Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2019; 7(16): 2309-2315
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2309
Published online Aug 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2309
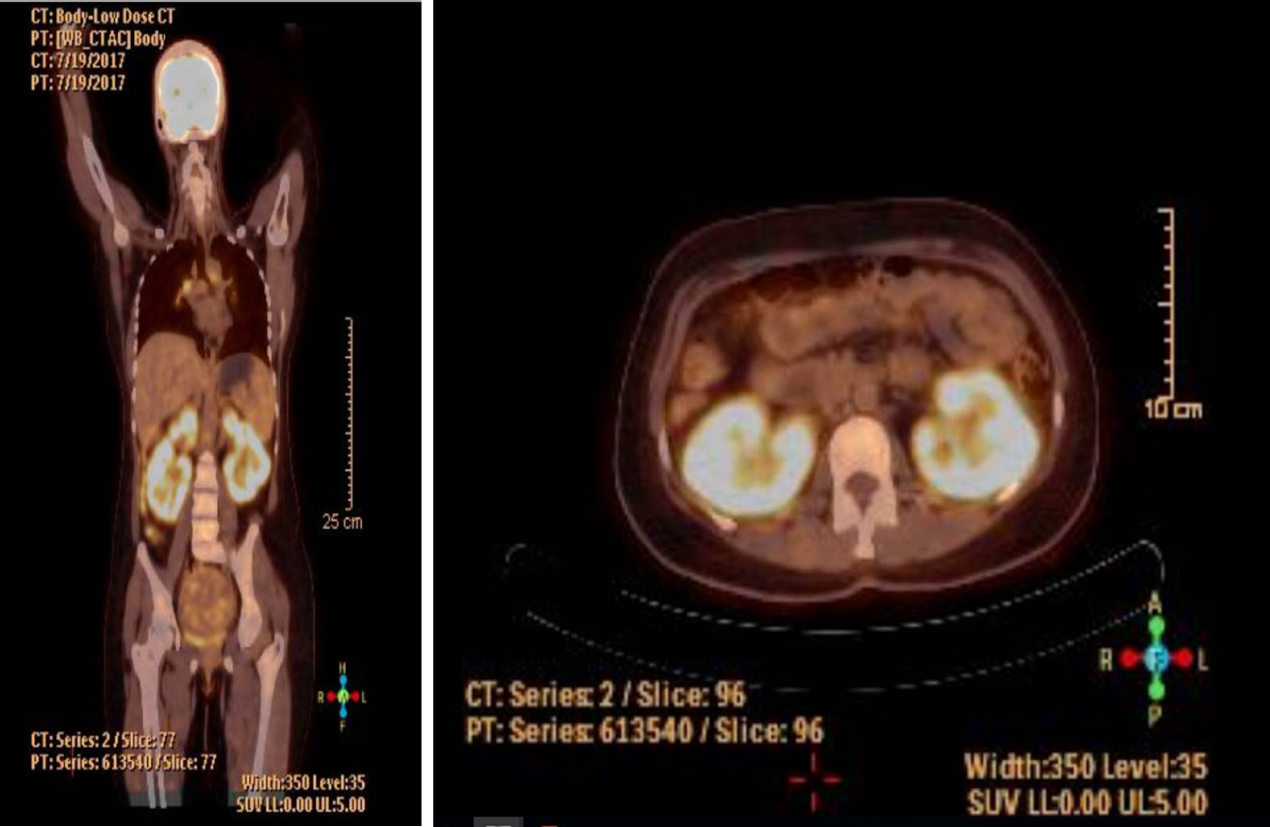
Figure 1 Positron-emission tomography-computed tomography scan reported as increased fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in infiltrative soft tissue areas in both kidneys (standardized uptake value max: 8.
01).
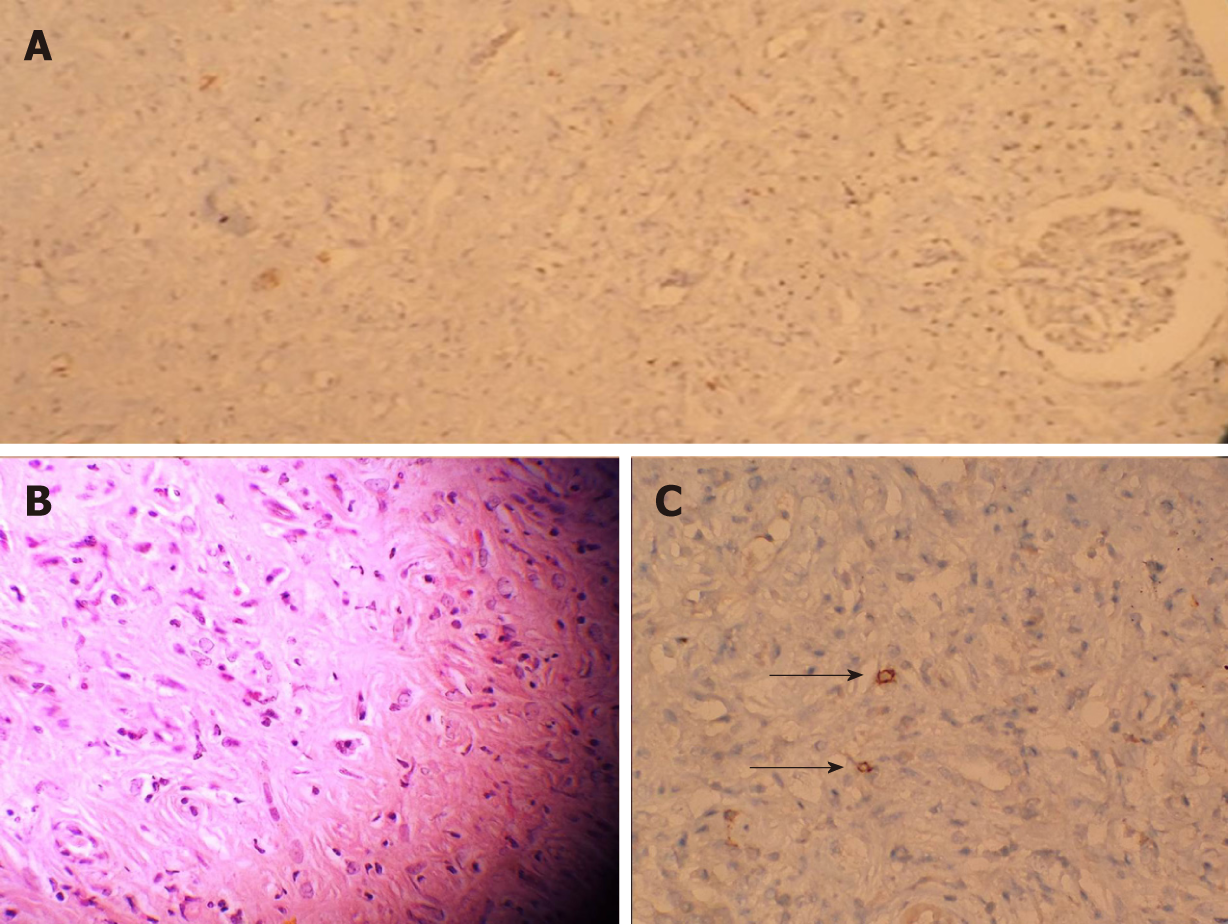
Figure 2 Histological section of kidney staining.
A: In the examination of kidney biopsy specimen only one glomerulus and a few tubules were observed due to both intense inflammation and fibrosis (H and E: × 10); B: Histological section of kidney parenchyma showing interstitial nephritis characterized by the presence of inflammatory infiltration by lymphocytes and eosinophlis (H and E: × 40); C: Black arrows show the IgG4 staining positive cells in immunostaining with anti- IgG4 antibody (× 40).
- Citation: Eroglu E, Sipahioglu MH, Senel S, Ertas SK, Savas S, Ozturk F, Kocyigit I, Tokgoz B, Oymak O. Successful treatment of tubulointerstitial nephritis in immunoglobulin G4-related disease with rituximab: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(16): 2309-2315
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i16/2309.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i16.2309