Copyright
©The Author(s) 2016.
World J Clin Cases. Apr 16, 2016; 4(4): 112-117
Published online Apr 16, 2016. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i4.112
Published online Apr 16, 2016. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v4.i4.112
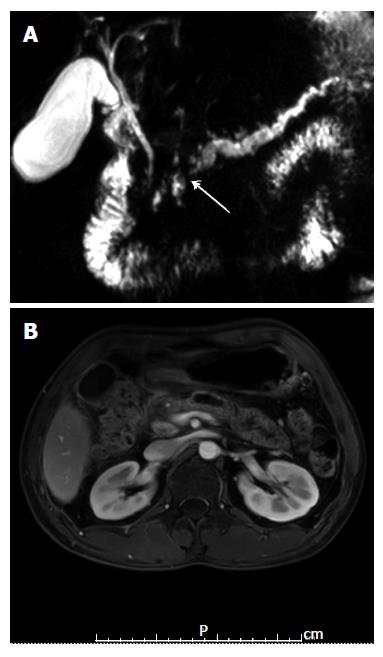
Figure 1 Radiologic imaging finding showing an atrophic pancreatic parenchyma dilatation of pancreatic duct to 7 mm in diameter.
A: Magnetic resonance image; B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography.
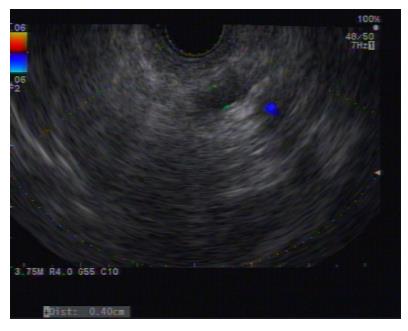
Figure 2 Echoview of the main pancreatic duct, from the body to tail, showing irregular and tortuous configuration and dilation up to 7 mm.
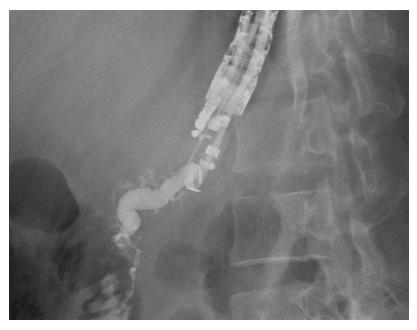
Figure 3 Pancreatography showing the main pancreatic duct to be irregular, tortuous, and dilated.
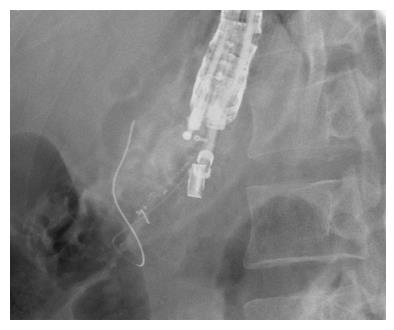
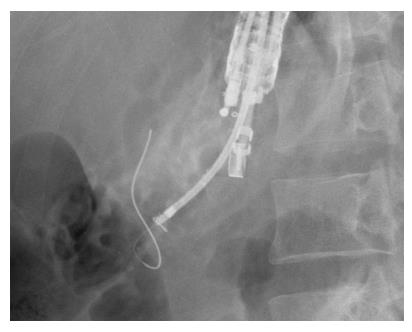
Figure 4 Fluoroscopic view showing the guidewire at the point it was hindered from passing through the papilla.
Figure 5 Fluoroscopic views during the neo-tract dilation.
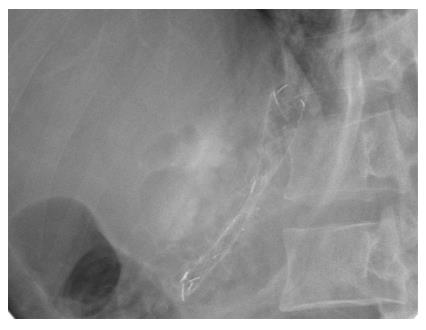
Figure 6 Fluoroscopic views after stent deployment.
- Citation: Chang A, Aswakul P, Prachayakul V. Chronic pancreatic pain successfully treated by endoscopic ultrasound-guided pancreaticogastrostomy using fully covered self-expandable metallic stent. World J Clin Cases 2016; 4(4): 112-117
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v4/i4/112.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v4.i4.112