Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2019; 7(14): 1775-1783
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1775
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1775
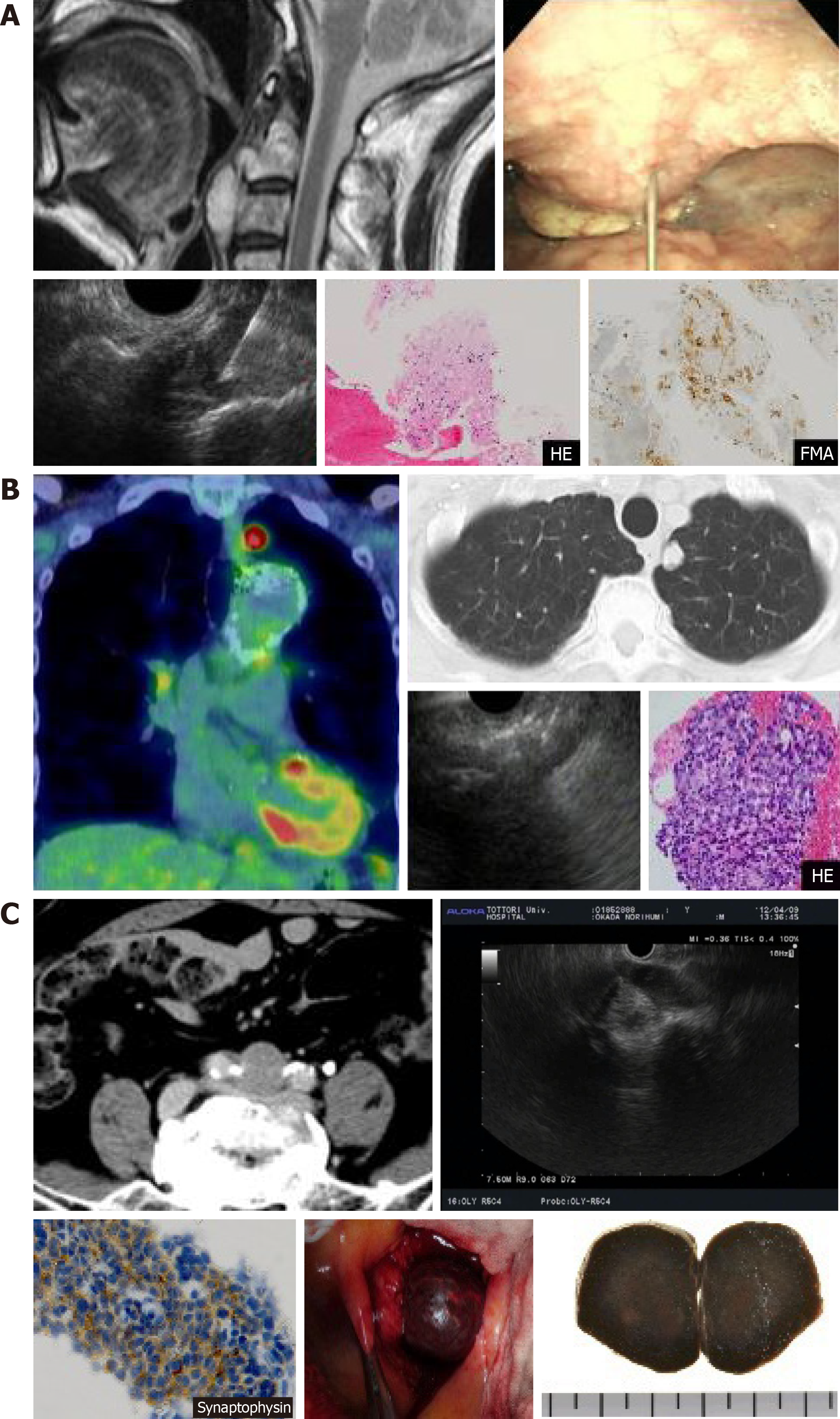
Figure 1 Imaging findings and pathological diagnosis using endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy in diseases outside the biliary/pancreatic area.
A: Otorhinology: cervical spine chordoma; B: Respiratory: adenocarcinoma of the lung; C: Metastasis of liver neuroendocrine tumors to the lymph nodes of the bifurcation of the common iliac artery.
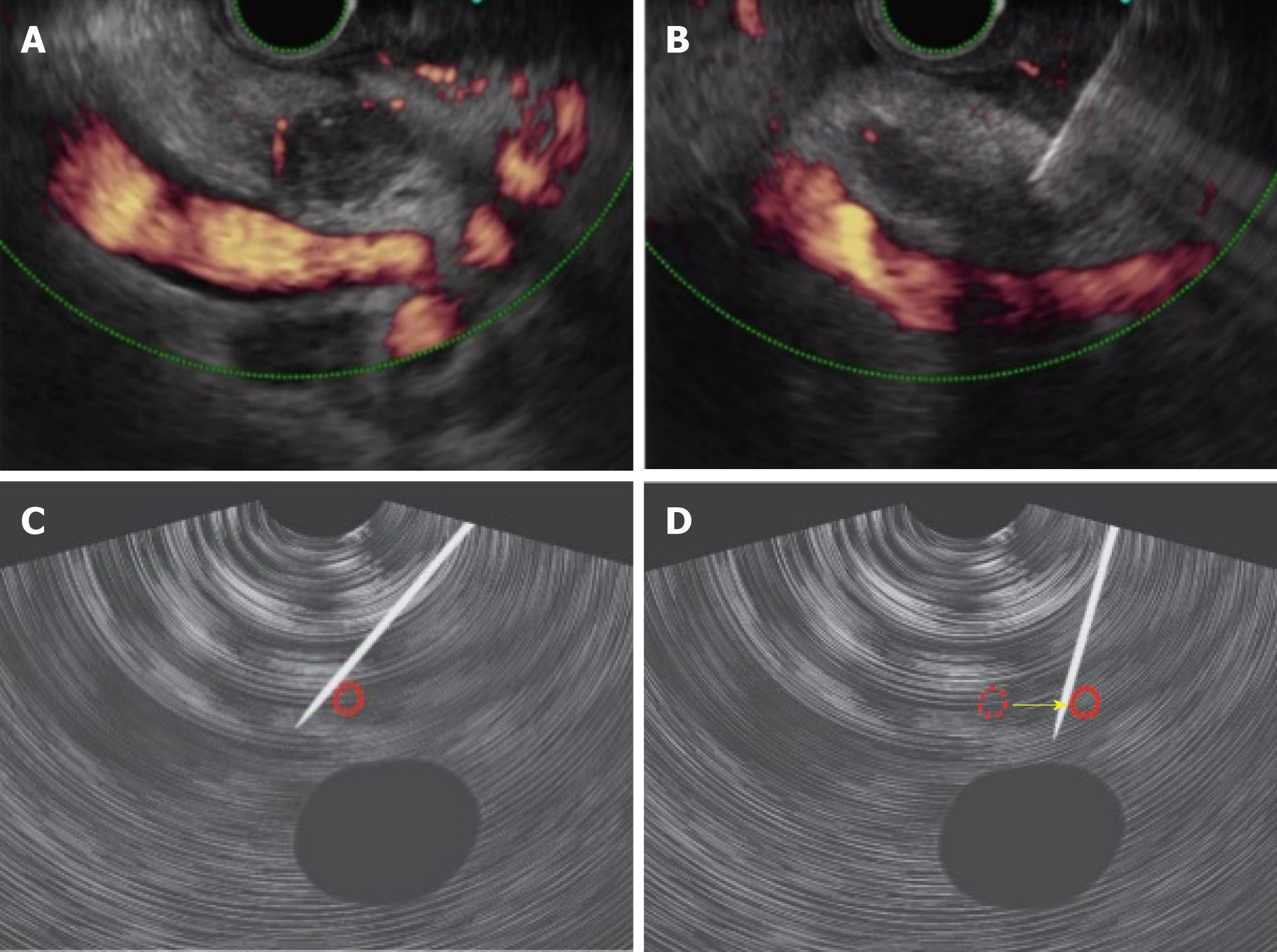
Figure 2 Case of main pancreatic duct dilatation, where rendering using the “pull-out” method ensured the puncture route.
A: With normal transgastric scanning, main pancreatic duct dilatation/meandering made it difficult to ensure the puncture route; B: Scanning after pull-out from the duodenum made it possible to ensure a safe puncture route.
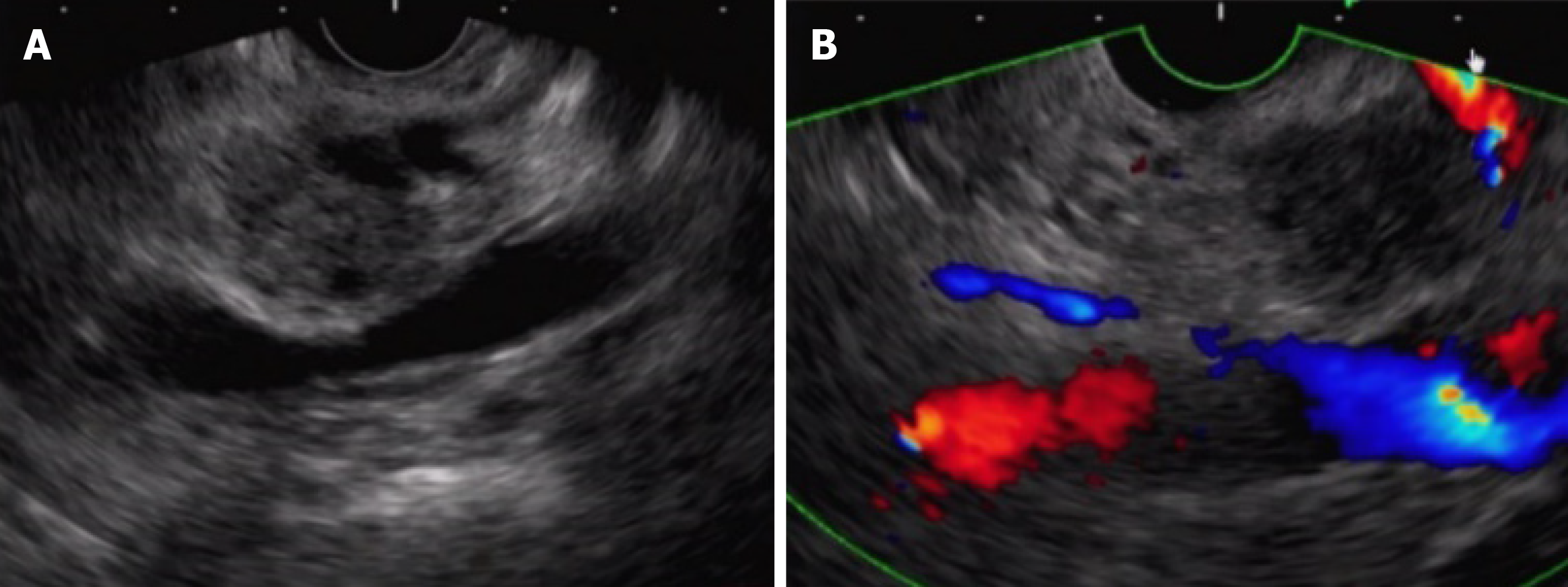
Figure 3 Distal cholangiocarcinoma where the “blood vessel push-aside” method made it possible to ensure the puncture route.
A: It was difficult to ensure the puncture route due to blood vessels around the lesion; B: Pushing the puncture needle up against the back side of the blood vessels to push them aside made it possible to ensure the puncture route; C: Puncture was made on the far side of the blood vessels (left side of the endoscopic ultrasound image); D: Lifting of the raising base and an upward angle ensured the puncture route.
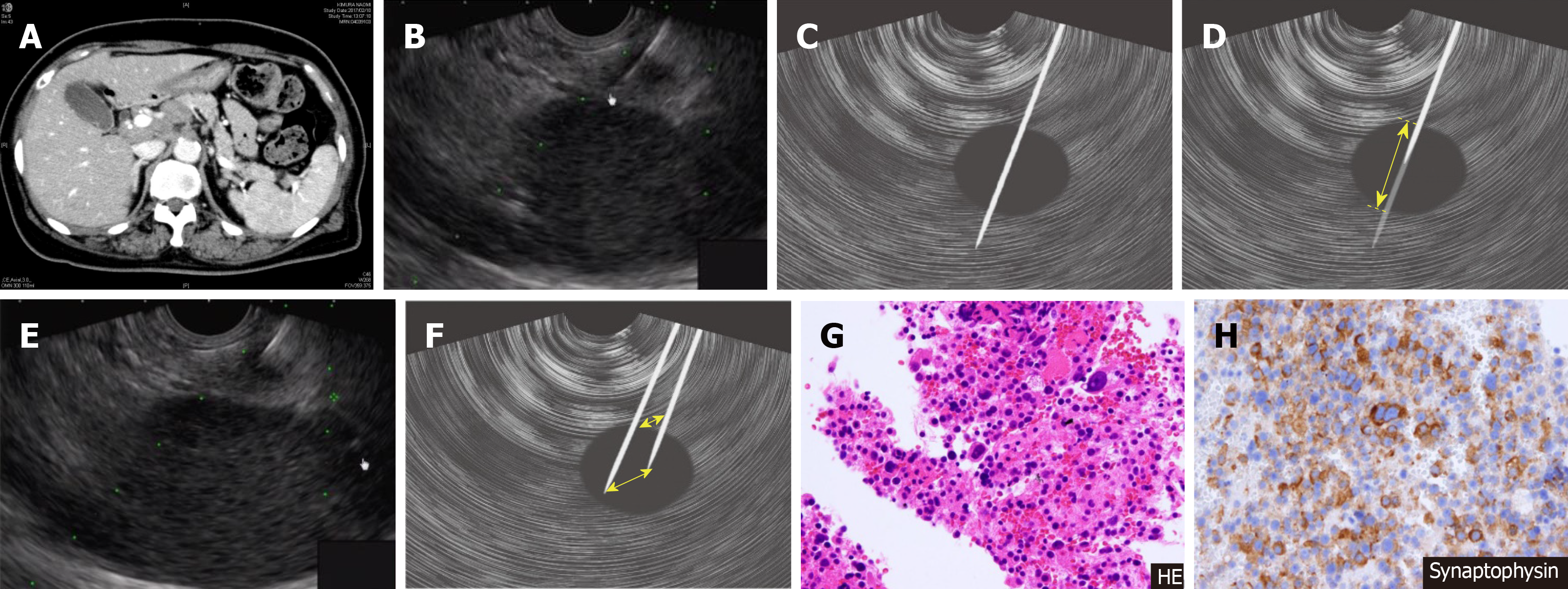
Figure 4 Pancreatic tail neuroendocrine tumor where the “skewering + respiratory fluctuations” method made it possible to ensure the puncture route.
A and B: Difficult to ensure the stroke width because the kidney is adjacent to the small mass; C: Tumor is penetrated so that it is “skewered”; D: Tissue was collected by stroking, which is useful for small masses; E: With the needle kept in position, respiratory fluctuations were used to collect the tissue; F: Needle kept in place throughout the puncture, Respiratory fluctuations yielded similar results to fanning; G and H: Sample tissue was also collected for hematoxylin-eosin staining and immunohistological staining, yielding a diagnosis of neuroendocrine tumor of the pancreas.
- Citation: Matsumoto K, Takeda Y, Onoyama T, Kawata S, Kurumi H, Koda H, Yamashita T, Isomoto H. Endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine-needle aspiration biopsy - Recent topics and technical tips. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(14): 1775-1783
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i14/1775.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1775