Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2025; 13(21): 104723
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.104723
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.104723
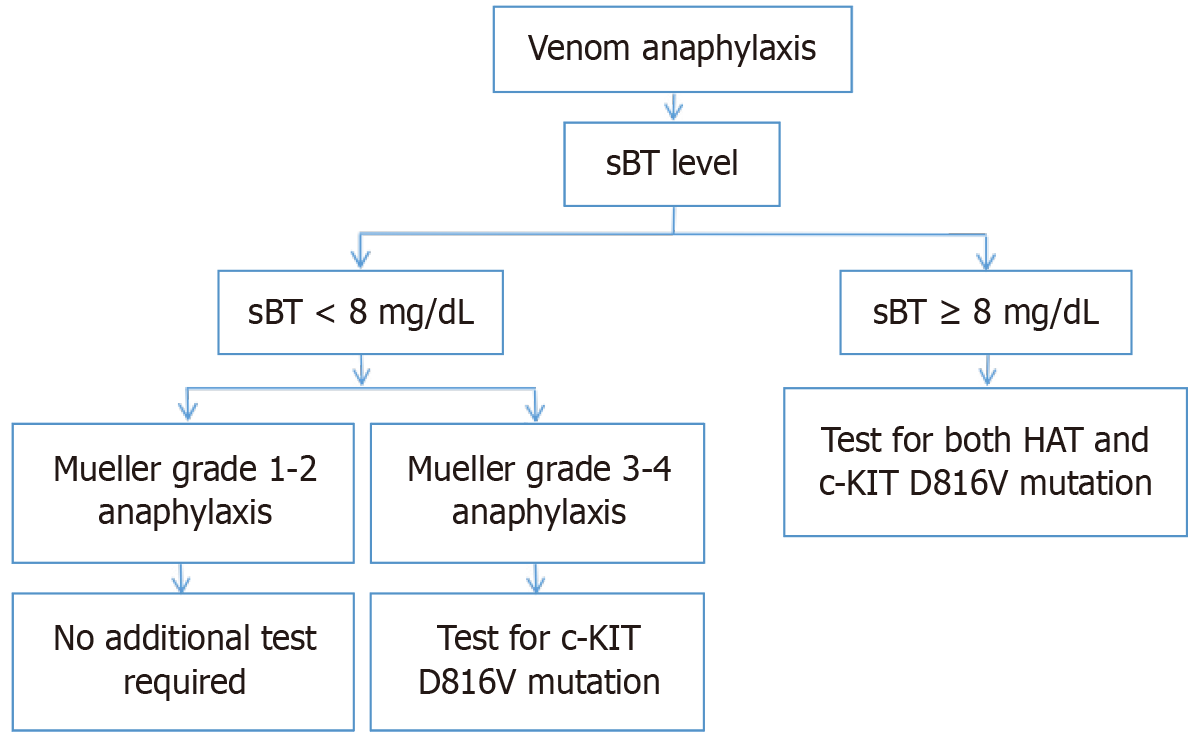
Figure 1 Approach in venom anaphylaxis.
HAT: Hereditary alpha tryptasemia; c-KIT: Tyrosine kinase protein; sBT: Serum basal tryptase.
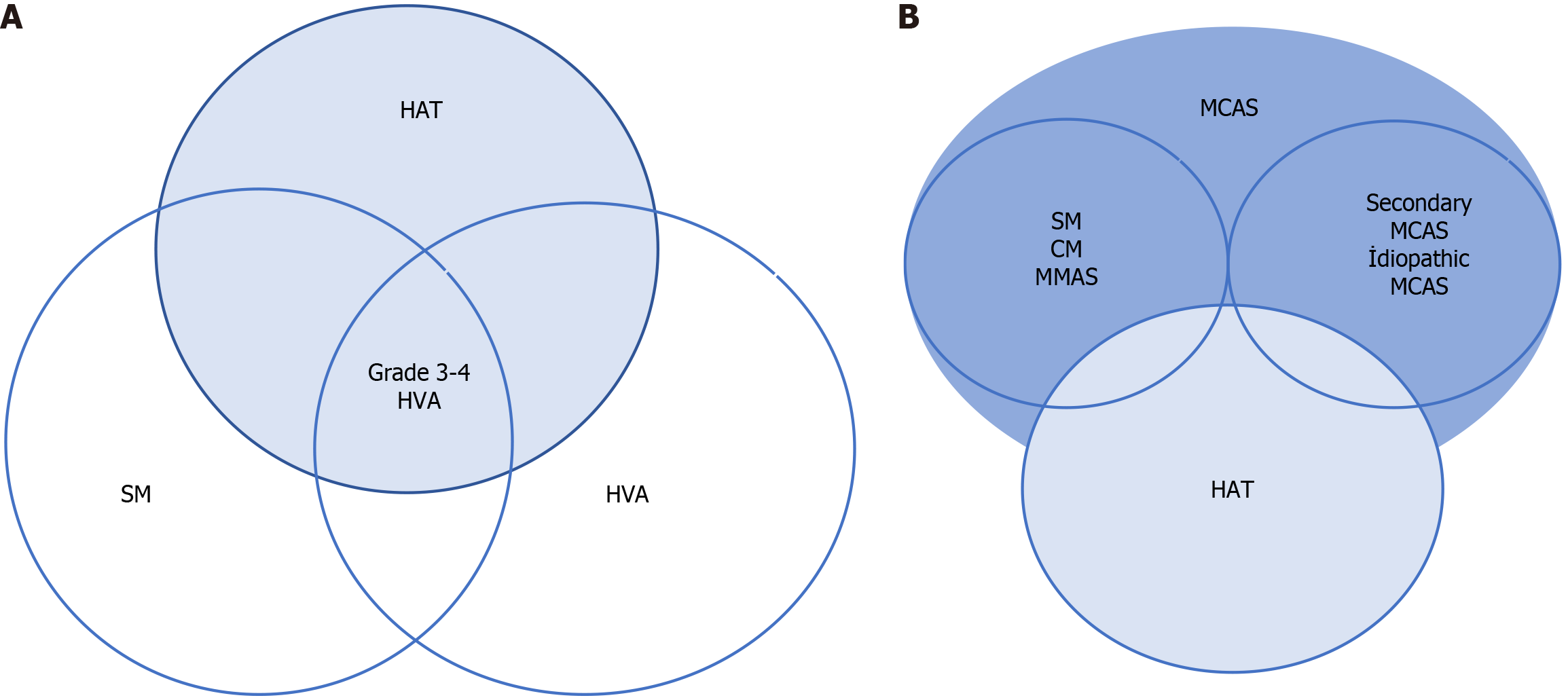
Figure 2 Relationship.
The relationship between hereditary alpha tryptasemia (HAT), systemic mastocytosis (SM), hymenoptera venom anaphylaxis (HVA) and mast cell activation syndrome (MCAS). A: The relationship between HAT, SM, and HVA; B: Relationship between HAT and MCAS. HAT: Hereditary alpha tryptasemia; HVA: Hymenoptera venom anaphylaxis; MCAS: Mast cell activation syndrome; MMAS: Monoclonal mast cell activation syndrome; SM: Systemic mastocytosis; CM: Cutaneous mastocytosis.
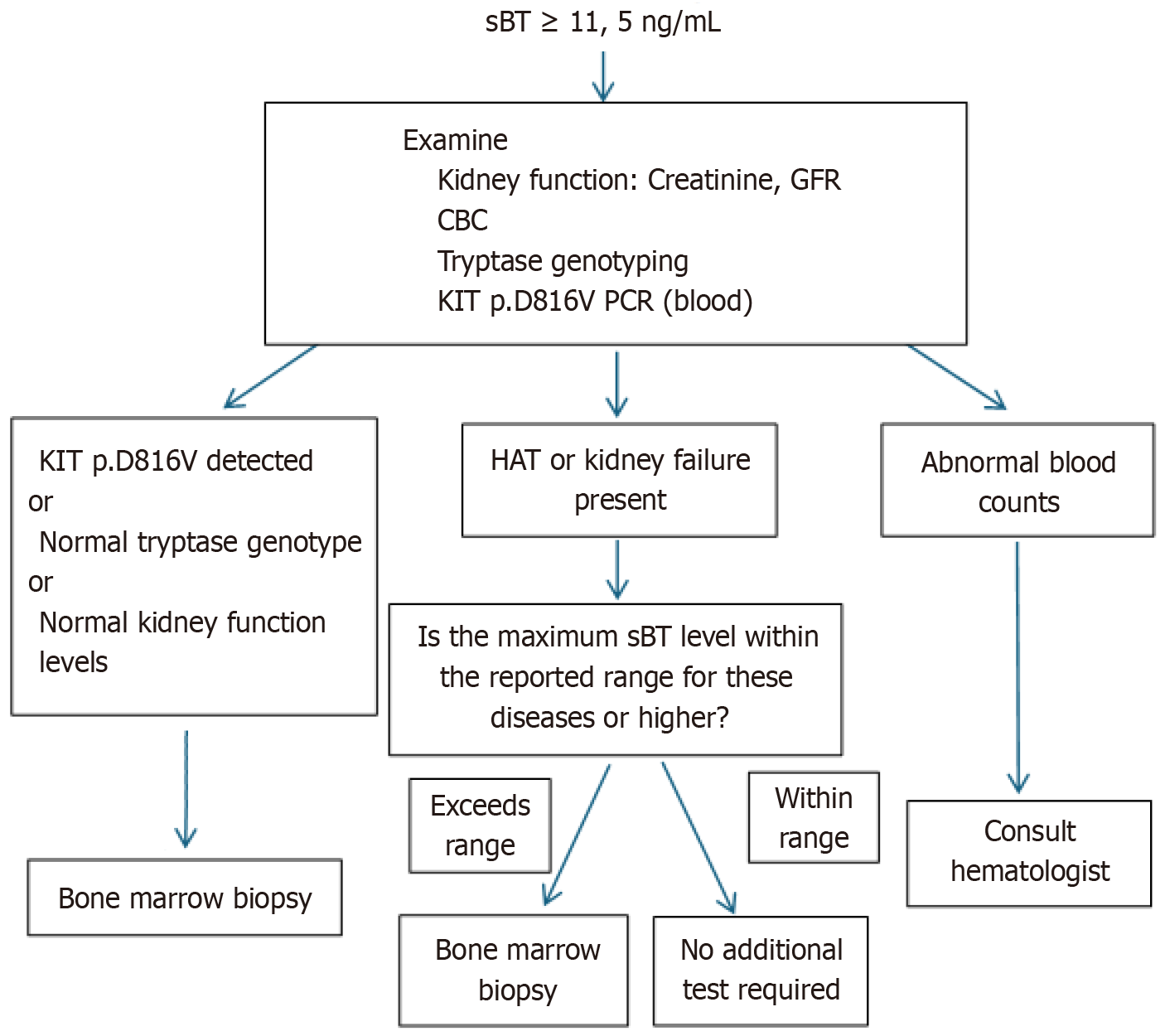
Figure 3 Clinical and laboratory approach to elevated serum basal tryptase.
CBC: Complete blood count; GFR: Glomerular filtration rate; KIT: Tyrosine kinase protein; SBT: Serum basal tryptase; HAT: Hereditary alpha tryptasemia.
- Citation: Tüsüz Önata E, Özdemir Ö, Savaşan S. Hereditary alpha tryptasemia and clinical implications. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(21): 104723
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i21/104723.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.104723