Copyright
©The Author(s) 2025.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2025; 13(20): 102651
Published online Jul 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i20.102651
Published online Jul 16, 2025. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v13.i20.102651
Figure 1 Clinical features of the patient.
A: Physical findings include a short philtrum, long eyelashes, a prominent nose with narrow nasal root and broad nasal tip, dental malocclusion, and clubbing of fingers; B: A pedigree of the analyzed family in this study. The proband with Floating-Harbor syndrome is indicated by an arrow; C: Protein sequence alignment of human SRCAP with orthologues from mouse, rat and bovine, showing that threonine at position 2412 are evolutionary conserved (outlined in red); D and E: Structural models of the SRCAP protein predicted with AlphaFold3. SRCAP structures of wild-type and p.Thr2412fs are shown, respectively. The box specified residue at position 2412 highlighted as sticks; F: Sanger sequences of the SRCAP gene variant in the proband, the fetus and their parents. The frameshift variant c.7235delinsGT (p.Thr2412fs) was detected in the proband (III-1), but not detected in the fetus (III-2), father (II-1) and mother (II-2).
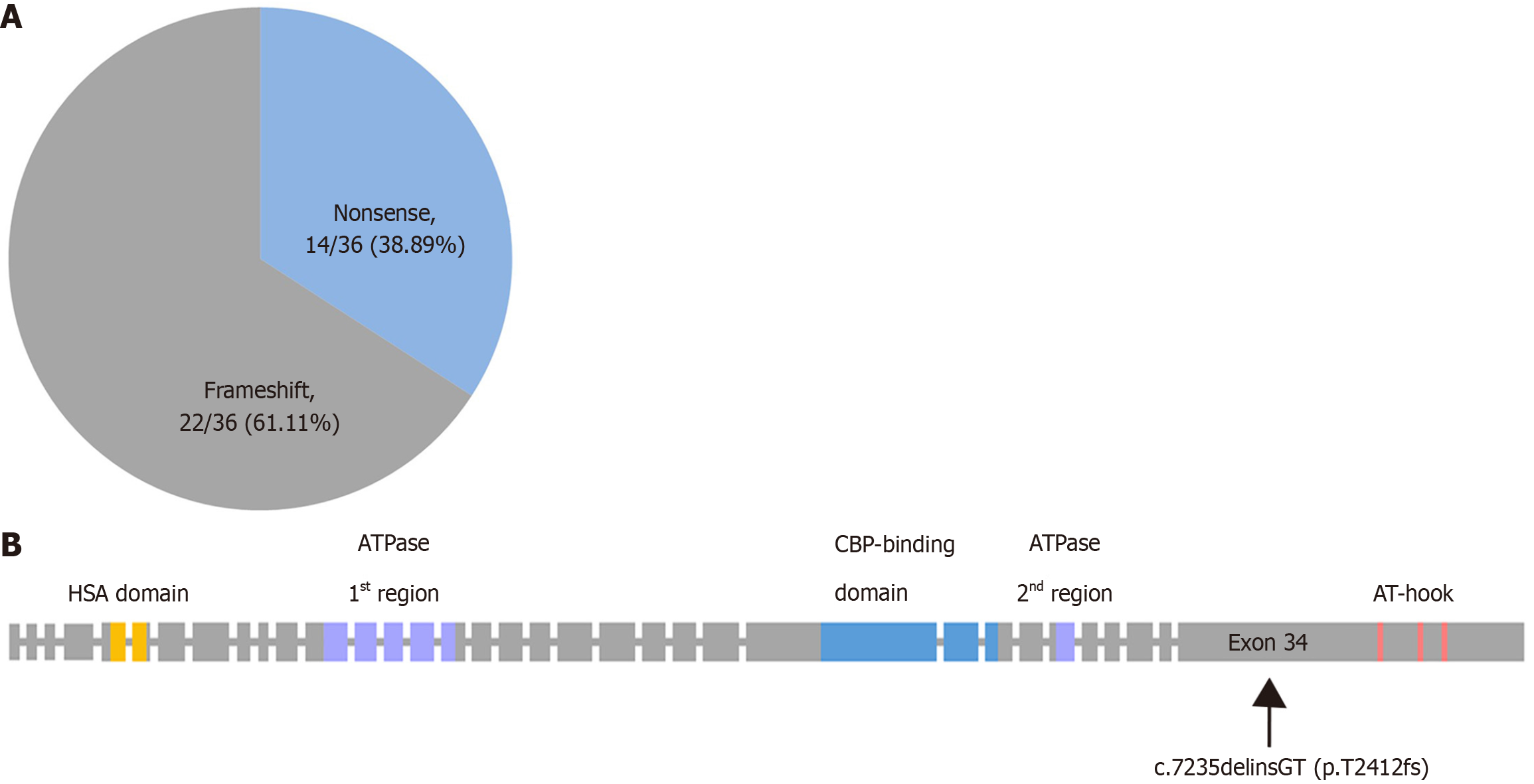
Figure 2 Intron-exon structure bearing domain structure of the SRCAP gene.
A: The ratio of variant types of SRCAP in the Human Gene Mutation database; B: Locations of c.7235delinsGT (p.Thr2412fs) variant found in our proband are shown. HSA, Helicase-SANT-associated domain.
- Citation: Xiao X, Wang P, Wang H, Xie HB, Liu SL. Identifying a novel SRCAP variant in floating-harbor syndrome and prenatal genetic diagnosis in this Chinese family: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2025; 13(20): 102651
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v13/i20/102651.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v13.i20.102651