Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2018; 6(8): 224-232
Published online Aug 16, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i8.224
Published online Aug 16, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i8.224
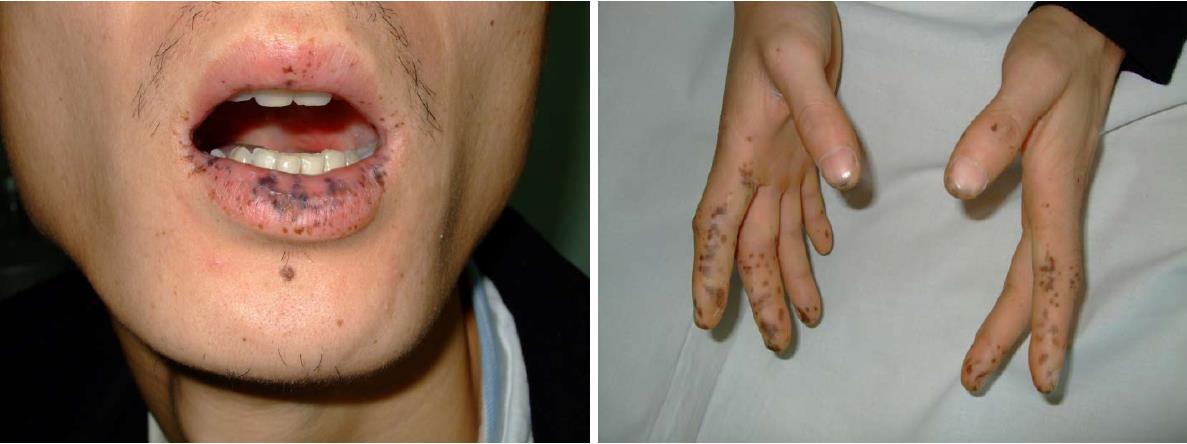
Figure 1 Mucocutaneous pigmentation of the patient.
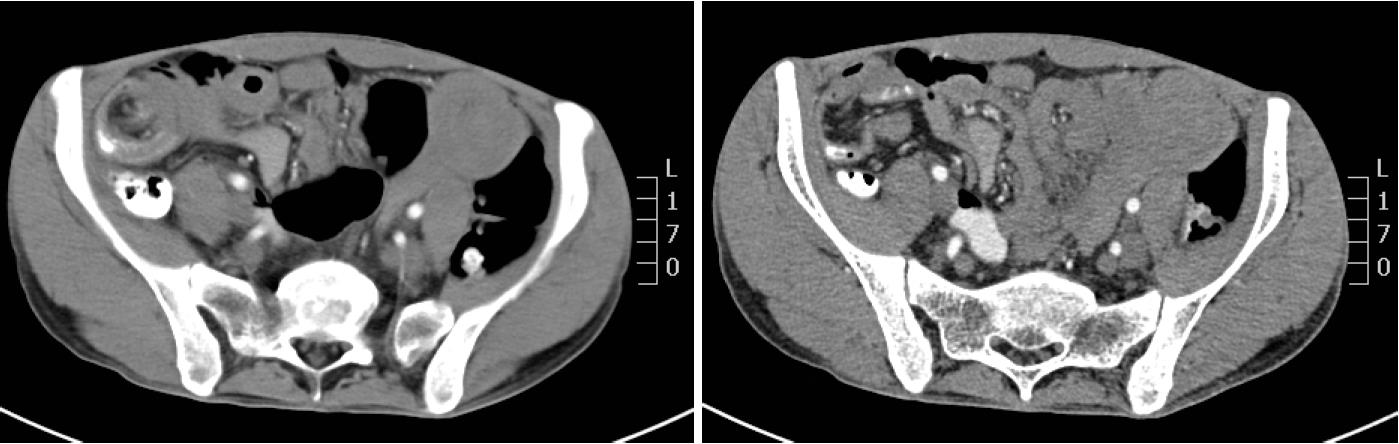
Figure 2 Abdominal and pelvic CT scan.
It showed that many polyps are distributed in the descending duodenum and the small intestine, and the local intestinal canal was torsional.
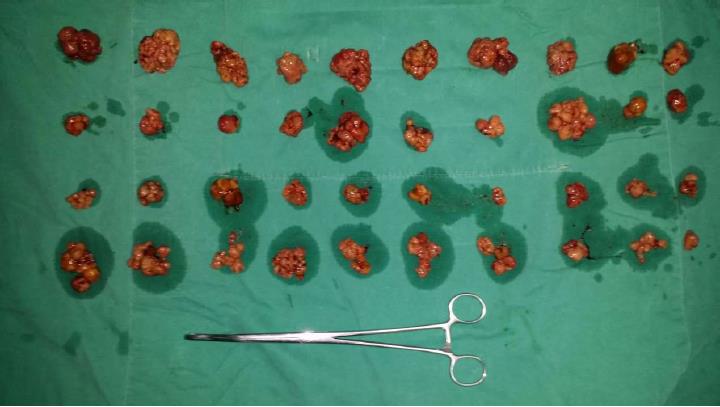
Figure 3 Hamartoma polyps removed from the patient’s gastrointestinal tract.
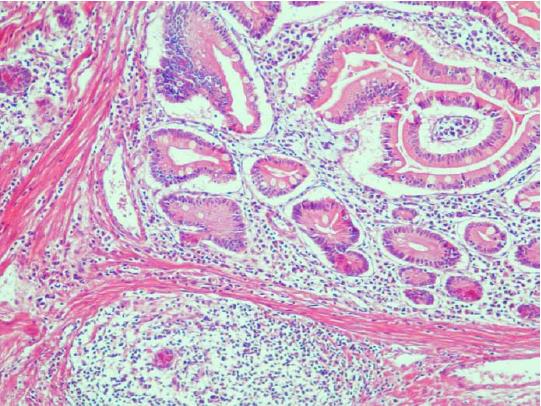
Figure 4 Postoperative pathological reports showed Peutz-Jeghers syndrome hamartoma polyps (HE, original magnification × 200).
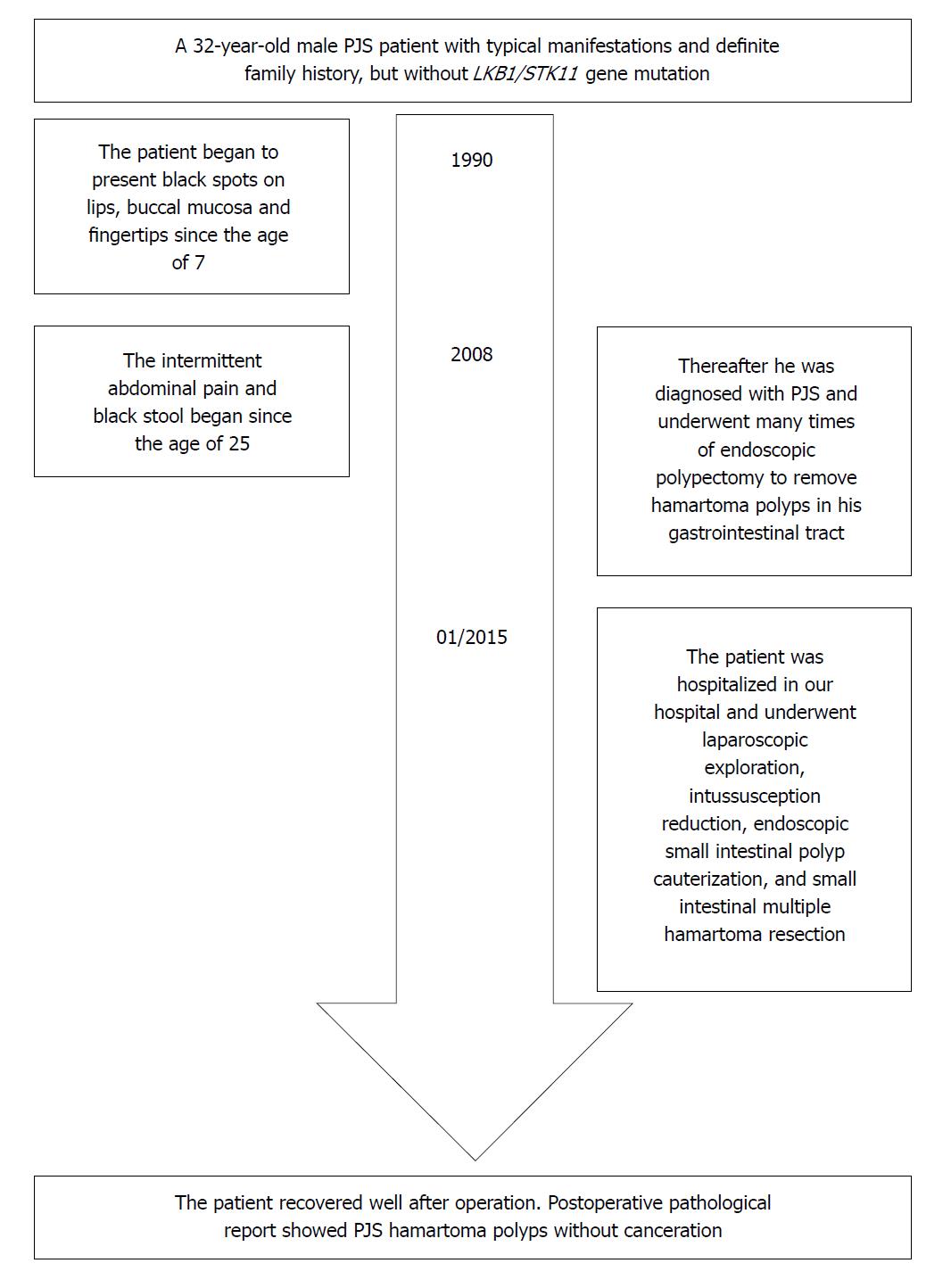
Figure 5 Timeline of the patient.
PJS: Peutz-Jeghers syndrome.
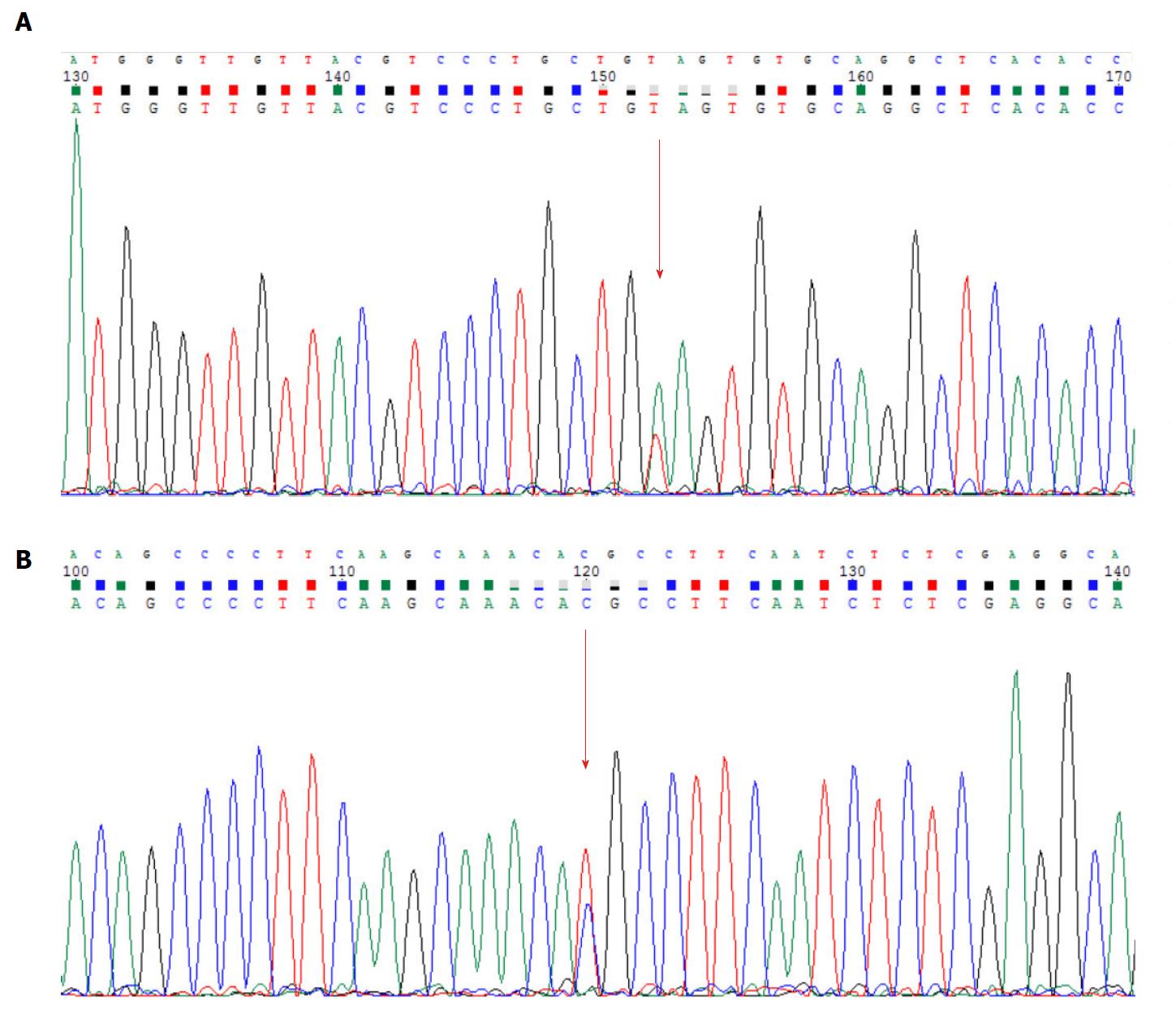
Figure 6 Results of the Sanger sequencing.
Mutation sites are marked with arrows. A: MSH6: c.3488A>T; B: APC: c.6662T>C.
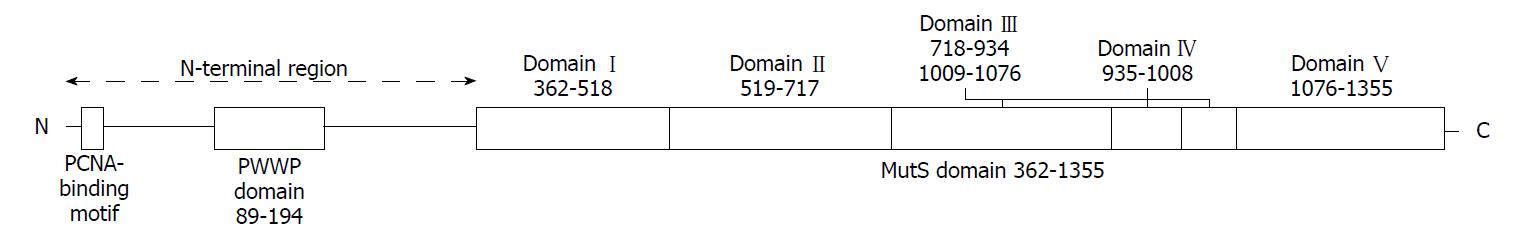
Figure 7 Domain organization of human MSH6[26].
It mainly consists of PCNA-binding motif, PWWP domain and the MutS domain.
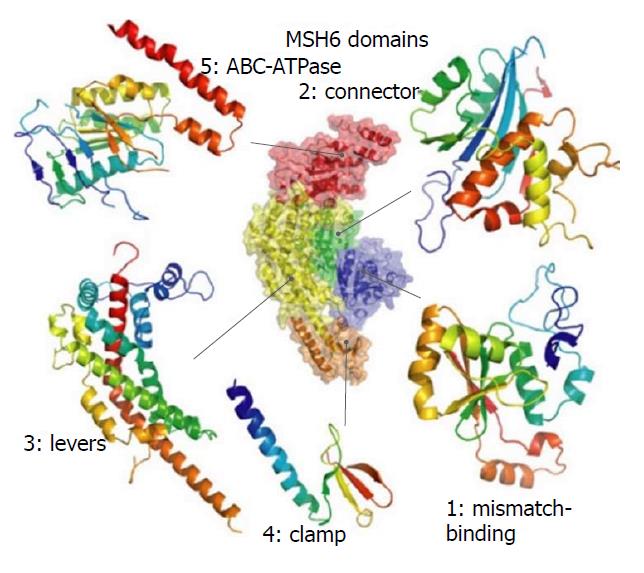
Figure 8 The domain structure of MSH6.
Figures were generated with PyMOL[29].
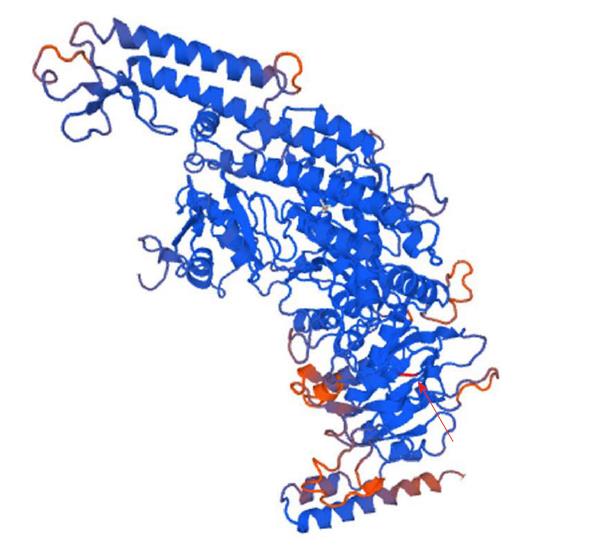
Figure 9 Structure of the mutant MSH6 (p.
Glu1163Val). Arrow indicates the position of the mutation. The figure was generated with Swiss-Model online software.
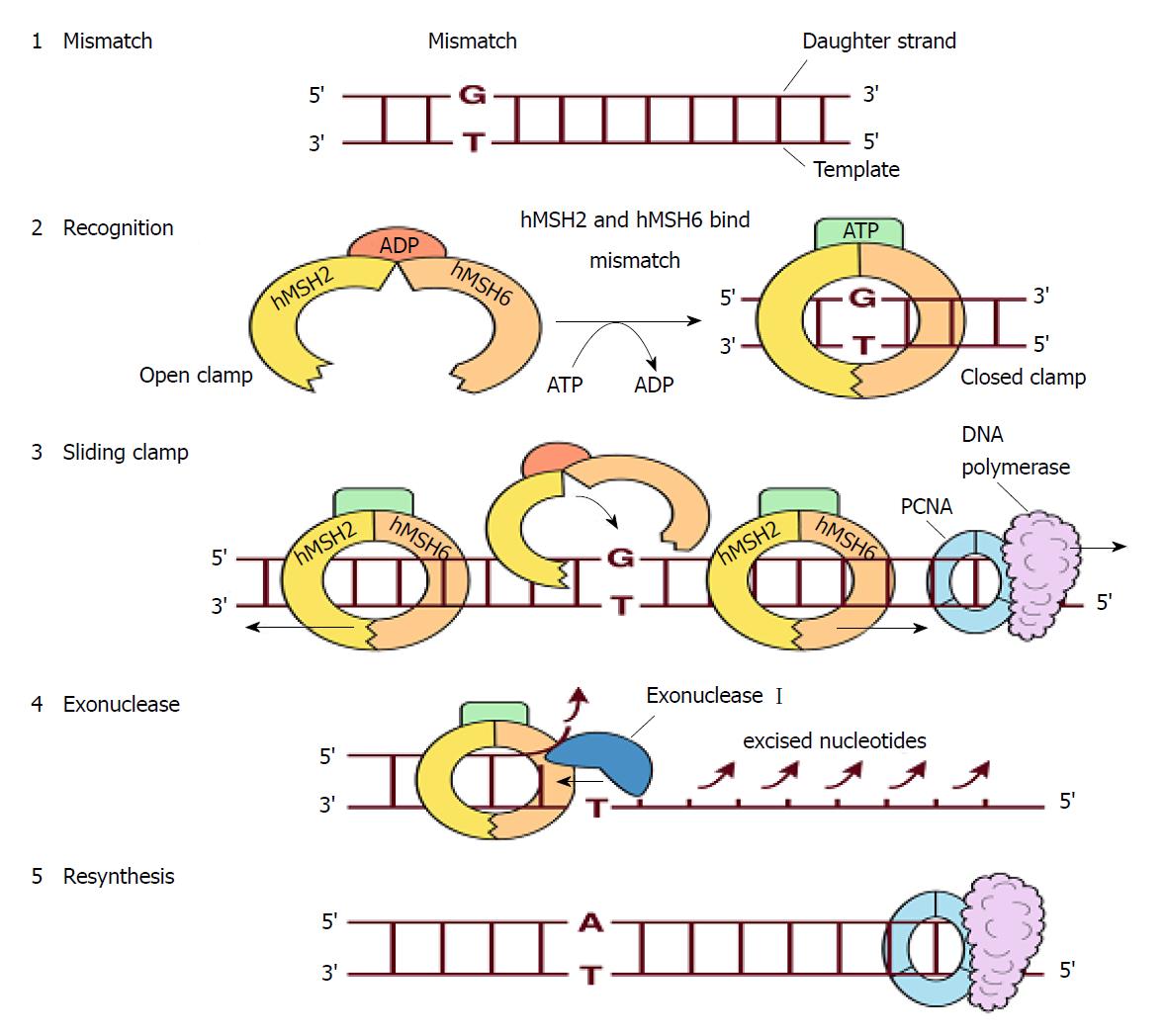
Figure 10 Repairing single-base mismatch in S phase by MutSα[30].
1: A mismatch appears in the daughter strand; 2: Upon encountering the mispair, the MutSα, which consists of hMSH2, hMSH6 and ADP, switches to a closed, sliding clamp along the DNA. This process is accompanied by exchanging of ATP for ADP; 3: Multiple MutSα clamps may be recruited to the mismatch. Moving in the 5′ > 3′ direction, the MutSα will meet and displace the PCNA-DNA polymerase complex in DNA synthesis; 4: Exonuclease I excises the nucleotides of the daughter strand back to the site of the mismatch; 5: The daughter strand is resynthesized and the error is corrected.
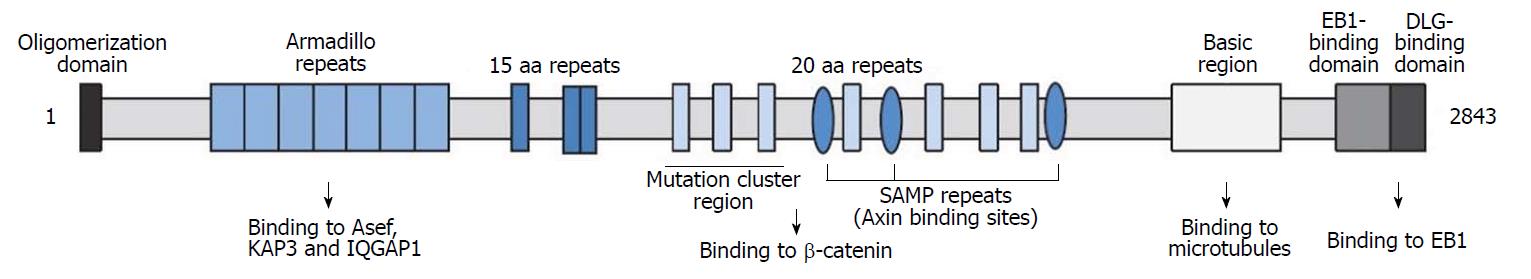
Figure 11 Major structure and functions of APC[35].
It is made up of oligomerization domain, armadillo repeats domain, 15-amino acid or 20-amino acid repeats domain, SAMP repeats domain, mutation cluster region, basic region, EB1-binding domain and DLG-binding domain.
- Citation: Duan FX, Gu GL, Yang HR, Yu PF, Zhang Z. Must Peutz-Jeghers syndrome patients have the LKB1/STK11 gene mutation? A case report and review of the literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(8): 224-232
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i8/224.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i8.224