Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 16, 2014; 2(12): 732-741
Published online Dec 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.732
Published online Dec 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.732
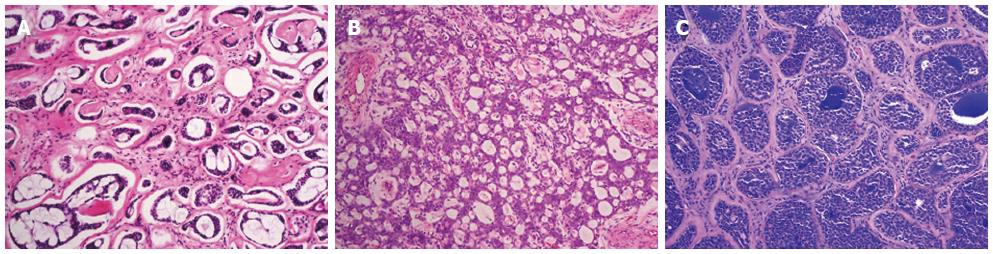
Figure 1 Adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast.
Adenoid cystic carcinomas predominantly showing tubular-trabecular (A), cribriform (B), and solid-basaloid patterns (C). Original magnification × 100.
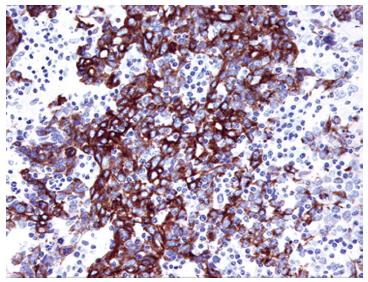
Figure 2 Immunoreactivity of cytokeratin 5/6 in solid pattern of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast.
The tumor cells are immunoreactive for cytokeratin 5/6, indicating myoepithelial-basal cell origin of tumor cells. Original magnification × 200.
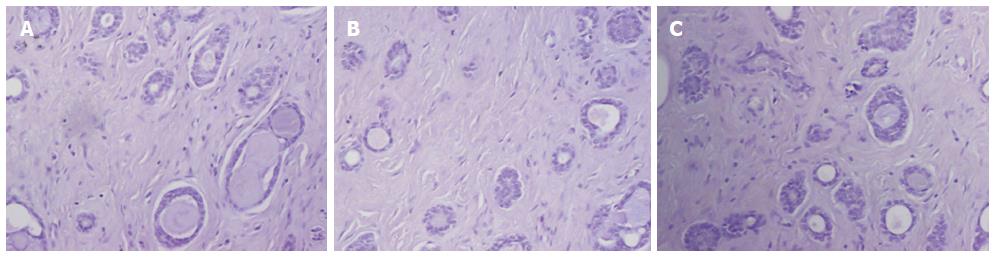
Figure 3 Immunohistochemical findings in adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast.
A: Estrogen receptor; B: Progesterone receptor; C: Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2. All these markers are negative in a case of adenoid cystic carcinoma of the breast. Original magnification × 100.
- Citation: Miyai K, Schwartz MR, Divatia MK, Anton RC, Park YW, Ayala AG, Ro JY. Adenoid cystic carcinoma of breast: Recent advances. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(12): 732-741
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i12/732.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i12.732