Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Nov 6, 2018; 6(13): 632-640
Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.632
Published online Nov 6, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.632
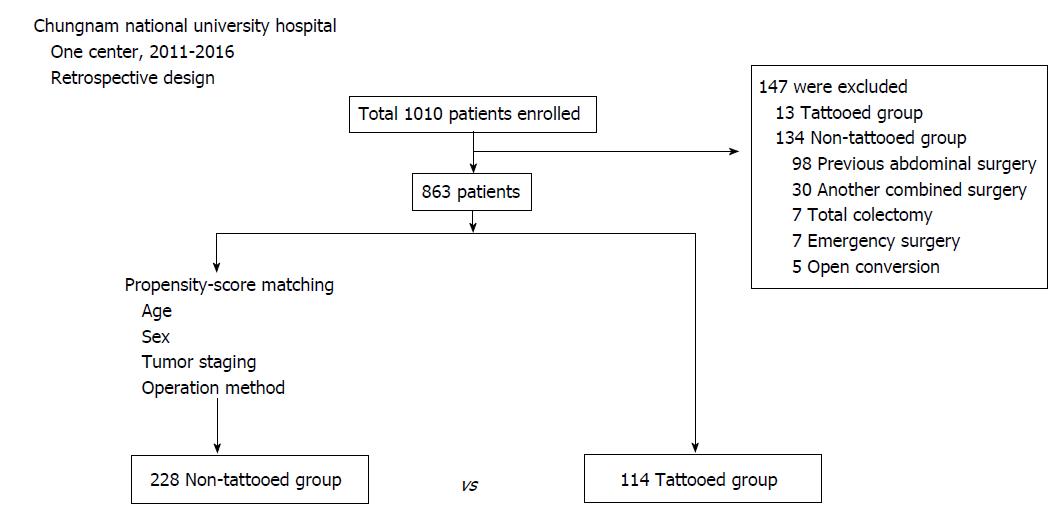
Figure 1 Flow chart of patients enrolled in this study.
The 114 tattooed group subjects and the 228 non-tattooed group subjects were selected by propensity score matching. A total of 342 patients was enrolled.
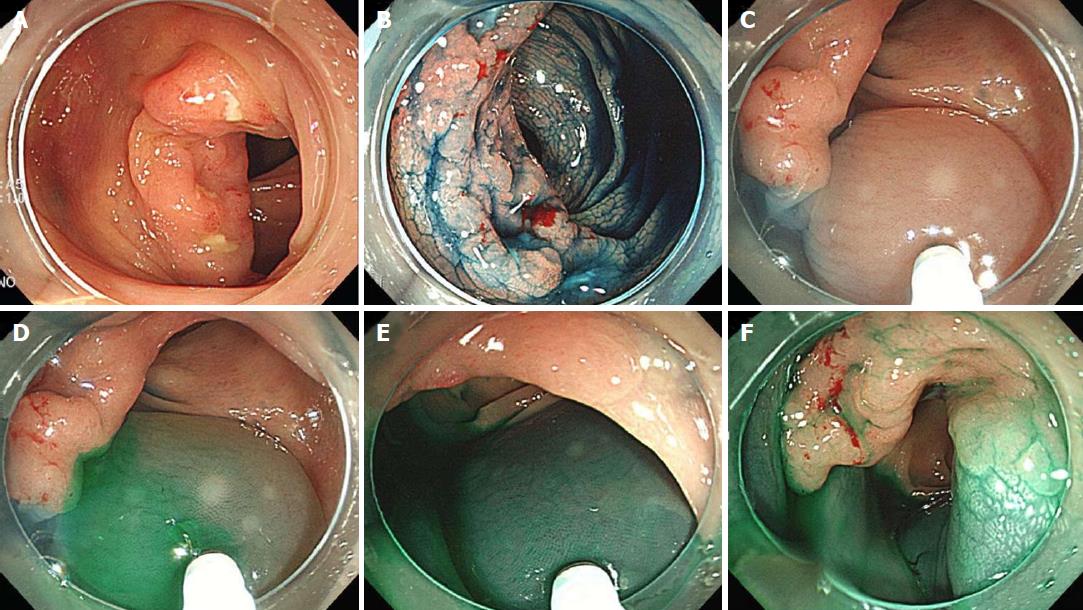
Figure 2 Endoscopic tattooing using indocyanine green.
Indocyanine green (ICG) tattooing was performed one day prior to colonoscopic surgery by the circumferential method. A: White light endoscopy image of early sigmoid colon cancer; B: Indigo carmine was used to determine the margin of the lesion; C: Between 1-2 mL of normal saline solution was injected into the submucosa to make an artificial pseudo polyp; D-F: Subsequently, the saline syringe was replaced by the ICG syringe, and 0.5-1 mL of dissolved ICG was injected. ICG: Indocyanine green.
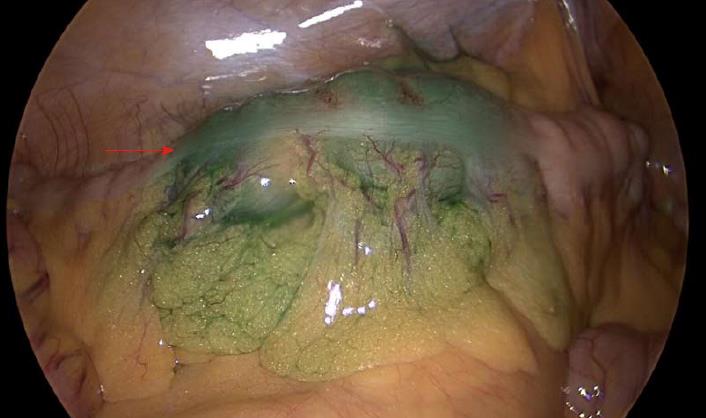
Figure 3 Intraoperative photo.
Tattooed area showing a green color (arrow). In the pathologic report, this lesion was 2.3 cm × 1.9 cm in size.
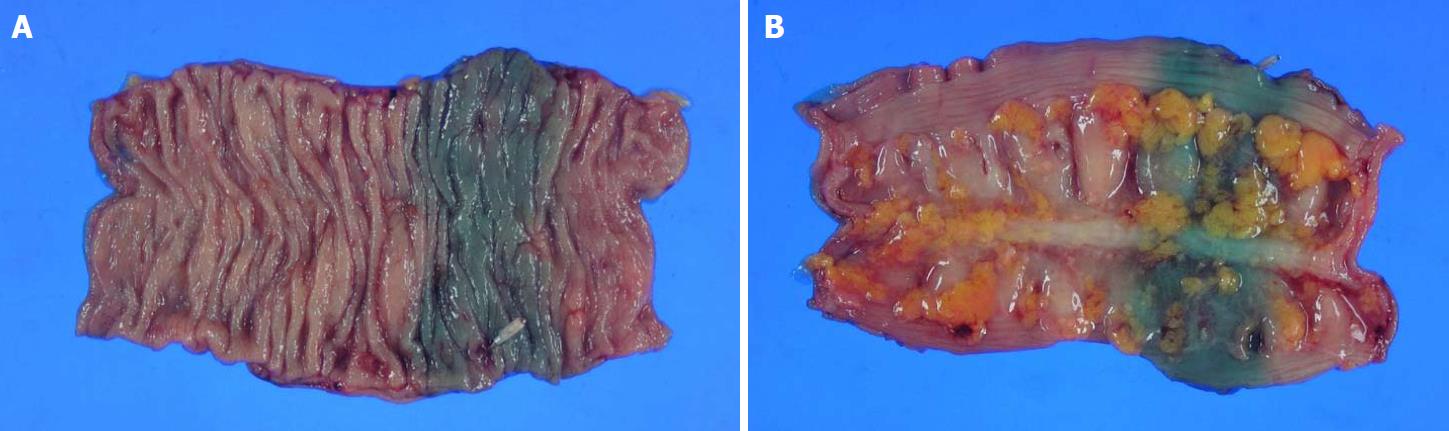
Figure 4 Pathologic specimen of the resected colon.
An obvious green color is observed in the inner (A) and outer (B) sides of the colon.
- Citation: Park JH, Moon HS, Kwon IS, Yun GY, Lee SH, Park DH, Kim JS, Kang SH, Lee ES, Kim SH, Sung JK, Lee BS, Jeong HY. Usefulness of colonic tattooing using indocyanine green in patients with colorectal tumors. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(13): 632-640
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i13/632.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i13.632