Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2025; 13(21): 104062
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.104062
Published online Jul 26, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.104062
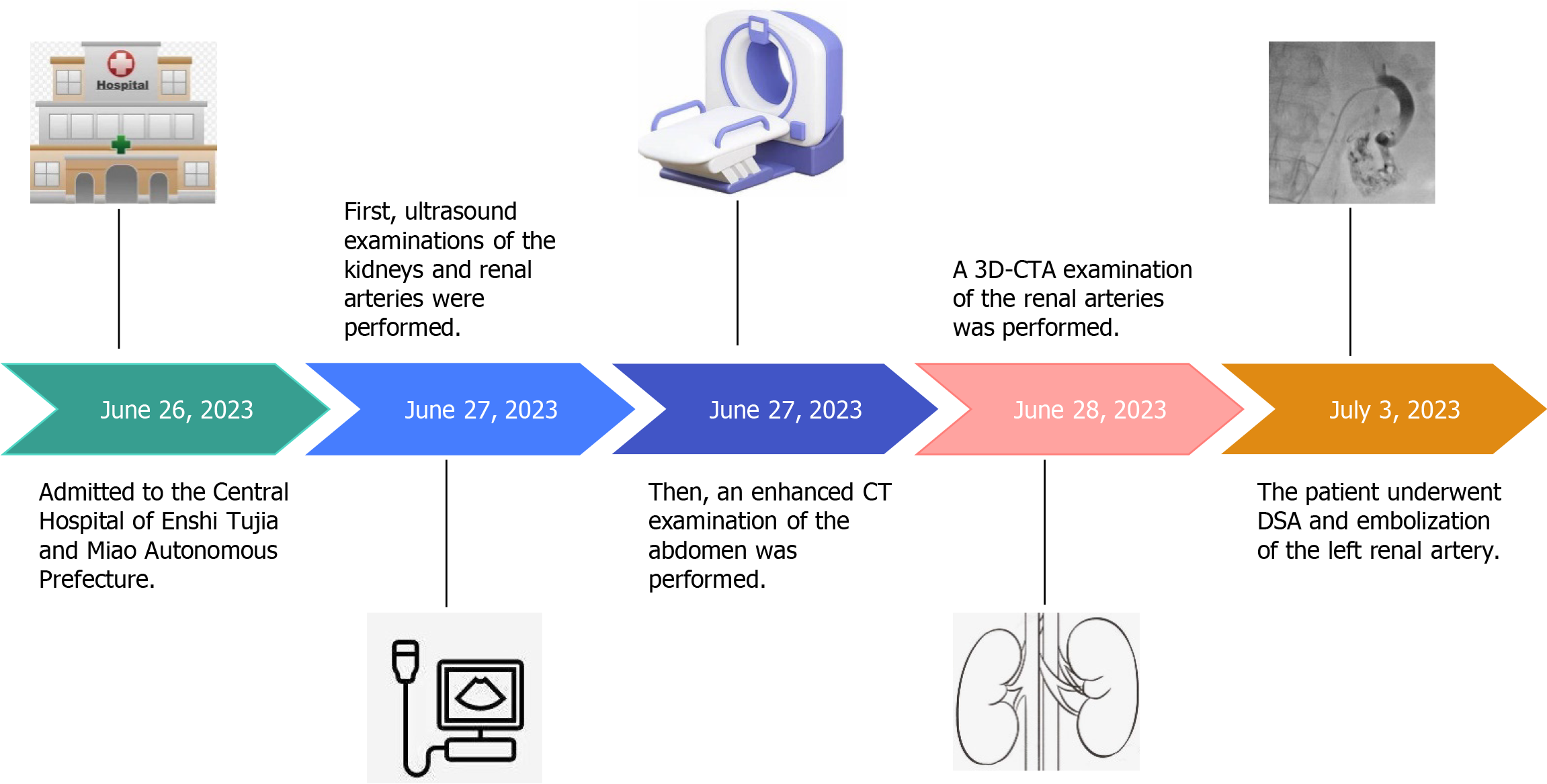
Figure 1 Timeline diagram of patient admission and imaging examinations.
3D-CTA: Three-dimensional computed tomography angiography; CT: Computed tomography; DSA: Digital subtraction angiography.
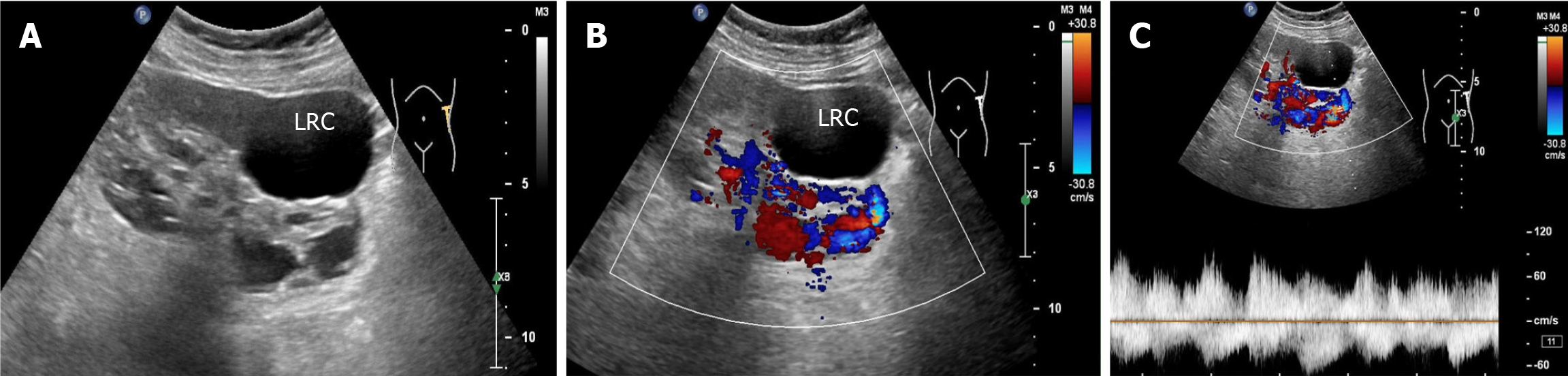
Figure 2 Ultrasonography of the left kidney.
A: Two-dimensional image showing several anechoic areas in the middle and lower poles of the left kidney; B: Color doppler flow imaging image showing no blood flow signal in the largest anechoic area of the left kidney and florid blood flow signals in the smaller anechoic areas of the left kidney and near the renal hilum; C: Spectral doppler image showing a burr-like arterial blood flow spectrum characteristic of blood flow within the anechoic area of the left kidney. LRC: Left renal cyst.
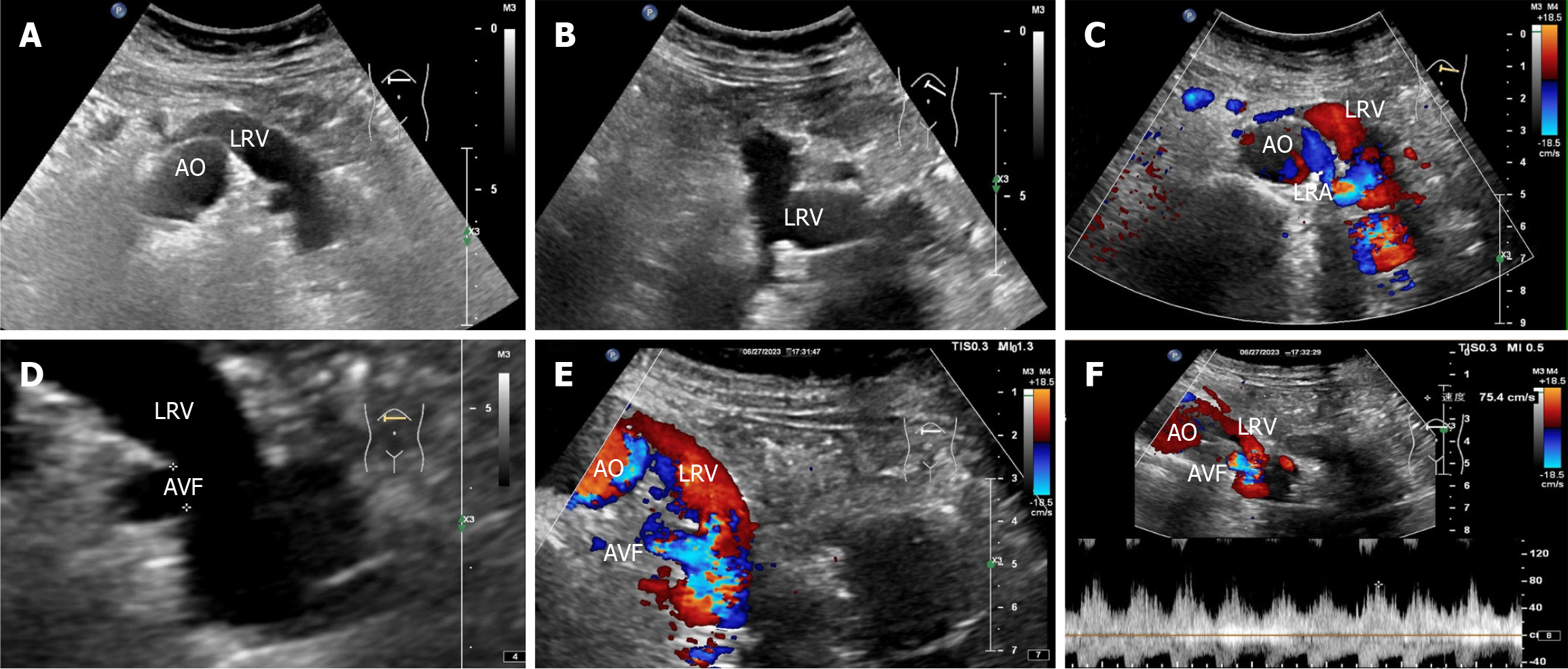
Figure 3 Renal vascular ultrasonography.
A and B: Two-dimensional image showing that the left renal vein is widened and uneven in thickness; C: Color doppler flow imaging reveals a brighter florid blood flow signal within the left renal vein, with the blood-supplying artery originating from the adjacent left renal artery; D: Magnified two-dimensional image showing a 0.5 cm wide fistula between the left renal vein and the left renal artery; E: Color doppler flow imaging reveals a bright florid blood flow signal in the left renal vein near the fistula; F: Spectral doppler reveals spectral arterialization of the left renal vein with a non-smooth envelope and burr-like changes. AO: Abdominal aorta; LRV: Left renal vein; LRA: Left renal artery; AVF: Arteriovenous fistula.
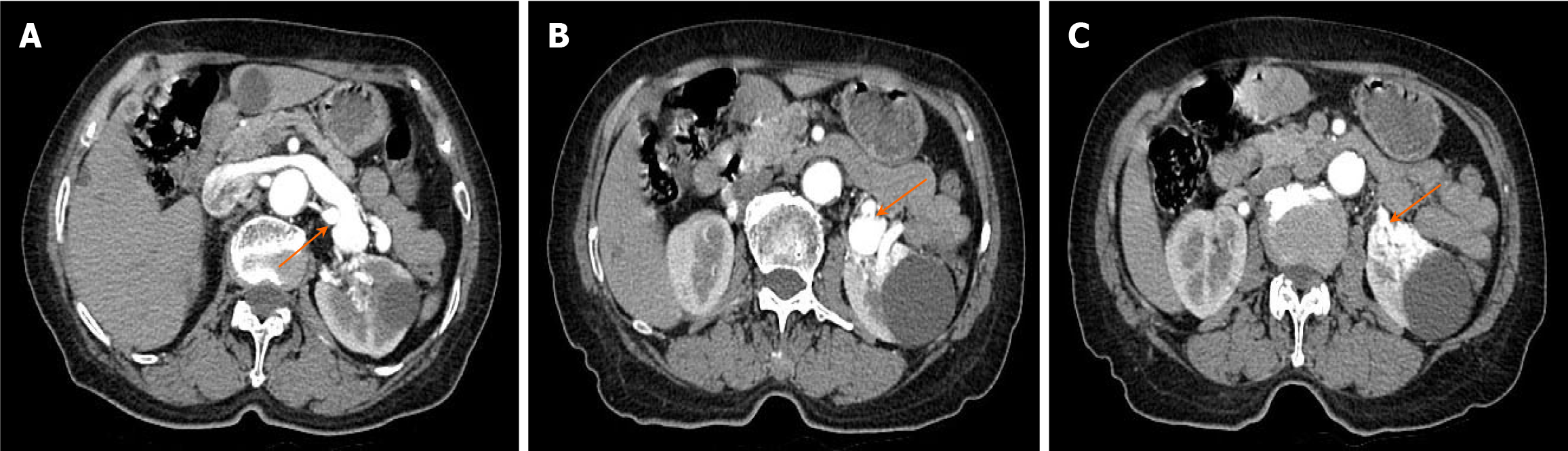
Figure 4 Computed tomography enhancement examination.
A: Early visualization of the left renal vein in the arterial phase, with the left renal artery as the blood-supplying artery. The left renal vein is markedly thickened, with localized verrucous dilatation; B: The left renal artery branch is in traffic with the left renal vein, and a rounded hypodense shadow is observed in the middle of the left kidney, which is not significantly strengthened after contrast; C: Nodular isodense shadow in the middle and lower pole of the left kidney, with note able uneven enhancement after contrast, and the left renal artery branch is seen to traffic with the left renal vein. Orange arrow: Left renal arteriovenous fistula.
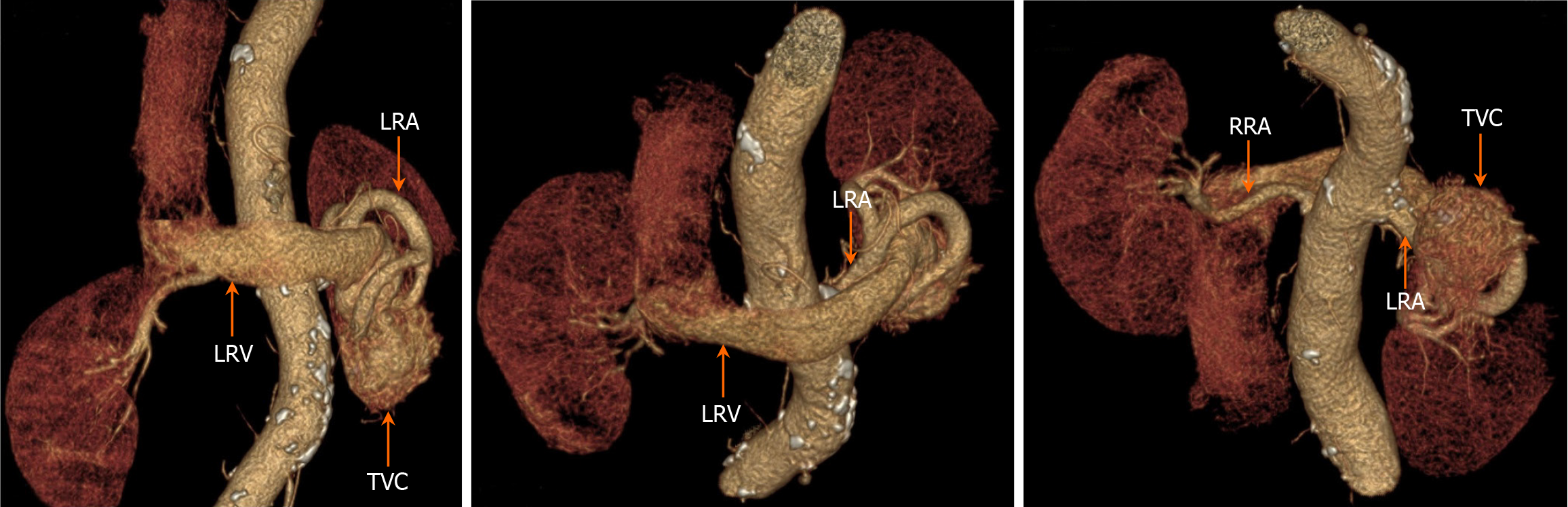
Figure 5 Three-dimensional computed tomography angiography examination revealed thickening of the left renal artery, localized communication with the left renal vein, aneurysmal dilatation of the left renal vein, and irregular clumping of vascular shadows at the lower pole of the left kidney, with vasculature-like enhancement inside.
LRV: Left renal vein; LRA: Left renal artery; TVC: Tortuous vascular mass.
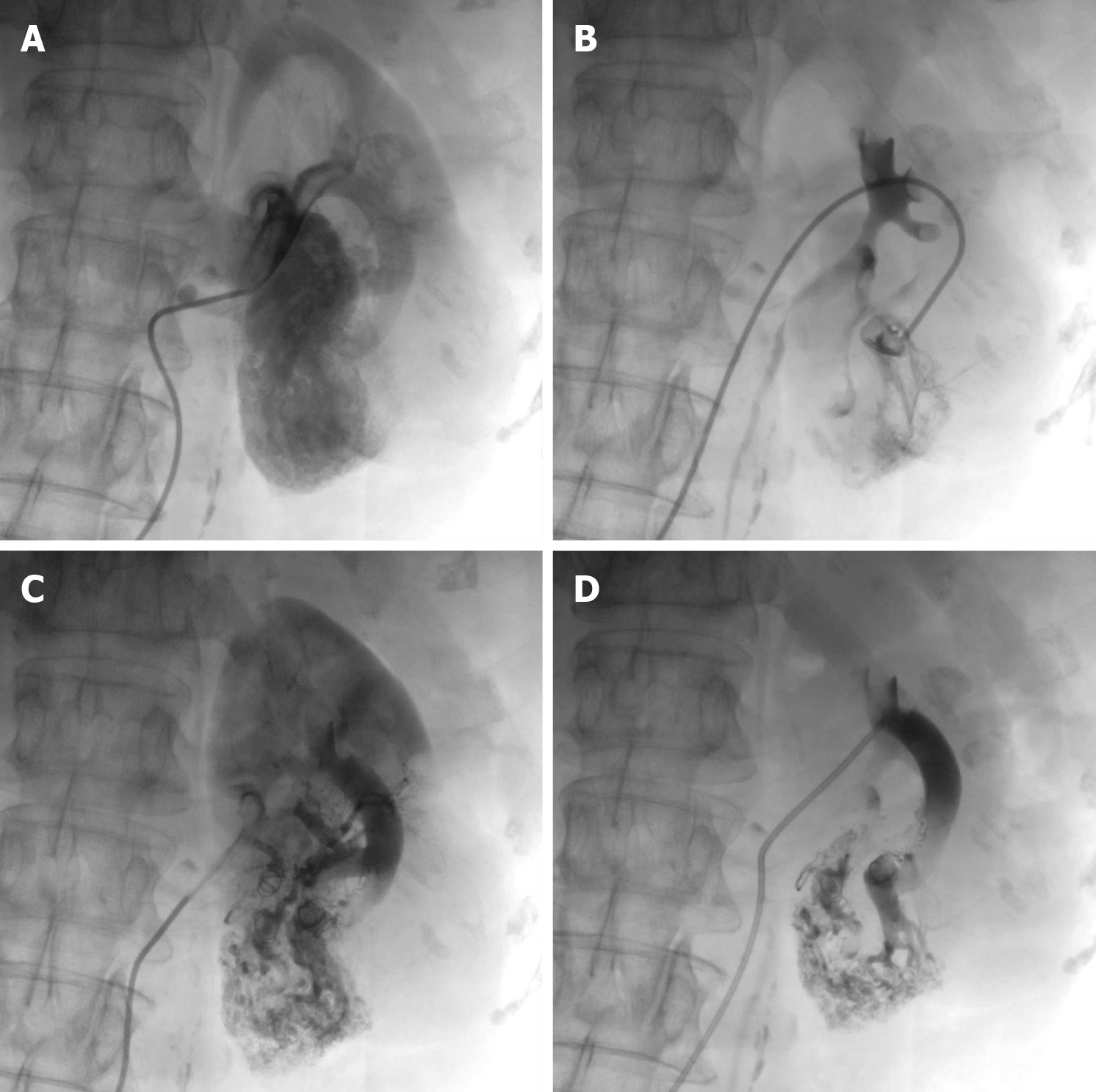
Figure 6 Digital subtraction angiography examination of the left renal artery.
A and B: Rapid visualization of the left renal vein. An arteriovenous fistula formation was observed in 4 branches of the left renal artery, contrast extravasation was observed, along with a large lamellar vascular malformation in the lower pole of the left kidney; C and D: The diseased artery was embolized with a spring coil. Postembolization review revealed complete embolization of the diseased artery, closure of the arteriovenous fistula, and no early visualization of the left renal vein.
- Citation: Lv SP, Qin LL, Mou H, Huang T, Wang KQ. Multimodal imaging techniques for the diagnosis of congenital left renal arteriovenous fistula: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(21): 104062
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i21/104062.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i21.104062