Copyright
©The Author(s) 2018.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 26, 2018; 6(12): 570-576
Published online Oct 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i12.570
Published online Oct 26, 2018. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v6.i12.570
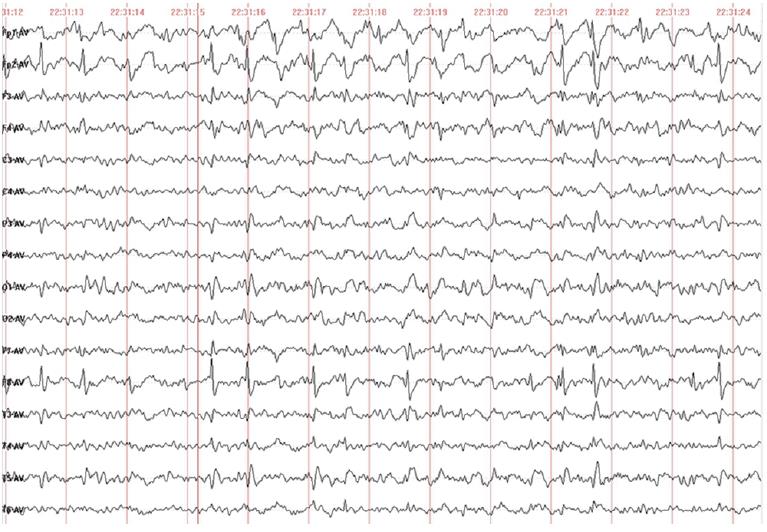
Figure 1 Electroencephalogram of the patient.
It showed generalized continuous spike-and-wave patterns in the bitemporal and frontal lobes, noticeable on the left side. Abnormal discharge was more pronounced during the sleep-electroencephalogram. Slower on background activity.
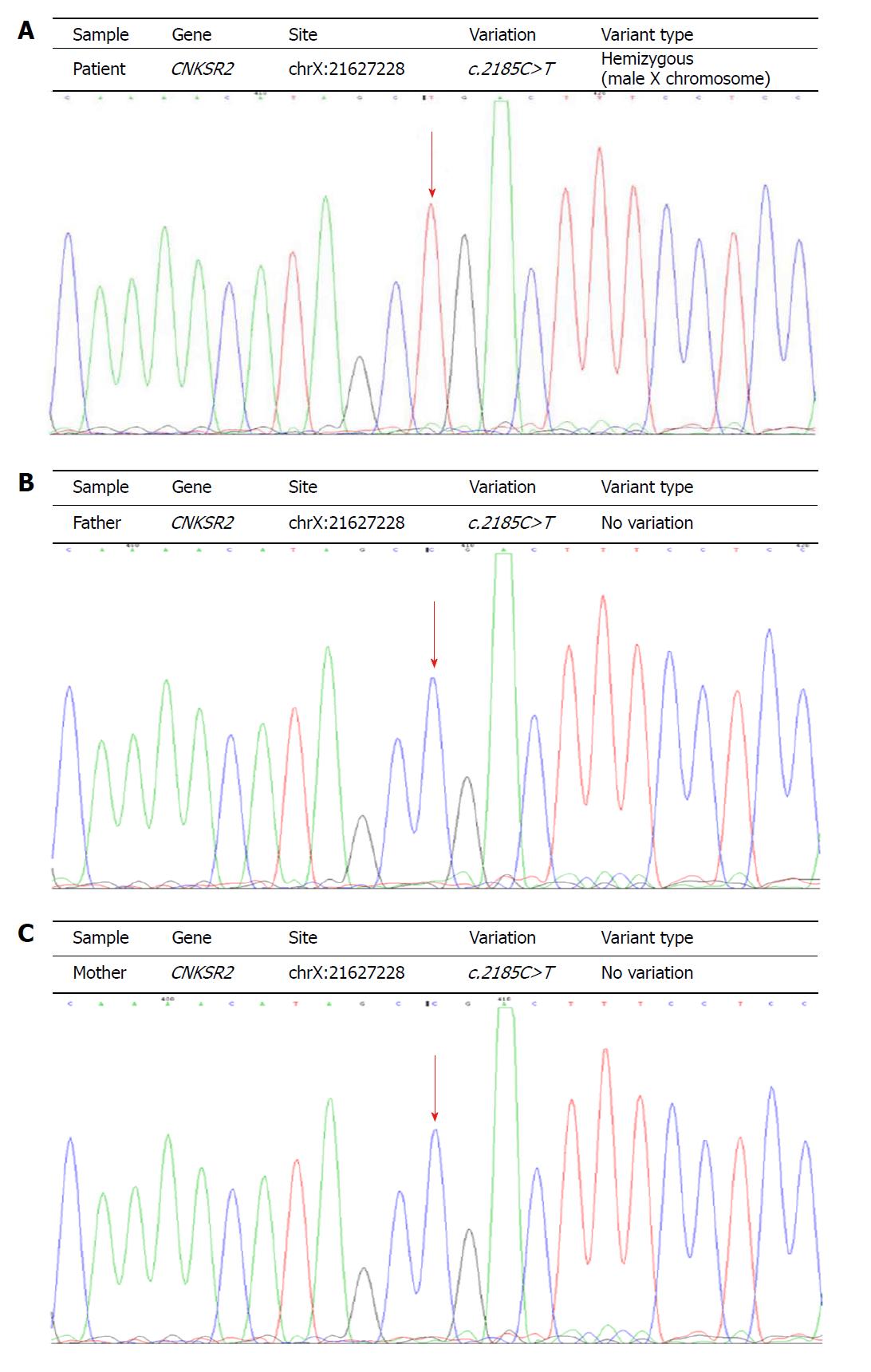
Figure 2 Gene sequences of three members in the family.
A: De novo mutation of the CNKSR2 gene (c. 2185C>T, p.Arg729Ter) in the patient; B, C: No mutation was observed at the same locus in the parents (arrows).
Figure 3 Secondary structures of wild-type and mutated CNKSR2 proteins predicted by PSIPRED.
A: The wild-type CNKSR2 gene encodes an intact peptide chain of 1034 amino acids; B: The mutated CNKSR2 gene leads to an early termination of the synthesis of the peptide chain and only No.1-728 amino acids are expressed.
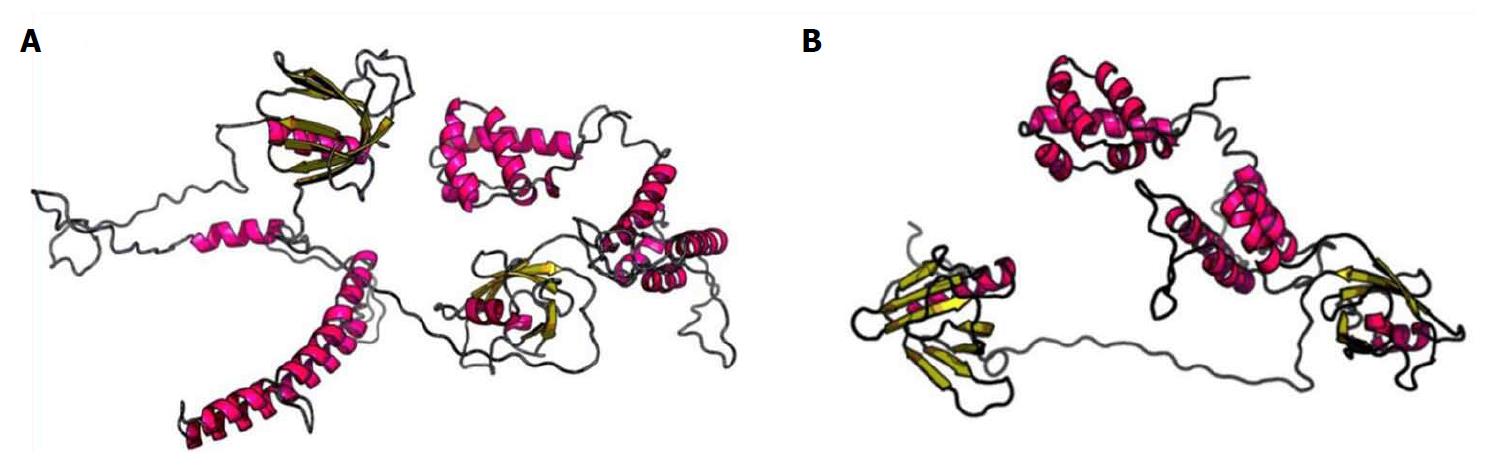
Figure 4 Tertiary structures of wild-type and mutated CNKSR2 proteins predicted by RaptorX.
The spatial structures of CNKSR2 proteins are significantly different between the wild-type (A) and the patient (B).
- Citation: Sun Y, Liu YD, Xu ZF, Kong QX, Wang YL. CNKSR2 mutation causes the X-linked epilepsy-aphasia syndrome: A case report and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2018; 6(12): 570-576
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v6/i12/570.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v6.i12.570