Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. May 16, 2014; 2(5): 151-156
Published online May 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i5.151
Published online May 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i5.151
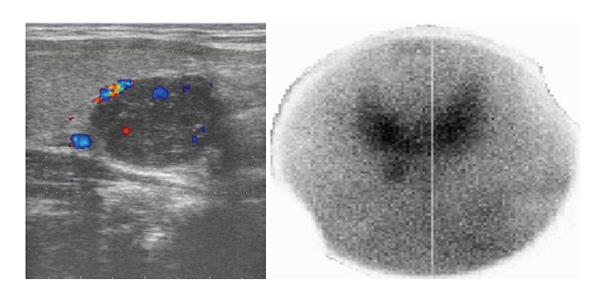
Figure 1 Doppler ultrasound of parathyroid gland showing well-defined hypoechoic mass with color signals of few surrounding vascular structures and Tc-99m sestamibi planar scan with pinhole collimator, 10 min post injection.
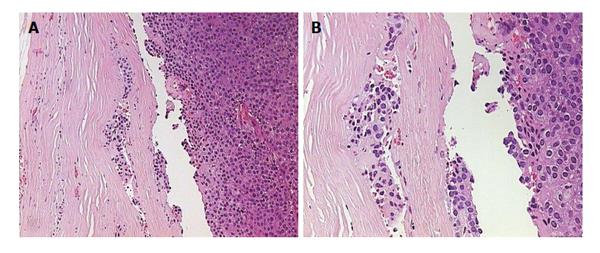
Figure 2 Pathology image of atypical adenoma.
A: No significant remodeling of stroma cells or polymorphism, tumor cells are monotonous, small cells with focal cytological atypia without mitotic figures; B: Pathology image of atypical adenoma with tumour cells infiltrating thick fibrous capsule.
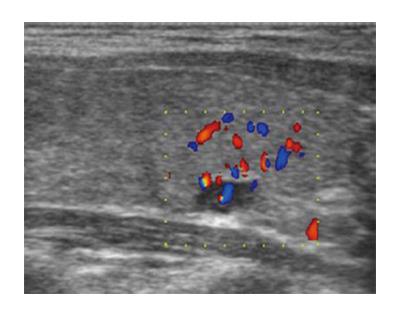
Figure 3 Doppler ultrasound of parathyroid carcinoma: small solitary mass in the area of previous surgery.
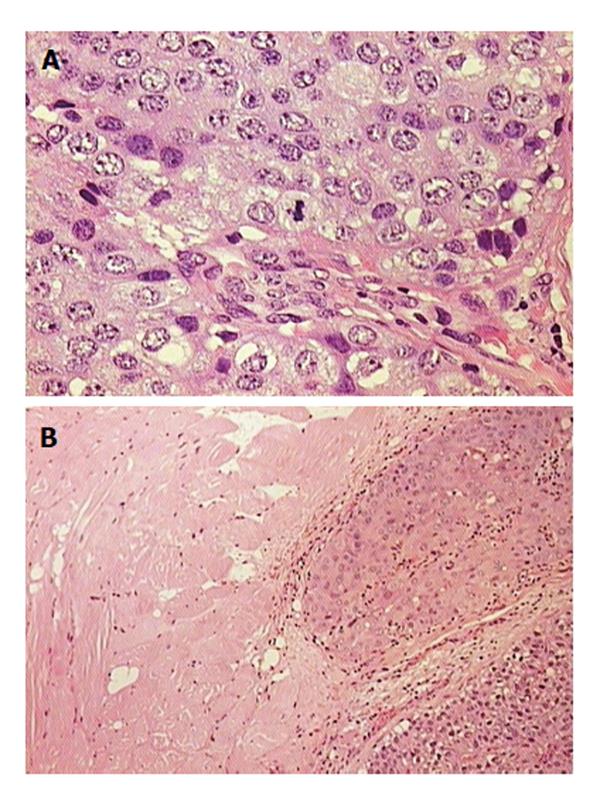
Figure 4 Pathology image of parathyroid carcinoma.
A: Mitotic cells; B: Infiltrating skeletal muscle.
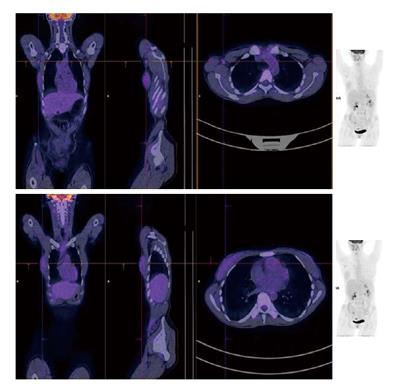
Figure 5 Positron emission tomography/low-dose X-ray computed tomography (positron emission tomography/low-dose computed tomography) with F-18 FDG.
Focal accumulation is observed in enlarged lymph nodes of the right axillary region and diffuse uptake is observed in the right breast.
- Citation: Baretić M, Tomić Brzac H, Dobrenić M, Jakovčević A. Parathyroid carcinoma in pregnancy. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(5): 151-156
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i5/151.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i5.151