Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 26, 2018; 6(14): 830-835
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.830
Published online Nov 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.830
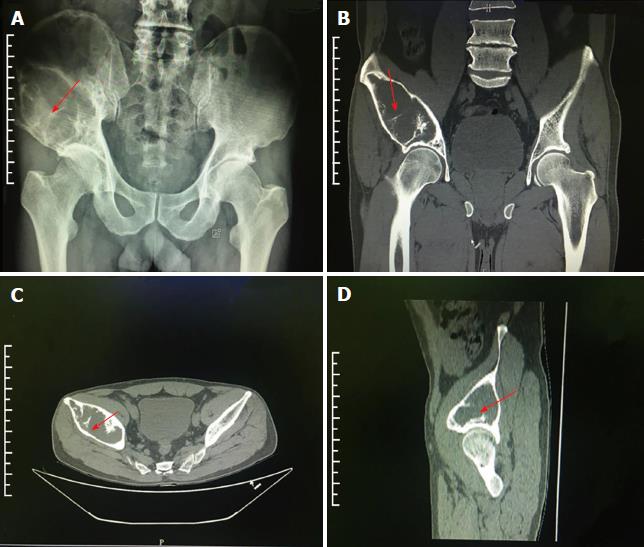
Figure 1 Radiography examination results.
A: Extensive bone destruction of the right ilium on radiography examination, with a size of about 10 cm × 5 cm × 5 cm, and bone density also changed; B: Computed tomography shows osteosclerosis in the surrounding area of the ilium tumor without significant periosteal reaction in the coronary site; C: Trans-sectional site; D: Sagittal position (arrow indicates the area of lesion).
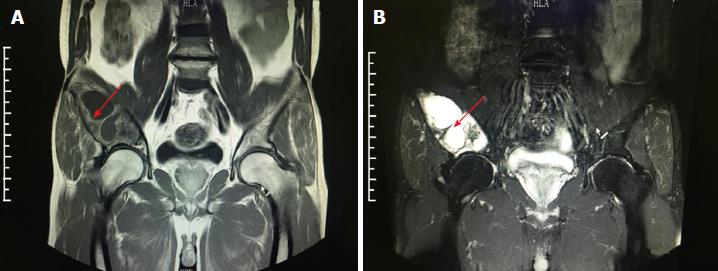
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging examination results.
A: Extensive bone destruction in right ilium. T1w suggests low-density change; B: T2w suggests high-density change, with surrounding soft issue swelling (arrow indicates the area of lesion).
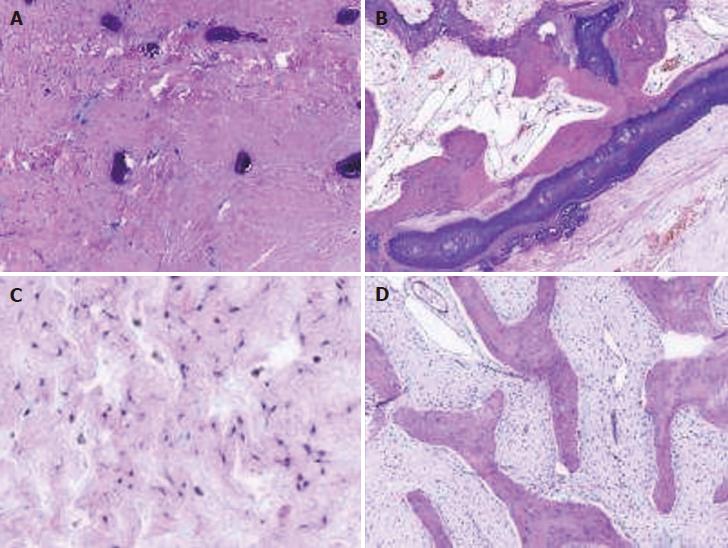
Figure 3 Pathological reports.
A: Calcified woven bone can be seen (HE; 40 ×); B: No osteoblast and osteoclast hyperplasia can be seen (HE; 40 ×); C: It shows Fibroblast and Mucoid matrix (HE; 40 ×); D: It shows fibro-osseous lesions, with discontinuity of the trabecular bone and calcification (HE; 40 ×). HE: Hematoxylin-eosin.
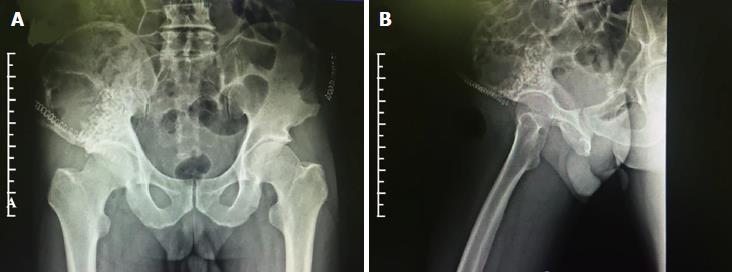
Figure 4 Postoperative radiography examinations.
A and B: Artificial bone and autogenous bone in the weight-bearing zone of top acetabular were in place with satisfactory coverage.
- Citation: Liu YB, Zou TM. Giant monostotic osteofibrous dysplasia of the ilium: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(14): 830-835
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i14/830.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i14.830