Copyright
©2014 Baishideng Publishing Group Inc.
World J Clin Cases. Oct 16, 2014; 2(10): 497-506
Published online Oct 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i10.497
Published online Oct 16, 2014. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v2.i10.497
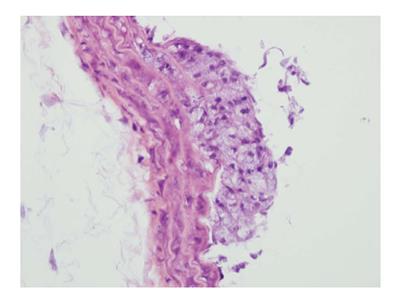
Figure 1 An atherosclerotic plaque at its early stage of development in the thoracic aorta of an apolipoprotein E-KO mouse is illustrated.
The plaque is primarily composed of apparent foam cells. HE staining × 400.
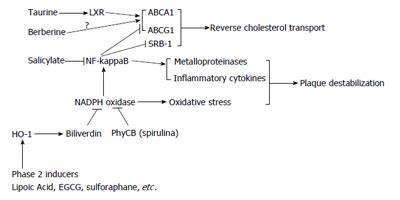
Figure 2 Nutraceutical/drug regulation of foam cell cholesterol transport and plaque stability.
LXR: Liver X receptors; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; NF-kappaB: Nuclear factor-kappaB; ABCA1: Adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter A1; ABCG1: Adenosine triphosphate binding cassette transporter G1; SRB-1: Scavenger receptor class B member 1; NADPH oxidase:: Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase:; EGCG: Epigallocatechin gallate; HO-1: Heme oxygenase-1; PhyCB: Phycocyanobilin.
- Citation: Uitz E, Bahadori B, McCarty MF, Moghadasian MH. Practical strategies for modulating foam cell formation and behavior. World J Clin Cases 2014; 2(10): 497-506
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v2/i10/497.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v2.i10.497