Copyright
©The Author(s) 2017.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2017; 5(3): 93-101
Published online Mar 16, 2017. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v5.i3.93
Published online Mar 16, 2017. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v5.i3.93
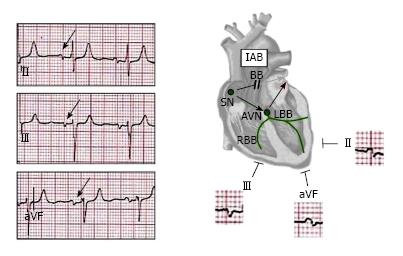
Figure 1 Scheme of the anatomo-electrophysiologic features of the Bayés syndrome[27].
AVN: AV node; BB: Bachmann bundle; IAB: Interatrial block; LBB: Left bundle branch; RBB: Right bundle branch; SN: Sinus node.
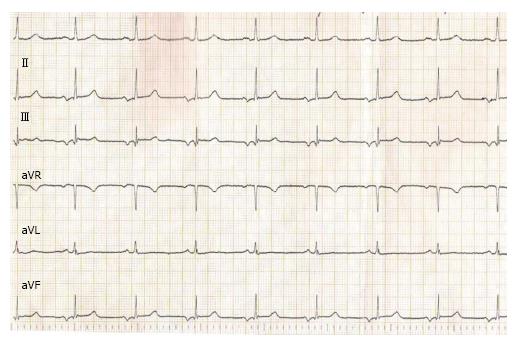
Figure 2 A 55-year-old male diagnosed with Bayés syndrome, with a history of paroxysmal atrial fibrillation showing normal values of echocardiographic measurements, except for a discrete left atrial enlargement (40 mm).
ECG shows the presence of advanced interatrial block. P-wave duration is wide (120 ms) and biphasic in inferior leads (II, III and aVF). ECG: Electrocardiogram.
- Citation: Arboix A, Martí L, Dorison S, Sánchez MJ. Bayés syndrome and acute cardioembolic ischemic stroke. World J Clin Cases 2017; 5(3): 93-101
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v5/i3/93.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v5.i3.93