Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2016; 4(8): 233-237
Published online Aug 16, 2016. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i8.233
Published online Aug 16, 2016. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i8.233
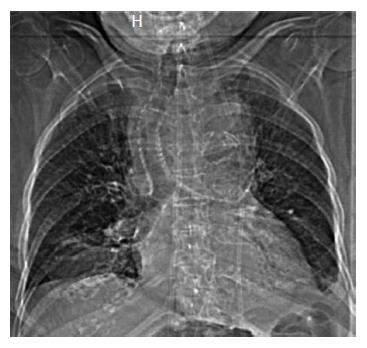
Figure 1 Chest radiography showed a widened mediastinum and tracheal deviation.
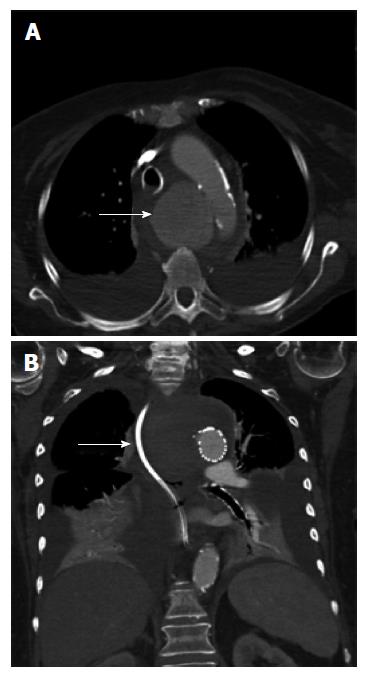
Figure 2 Computed tomography of the chest with intravenous contrast showed a saccular thoracic aortic aneurysm (5.
0 cm × 5.0 cm) (arrow). Pre (A) and post (B) TEVAR with surrounding hematoma compressing the trachea, esophagus and superior vena cava. TEVAR: Thoracic endovascular aortic repair.
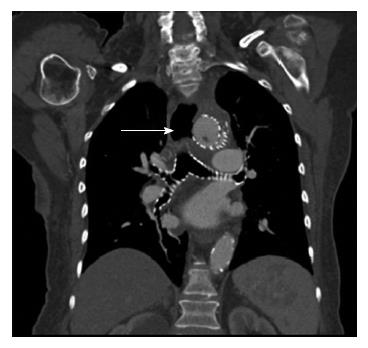
Figure 3 Computed tomography demonstrating an aortoesophageal fistula (arrow).
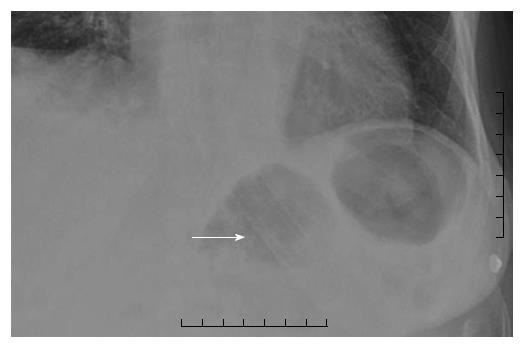
Figure 4 Chest X-ray demonstrating migration of the esophageal stent to the level of the gastroesophageal junction (arrow).
- Citation: Tao M, Shlomovitz E, Darling G, Roche-Nagle G. Secondary aorto-esophageal fistula after thoracic aortic aneurysm endovascular repair treated by covered esophageal stenting. World J Clin Cases 2016; 4(8): 233-237
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v4/i8/233.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v4.i8.233