Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Clin Cases. Sep 16, 2015; 3(9): 779-788
Published online Sep 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i9.779
Published online Sep 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i9.779
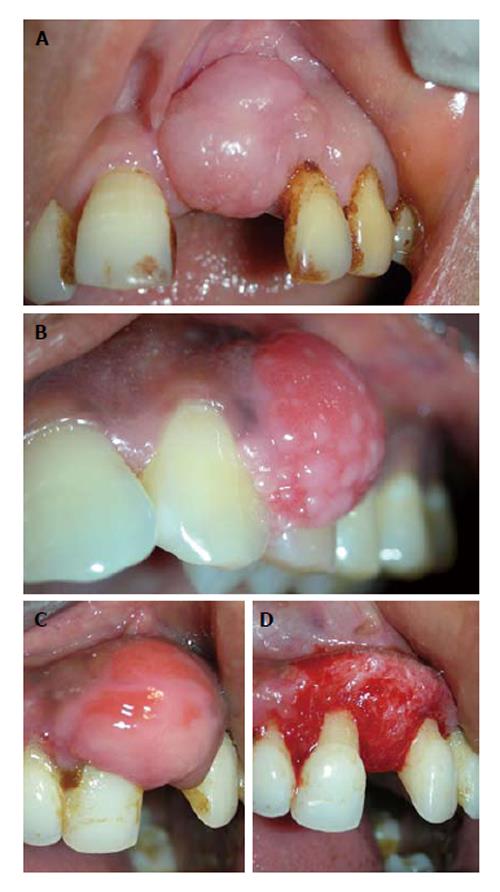
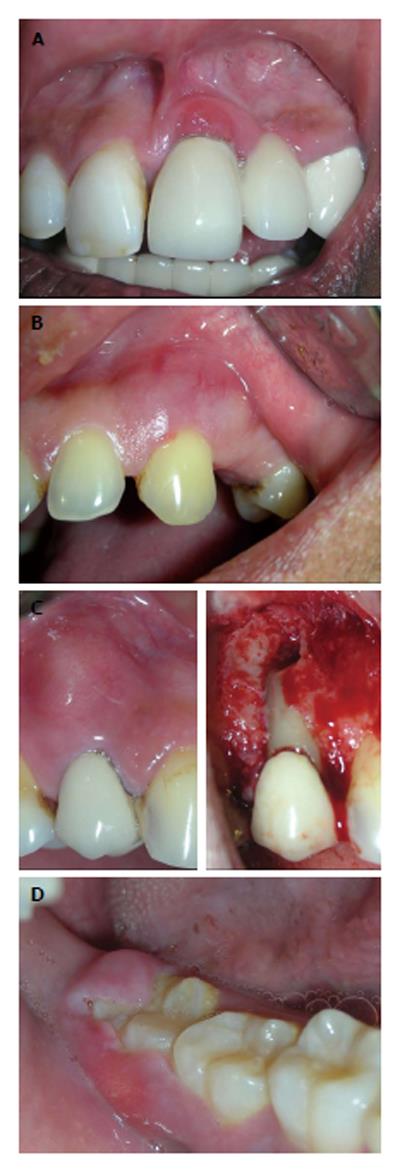
Figure 1 Fibrous epulis and its subtypes.
A: Peripheral fibroma, presenting as pink firm, uninflammed mass growing from under the gingiva; B: Peripheral cementifying fibroma, a subcategory of fibroma, shows additional foci of cementicles; C and D: Surgical exposure of the lesion showing extensive bone formation in the core of the lesion. Also presence of bony trabeculae was seen histologically.
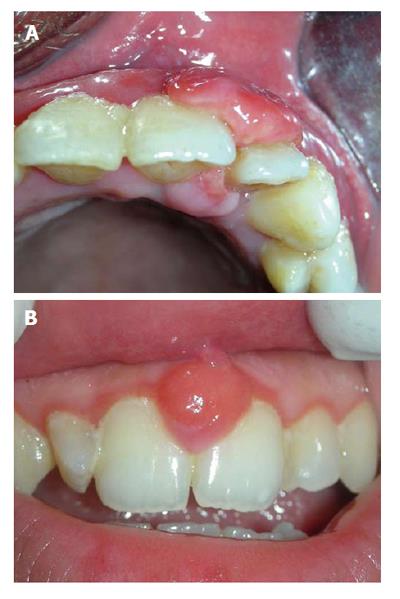
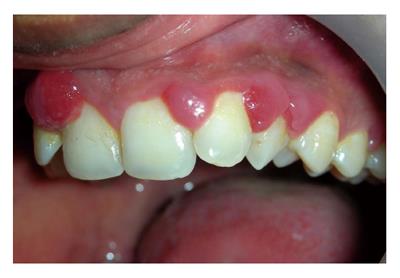
Figure 2 Angiogranulomas may present as: Pyogenic granuloma, a bilobular mass connected through the col area (A), and similar lesion occurring during pregnancy is termed as “pregnancy epulis” (B).
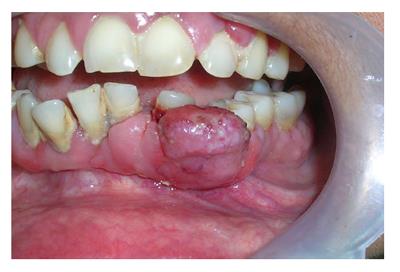
Figure 3 Lesion of peripheral giant cell granuloma.
This highly vascular lesion is characterized by purplish red-color and its tendency to bleed.
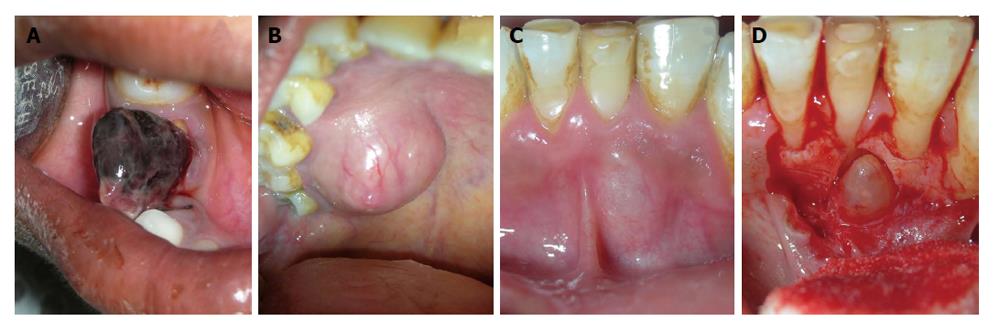
Figure 4 Other uncommon localized gingival enalargements which could be misdiagnosed as epulis.
A: Hemangioma located in mandibular right quadrant; B: Mucocele associated with palatal minor salivary gland; C and D: A lateral periodontal cyst projecting labially and causing localized gingival enlargement.
Figure 5 Abscess presenting as localized gingival enlargement.
A: Gingival abscess, near gingival margin or papilla; B: In periodontal abscess, the swelling is diffuse; C: Periapical abscess, near apex of concerned tooth; D: Abscess of pericoronal flap.
Figure 6 Inflammatory gingival enlargement.
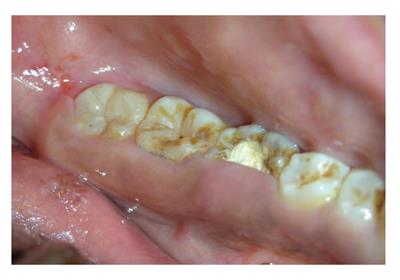
A: Plaque and calculus; B: Ill-fitting prosthesis; C: Orthodontic brackets.
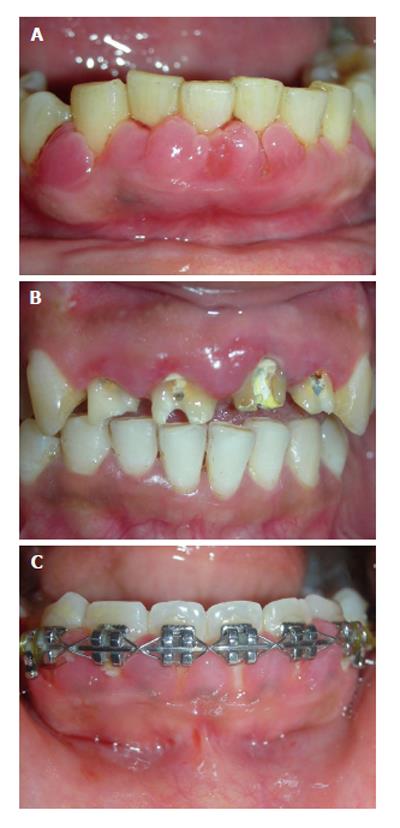
Figure 7 Drug influenced gingival overgrowth.
A: Superimposed with secondary inflammation; B: Fibrotic and leathery.
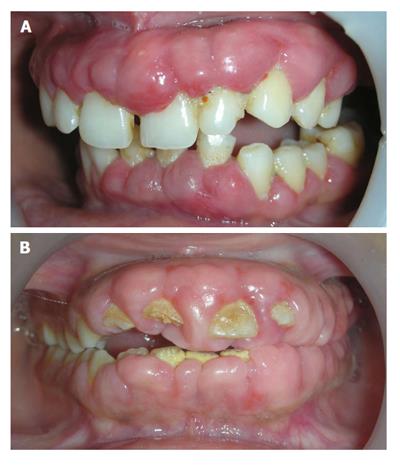
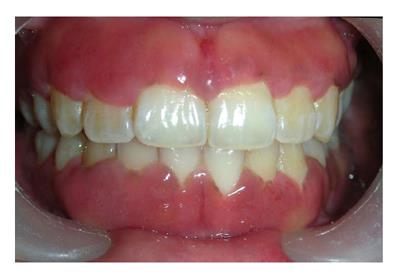
Figure 8 Unusual firm fibrotic gingival enlargements in a patient with hereditary gingival fibromatosis.
Figure 9 Typical multiple interproximal enlargements in a pregnant patient.
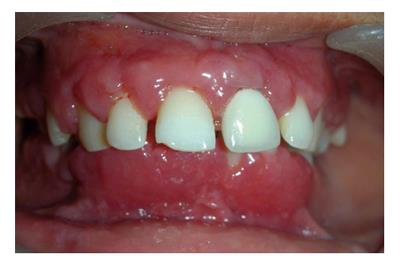
Figure 10 Appearance of gingiva in patient with plasma cell gingival enlargement.
The color is reddish and involves almost complete attached gingiva and slightly granular appearance.
Figure 11 Gingival condition in patient with Wegenersgranulomatosis, presents as reddish purple, exophytic gingival overgrowth.
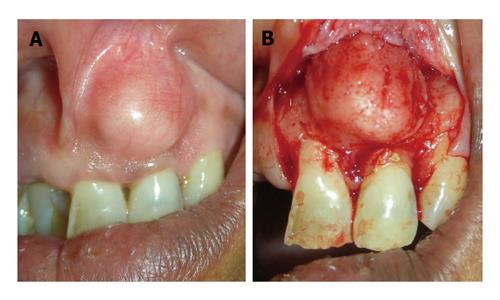
Figure 12 Case of false enlargement wherein.
A: The overlying gingiva presents with no abnormal clinical features except the massive increase in size of the area; B: Formed completely by underlying bone.
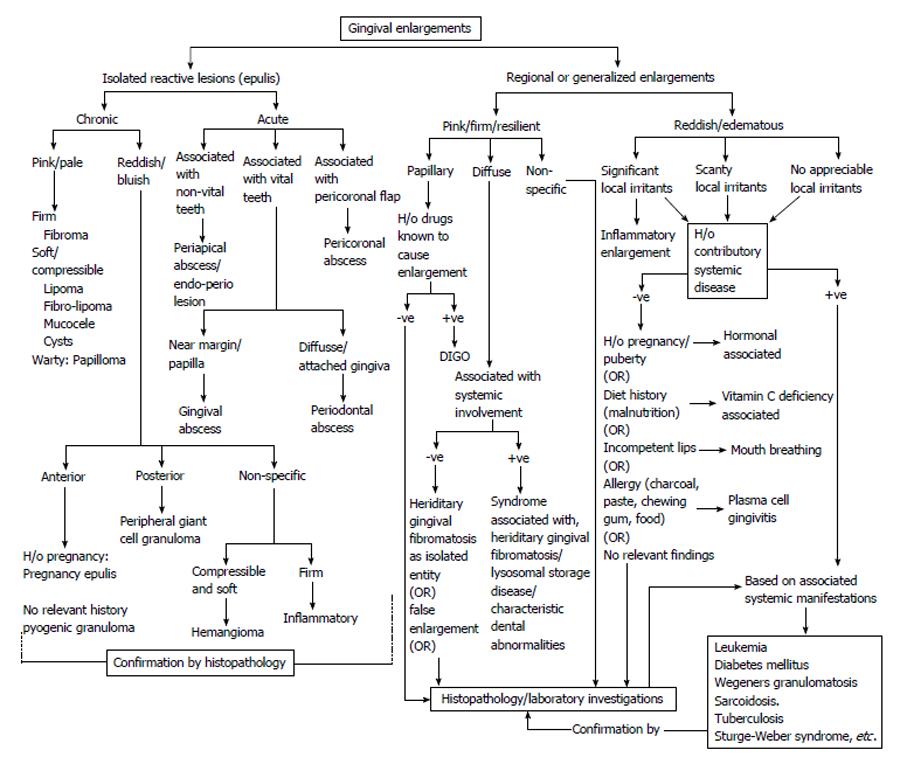
Figure 13 Decision tree for differential diagnosis of isolated, regional and generalized gingival enlargement.
DIGO: Drug induced gingival enlargement.
- Citation: Agrawal AA. Gingival enlargements: Differential diagnosis and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2015; 3(9): 779-788
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v3/i9/779.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v3.i9.779