Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2018; 6(14): 862-868
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.862
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.862
Figure 1 Flushing in the face and neck of the patient.
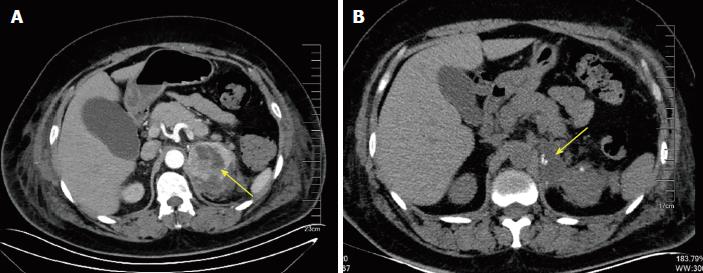
Figure 2 Abdominal computed tomography.
A: The arrow indicates a heterogeneous left adrenal mass; B: After operation, the left adrenal mass was removed (arrow) and a small amount of encapsulated effusion remained.
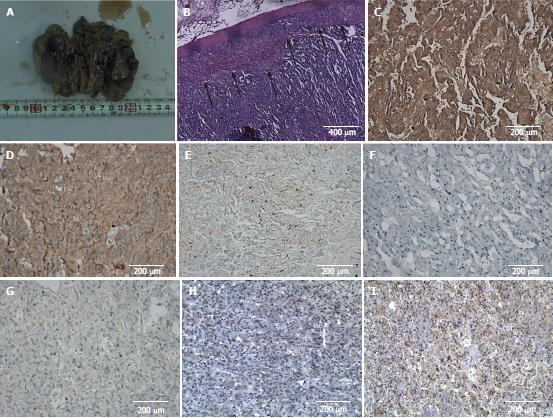
Figure 3 Histopathological and immunohistochemical staining.
A: A gross pathological finding of the resected adrenal tumor; B: Hematoxylin-eosin staining of tumor tissue, black arrows indicate the juncture of normal adrenal cortex and tumor tissue; C-I: Immunohistochemical staining for synaptophysin (C), chromogranin A (D), S-100 (E), creatine kinase (F), KI67 (G), vasoactive intestinal peptide (H), and somatostatin receptor 2 (I).
- Citation: Hu X, Cao W, Zhao M. Octreotide reverses shock due to vasoactive intestinal peptide-secreting adrenal pheochromocytoma: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(14): 862-868
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i14/862.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.862