Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2017; 5(6): 234-237
Published online Jun 16, 2017. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.234
Published online Jun 16, 2017. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.234
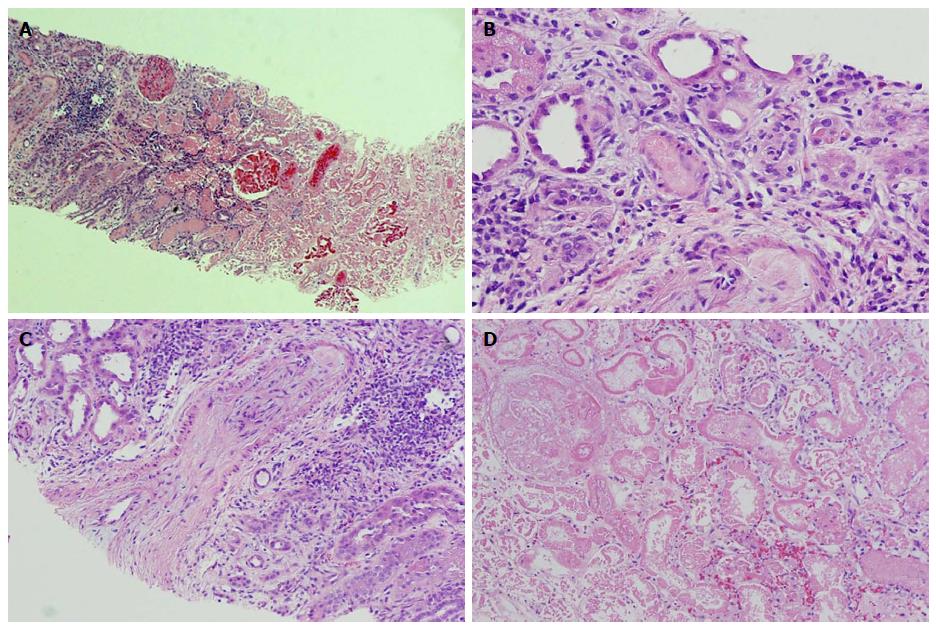
Figure 1 Renal pathology.
Pathological findings: A: Corticomedullary junction. The right side is necrotic renal cortex. On the left side of the image there is still viable corticomedullary junction. H and E, × 40; B: An arteriole obliterated with amorphous material (platelet and fibrin thrombus). H and E, × 200; C: An arcuate artery with almost completely obliterated lumen by severe fibrous to mucoid intimal thickening at the corticomedullary junction. H and E, × 100; D: Necrotic renal cortex without nuclear staining in the cells. H and E, × 200.
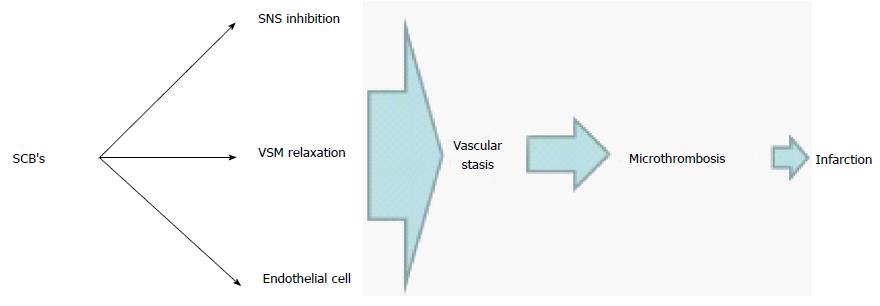
Figure 2 Proposed mechanism of synthetic cannabinoids-induced thrombotic microangiopathy.
Prolonged hypotension secondary to the inhibitory effect of the SCBs on the sympathetic tone and vascular smooth muscle cells along with endothelial release of nitric oxide can lead to stasis followed by endothelial ischemia and microthrombosis leading to renal cortical necrosis. SCBs: Synthetic cannabinoids; SNS: Sympathetic nervous system; VSM: Vascular smooth muscle.
- Citation: Mansoor K, Zawodniak A, Nadasdy T, Khitan ZJ. Bilateral renal cortical necrosis associated with smoking synthetic cannabinoids. World J Clin Cases 2017; 5(6): 234-237
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v5/i6/234.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v5.i6.234