Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2025; 13(24): 107098
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i24.107098
Published online Aug 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i24.107098
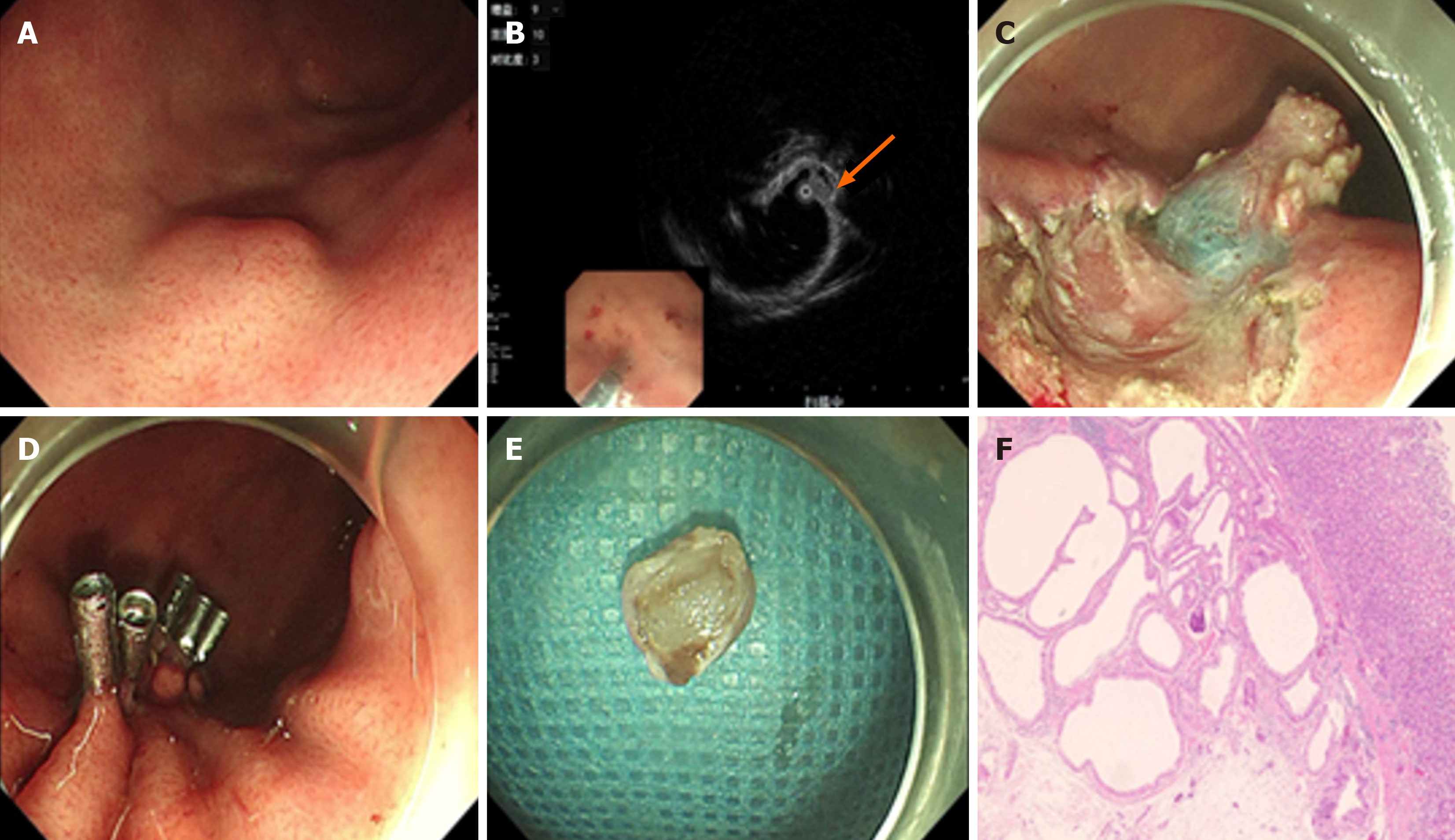
Figure 1 Gastroscopy in Case 1.
A: Gastroscopy revealed a submucocal tumor situated on the greater curvature of the gastric fundus; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography indicated that the lesion was located within the submucosal layer (arrow). The internal echogenicity presented as a hypoechoic nodule containing multiple anechoic sacs; C: Endoscopic submucosal dissection was carried out on the lesion; E: The tissue specimen was obtained; F: Histopathological examination confirmed cystic expansion of the gastric glands and their infiltration into the submucosa.
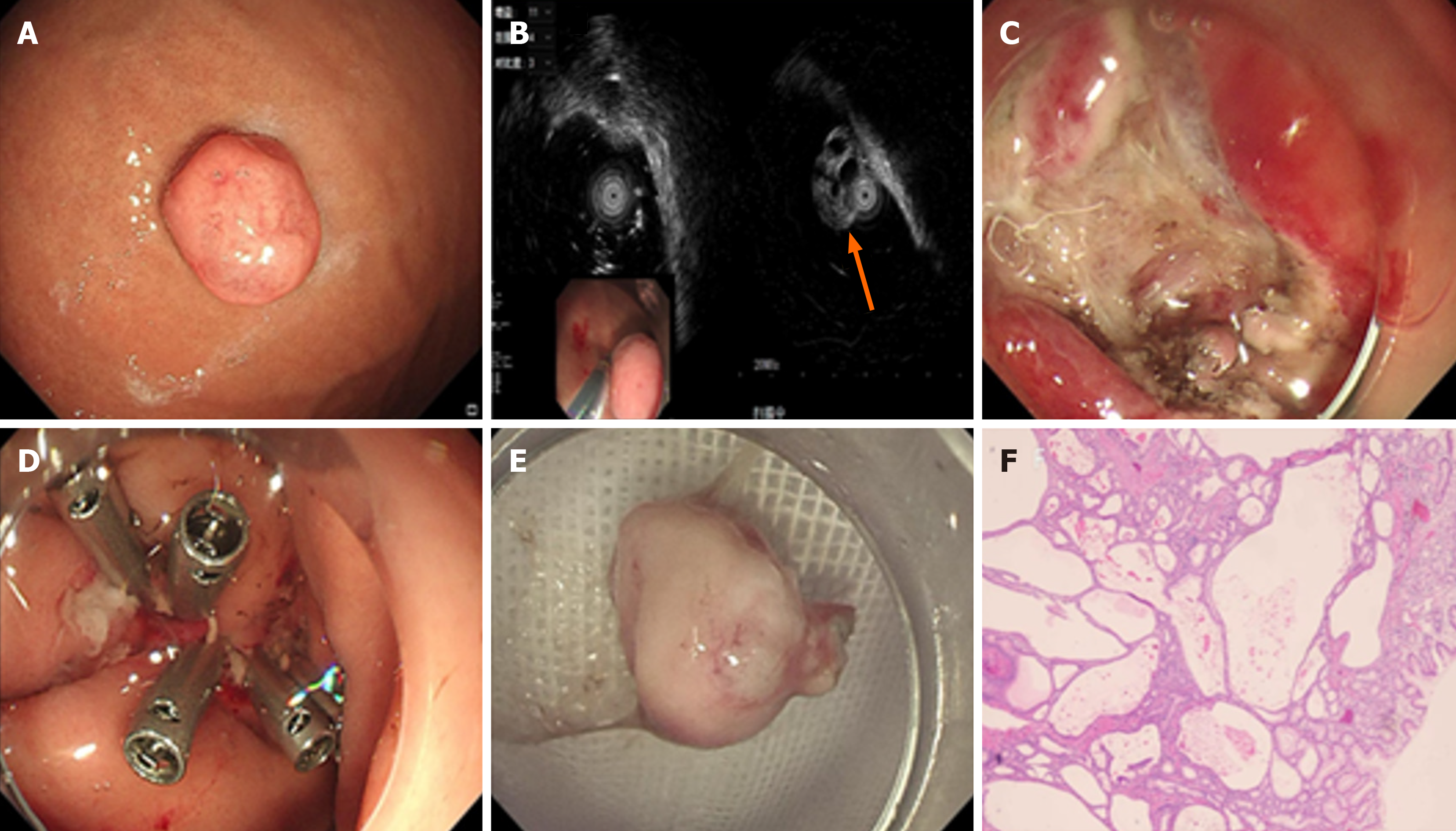
Figure 2 Gastroscopy in Case 2.
A: Gastroscopy revealed a pedunculated polypoid lesion located on the greater curvature of the gastric body; B: Endoscopic ultrasonography indicated that the solid-cystic lesion was positioned within the mucosal layer (arrow); C: Endoscopic mucosal resection was performed on the lesion, followed by an image of the resulting wound surface; D: The wound was closed using titanium clips; E: The tissue specimen was successfully obtained; F: Histopathological examination confirmed glandular hyperplasia and cystic dilatation in the deep gastric mucosa.
- Citation: Zheng XL, Xu L, Wang J. Initial misdiagnosis of gastritis cystica profunda: Two case reports. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(24): 107098
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i24/107098.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i24.107098