Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2018; 6(13): 666-670
Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.666
Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.666
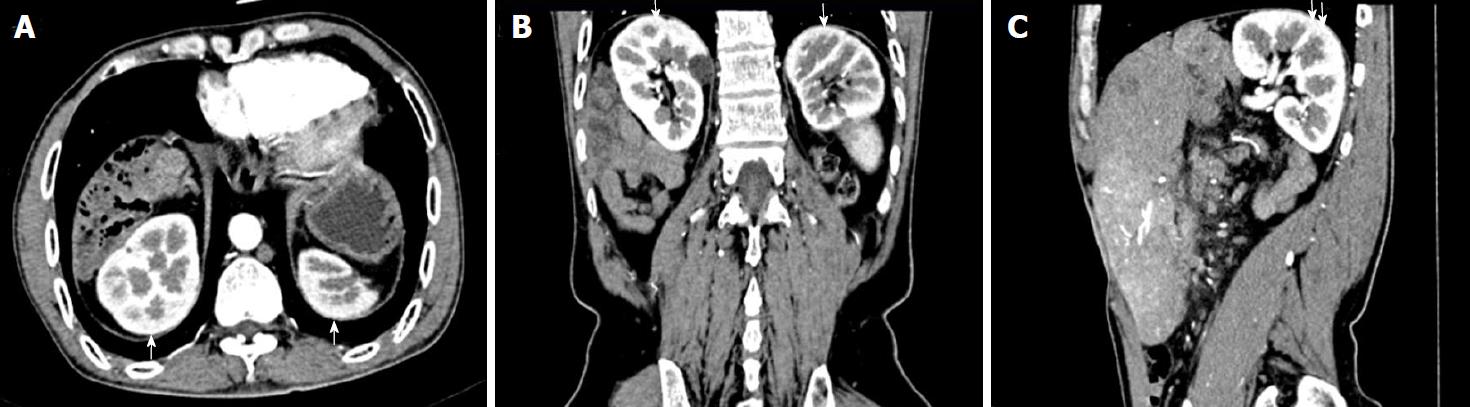
Figure 1 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography in arterial phase demonstrates the thoracic kidneys.
A: Transverse view scan shows the upper pole of the kidney (arrows), above the liver, is surrounded by the lower lobe of lung; B: Coronal view scan shows the kidneys (arrows) located immediately below the diaphragm, with part of the kidney protruding into the thorax; C: Sagittal view scan shows kidney (arrows) located immediately below the diaphragm.
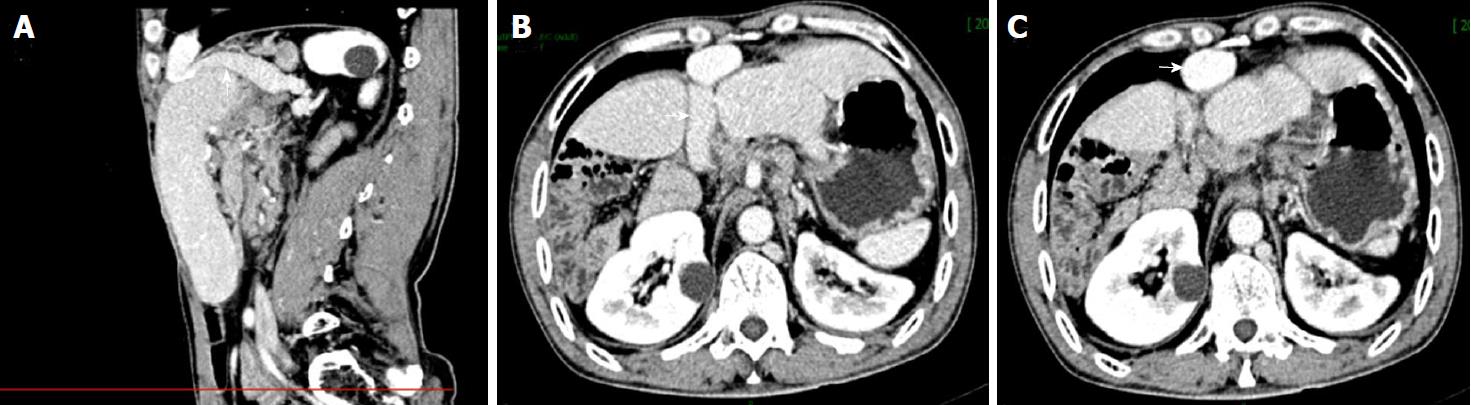
Figure 2 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography in venous phase shows heterotopic inferior vena cava located behind the anterior abdominal wall.
A: Sagittal view scan demonstrates the suprarenal segment of the inferior vena cava (IVC) coursed cranially and anteriorly along the space between the liver and diaphragm and bridged hepatic segment and the renal segment; B: Transverse view scan shows the suprarenal segment of the IVC crossed through the liver and drained into the anterior IVC; C: Transverse view scan shows the hepatic IVC (arrow) was located posterior to the anterior abdominal wall.
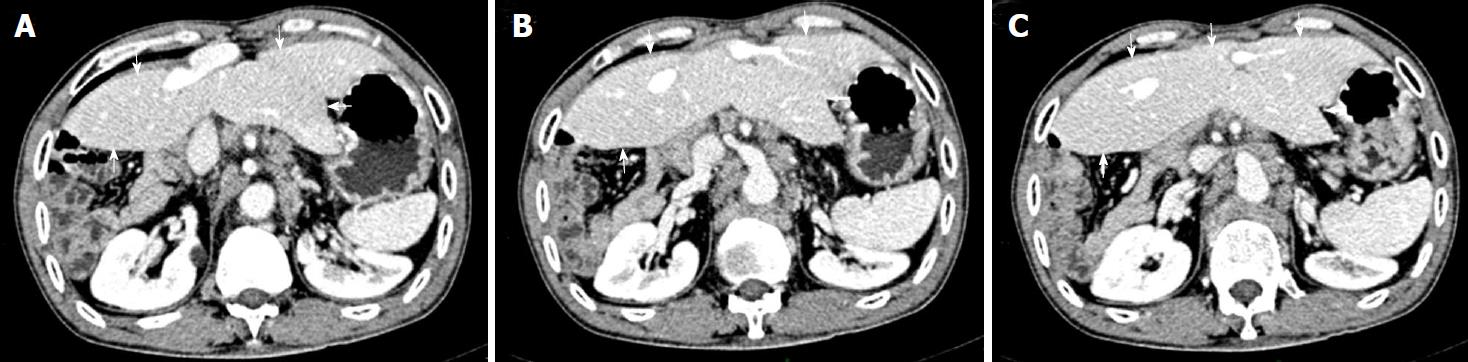
Figure 3 Contrast-enhanced computed tomography in venous phase from cranial to caudal positions shows a liver with abnormal morphology.
A: Transverse view scan above the hilar level of kidney shows the malformed liver (arrows); B: Transverse view scan at the hilar level of kidney shows the malformed liver (arrows); C: Transverse view scan below the hilar level of kidney shows the malformed liver (arrows).
- Citation: Peng XX, Cheng SA, Liang QL, Luo XB, Hong XC, Yuan GL, Zhang HJ. Bilateral thoracic kidneys combined with inferior vena cava located behind the anterior abdominal wall: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(13): 666-670
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i13/666.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.666