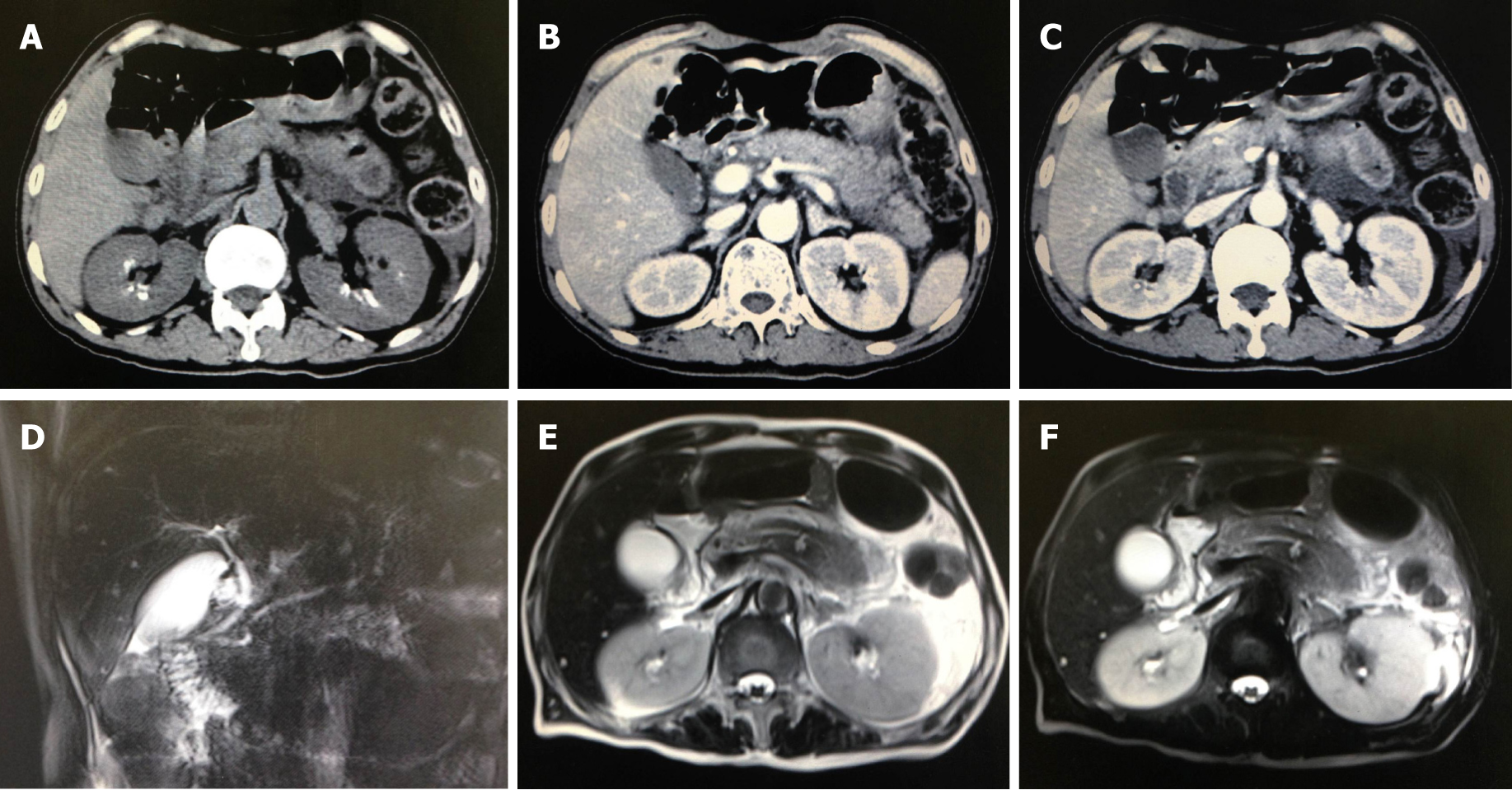
Figure 1 Abdomen computed tomography scan and magnetic resonance imaging.
A-C: Abdomen computed tomography demonstrated double kidney stones and a swelling pancreas. The exudation is focused on the surrounding of pancreas body and tail; D-F: Abdomen magnetic resonance imaging similarly revealed pancreatic tail contusion and exudative changes around the pancreas. There were no obvious changes in the biliary system.
Figure 2 Ultrasonography of neck showed a 3.
0 cm × 2.0 cm hypoechoic solid lesion posterior to right lobe of thyroid.
Figure 3 Changes of the concentration of parathyroid hormone and Ca2+.
The statistics reveals the expression changes of the concentration of parathyroid hormone (PTH) and Ca2+ during the period of admission. The operation was performed on the fourth day. Before the operation, the concentration of Ca2+ was maintained at a high-level. Both PTH and Ca2+ decreased dramatically and returned to normal levels after the operation.
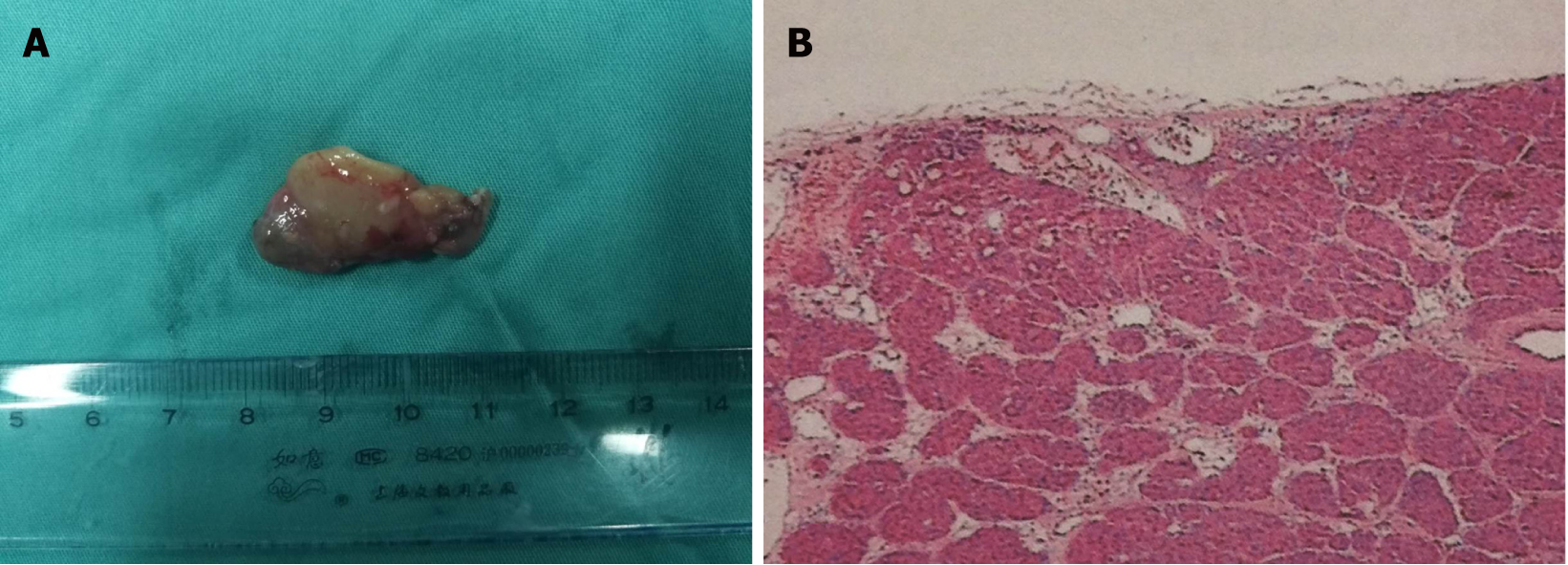
Figure 4 Resected specimen showed a 3.
0 cm × 2.0 cm hyperplastic material parathyroid mass after excision (A) and histopathology: right parathyroid adenoma (B). Magnification, x 100.
- Citation: Ma YB, Hu J, Duan YF. Acute pancreatitis connected with hypercalcemia crisis in hyperparathyroidism: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(16): 2367-2373
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i16/2367.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2367