Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2018; 6(14): 847-853
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.847
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.847
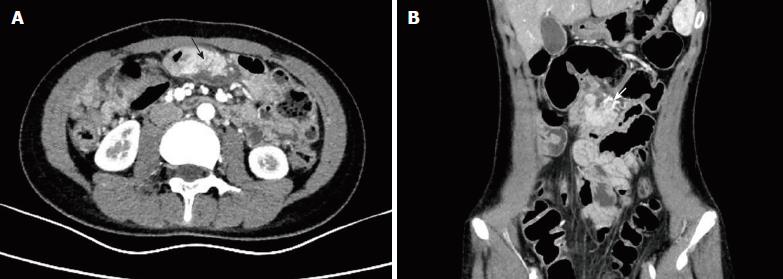
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography images of the abdomen.
A: Axial contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) image of the abdomen showing an enhanced oval, soft-tissue mass in the jejunal mesentery at the level of the umbilicus (black arrow); B: Coronal CECT image showing that the mass had its own blood supply (white arrow).
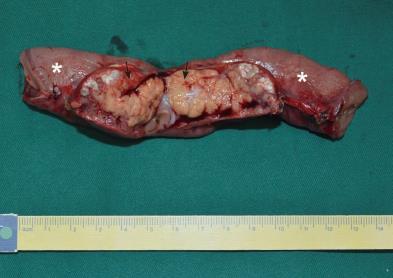
Figure 2 Photograph of the resected mass and the adjacent small bowel.
Photograph of the gross specimen demonstrates a 4 cm × 3 cm, yellowish, soft-tissue mass (black arrows) located in the jejunal mesentery and adhered to the serosal surface of the jejunum (white asterisks).
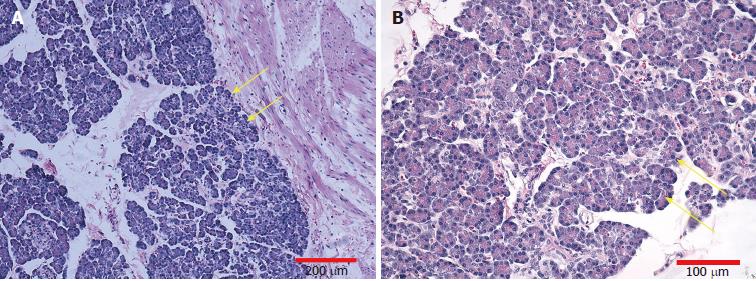
Figure 3 Histopathologic examination of the resected specimen.
Microscopic appearance showing that the lesion consisted of heterotopic pancreatic tissue (yellow arrows), including acini, islet cells, and pancreatic ducts, extending to the jejunal serosa (H and E staining; A: Magnification, × 100, scale bar = 200 μm; B: Magnification, × 200, scale bar = 100 μm).
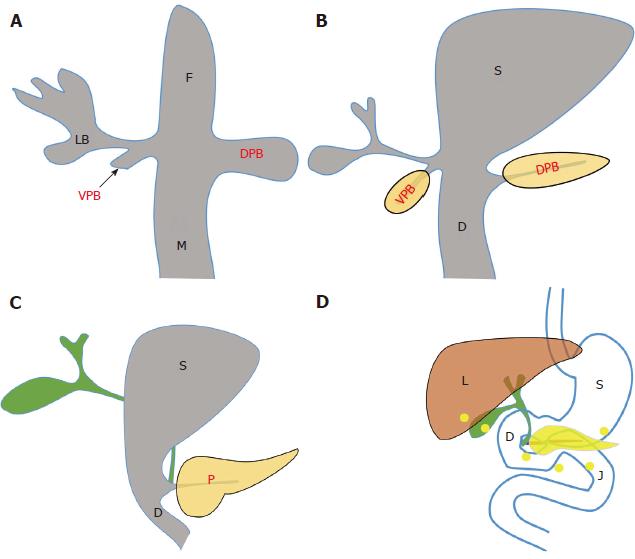
Figure 4 Schematic diagram of the “misplacement theory”.
A, B: The pancreas develops from the ventral and dorsal pancreatic buds, which develop at the junction of the foregut and midgut during the 4th week of gestation; C: As the foregut elongates, the developing ventral pancreas, gallbladder, and bile duct rotate clockwise posterior to the duodenum and join the dorsal pancreas in the retroperitoneum. The ventral pancreatic bud rotates clockwise and fuses with the dorsal bud at the 7th week of gestation; D: According to the misplacement theory, deposits of pancreatic tissue are “dropped” into the developing gastrointestinal system during rotation of the foregut when fragments of pancreas become separated and develop into mature elements. Yellow points in D indicate possible locations of heterotopic pancreas. F: Foregut; M: Midgut; VPB: Ventral pancreatic bud; DPB: Dorsal pancreatic bud; LB: Liver bud; S: Stomach; D: Duodenum; P: Pancreas; L: Liver; J: Jejunum.
- Citation: Tang XB, Liao MY, Wang WL, Bai YZ. Mesenteric heterotopic pancreas in a pediatric patient: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(14): 847-853
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i14/847.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.847