Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2014; 2(7): 257-264
Published online Jul 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i7.257
Published online Jul 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i7.257
Figure 1 Moderators of the relationship between resting energy expenditure and body mass index.
A: General linear model analysis (age adjusted) showed the effect of resting energy expenditure (REE) by diagnosis. Diagnosis was coded as dummy variables: 0 = Anorexia nervosa, 1 = Bulimia nervosa; B: The interaction showed in part A was broken down within diagnoses. Graphs reports results from linear regression analyses (age adjusted) of the opposite pattern of association between REE and body mass index (BMI) in anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa subjects.
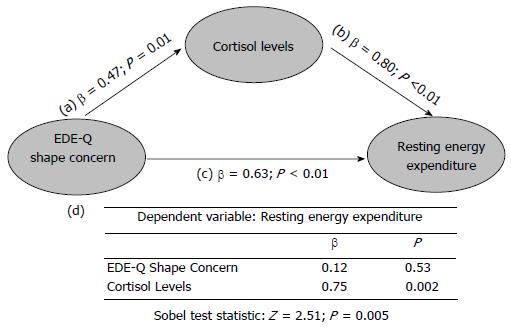
Figure 2 Mediator Model for the relationship between shape concern, cortisol levels and resting energy expenditure.
The model included a direct impact (Path c) of the independent variable [eating disorder examination questionnaire (EDE-Q) shape concern]on the dependent variable (REE), the impact of the mediator (cortisol levels; Path b), and the impact of the independent variable on the mediator (Path a). The β values of separate regression analyses are reported in the graph. Table (d section of the figure) reported the regression analysis of the combined effect of EDE-Q shape concern, and cortisol levels on REE. The bottom part of the graph reports the results of the Sobel test, in order to calculate the indirect effect of shape concern on REE via the mediator (cortisol levels).
- Citation: Castellini G, Castellani W, Lelli L, Sauro CL, Dini C, Lazzeretti L, Bencini L, Mannucci E, Ricca V. Association between resting energy expenditure, psychopathology and HPA-axis in eating disorders. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(7): 257-264
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i7/257.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i7.257