Copyright
©The Author(s) 2015.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2015; 3(6): 484-494
Published online Jun 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i6.484
Published online Jun 16, 2015. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v3.i6.484
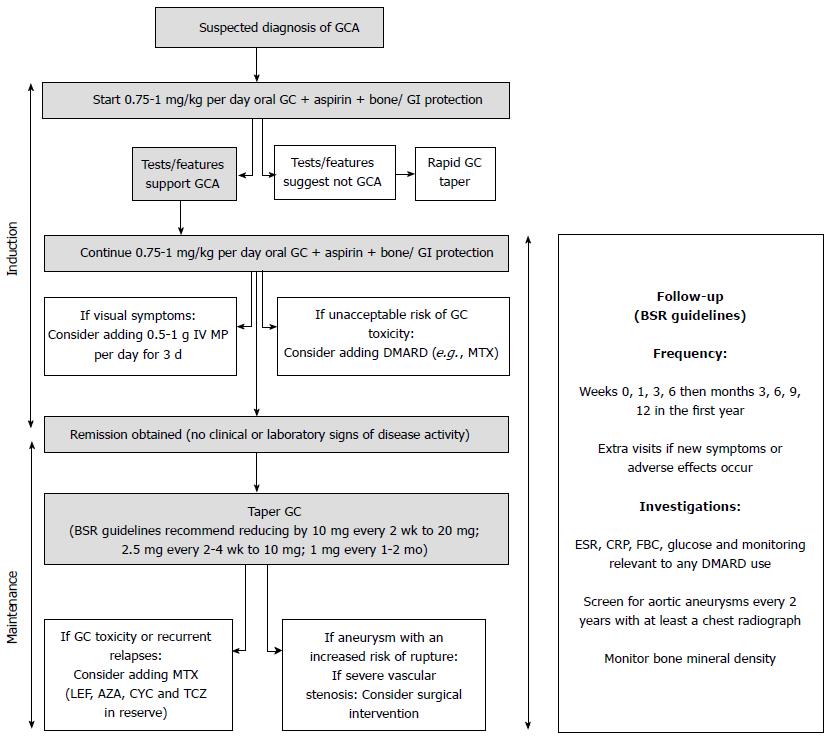
Figure 1 Current schema for giant cell arteritis treatment.
AZA: Azathioprine; BSR: The British Society for Rheumatology; CRP: C-reactive protein; CYC: Cyclophosphamide; DMARDs: Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs; ESR: Erythrocyte sedimentation rate; FBC: Full blood count; GC: Glucocorticoids; GI: Gastrointestinal; GCA: Giant cell arteritis; IV: Intravenous; LEF: Leflunomide; MP: Methylprednisolone; MTX: Methotrexate; TCZ: Tocilizumab.
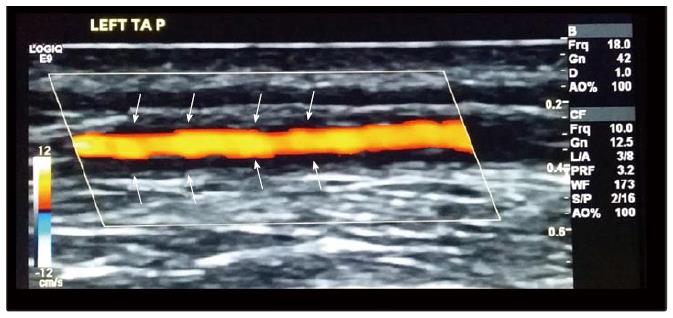
Figure 2 Ultrasound of the left temporal artery showing a dark halo (arrows) around the vessel wall of the parietal branch compatible with vascular inflammation.
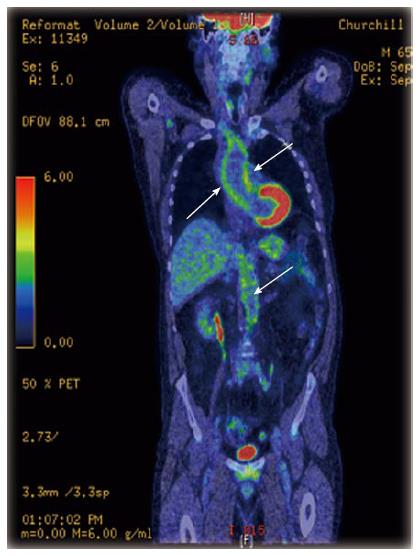
Figure 3 Whole body positron emission tomography-computerised tomography scan of a patient with large vessel vasculitis, showing increased fluorodeoxyglucose uptake in the ascending and abdominal aorta (arrows).
- Citation: Ponte C, Rodrigues AF, O’Neill L, Luqmani RA. Giant cell arteritis: Current treatment and management. World J Clin Cases 2015; 3(6): 484-494
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v3/i6/484.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v3.i6.484