Copyright
©The Author(s) 2019.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2019; 7(14): 1732-1752
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1732
Published online Jul 26, 2019. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1732
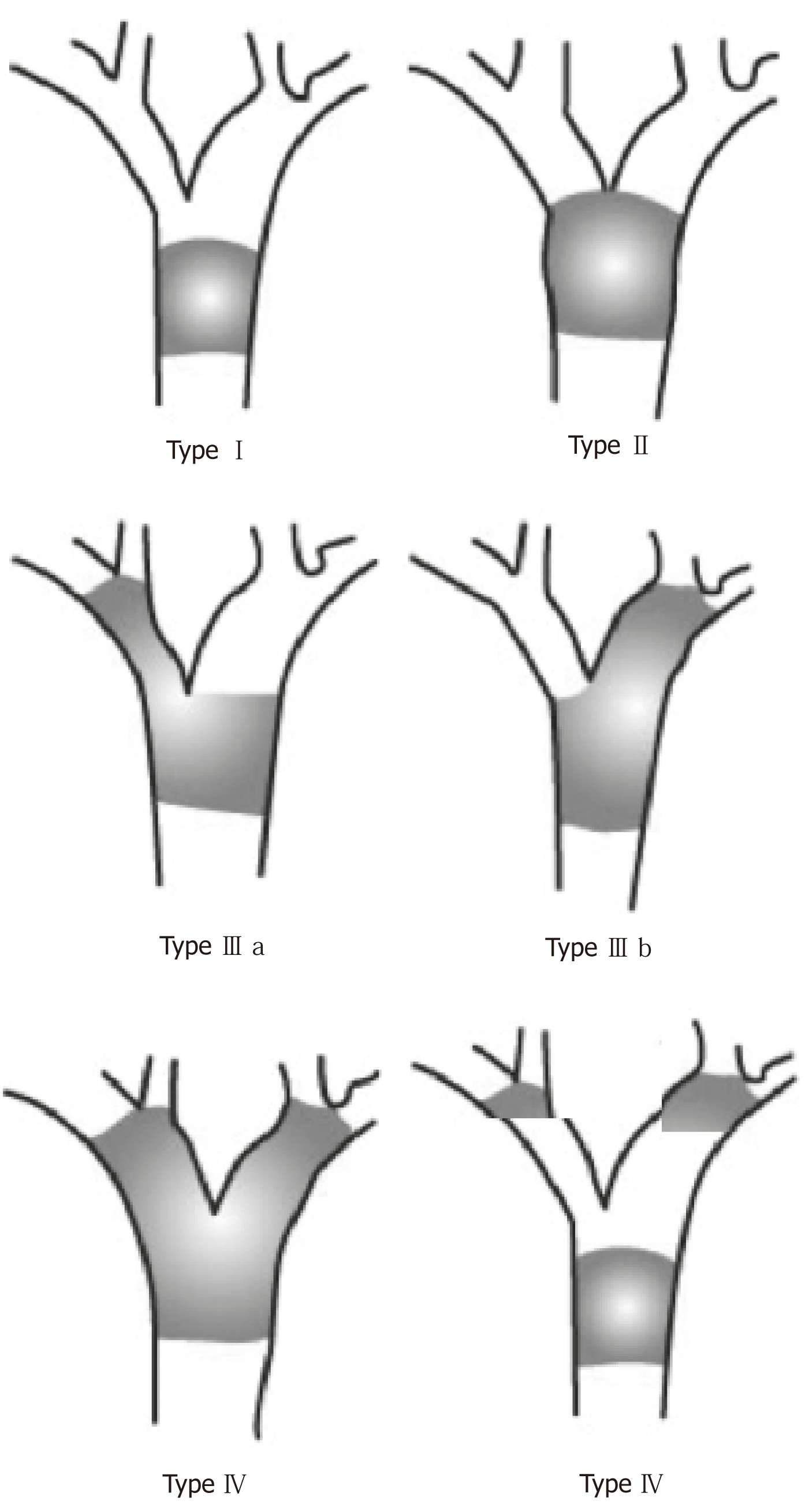
Figure 1 Bismuth-Corlette classification of pCCA (modified from Guidi et al[109]).
Type I: The tumor is located below the confluence of the left and right hepatic ducts and involves the common hepatic duct. Type II: The tumor involves the bifurcation of the common hepatic duct but does not affect the left or right hepatic ducts. Type III: The tumor occludes the common hepatic duct and the right hepatic duct (IIIa) or left hepatic duct (IIIb). Type IV: The tumor involves both the right and the left hepatic ducts or there is bilateral involvement or involvement of multiple intrahepatic segments.
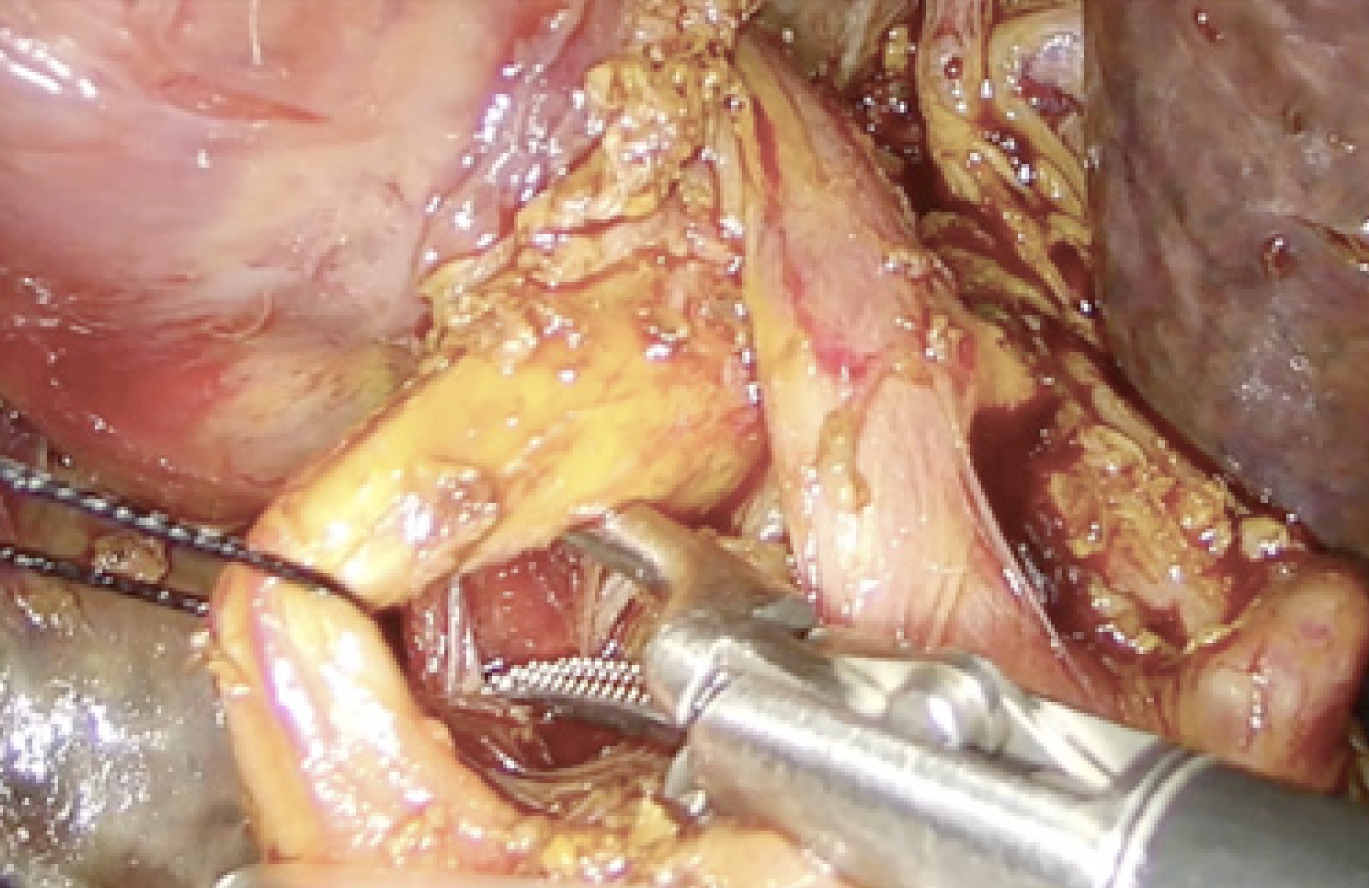
Figure 2 Lymph node dissection in the hepatic hilum (N1) during the resection of a Klatskin tumor.
- Citation: Huguet JM, Lobo M, Labrador JM, Boix C, Albert C, Ferrer-Barceló L, Durá AB, Suárez P, Iranzo I, Gil-Raga M, Burgos CB, Sempere J. Diagnostic-therapeutic management of bile duct cancer. World J Clin Cases 2019; 7(14): 1732-1752
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v7/i14/1732.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v7.i14.1732