Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2024; 12(9): 1649-1659
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1649
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1649
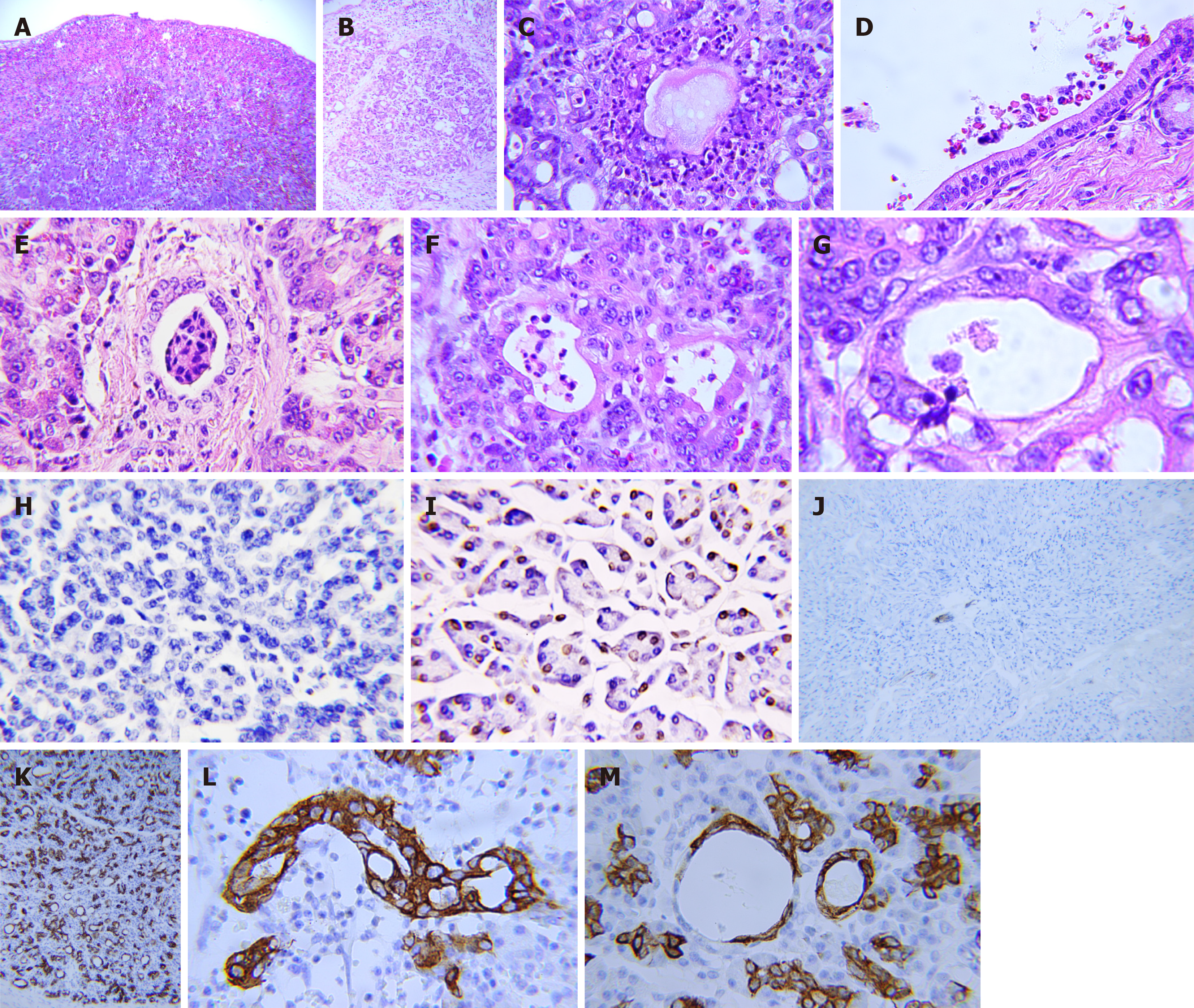
Figure 1 Pathology in the pancreatic stump with postoperative pancreatic fistula after pancreaticoduodenectomy.
A: Subserosal hematoma; B: Infiltration of inflammatory cells in glandular lobes and interlobular structures; C: Necrotic foci; D: Concentration of inflammatory cells and red blood cells in the main pancreatic duct; E: Destruction of inflammatory cells in the interlobular duct; F: Decomposition of inflammatory cells in the acinar duct metaplasia (ADM)-formed ducts; G: Transmigration of a neutrophil through the ADM-formed duct; H: Weakening or disappearance of apoptosis in the pancreatic stump after pancreatico
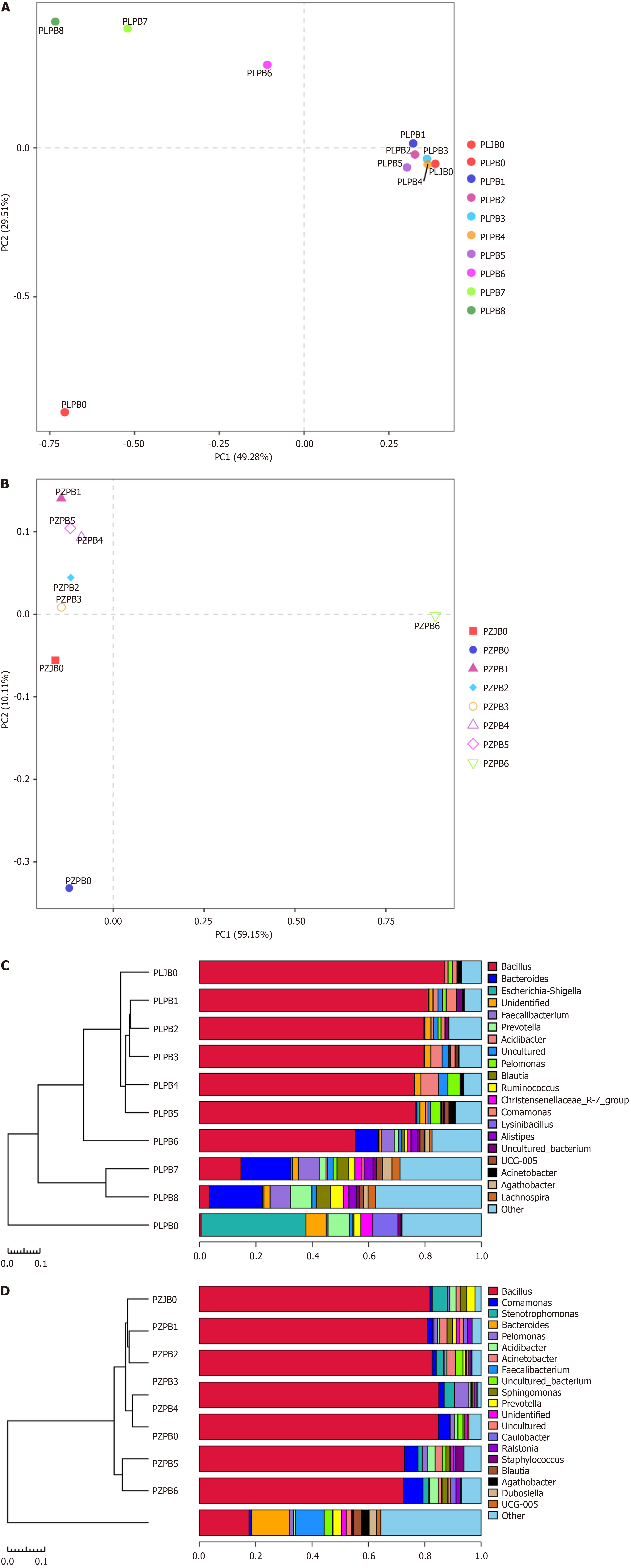
Figure 2 Principal component analysis and unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean analysis of bacterial distribution in both patients’ specimens.
A: Principal component analysis (PCA) of bacterial distribution in patient 1; B: PCA of bacterial distribution in patient 2; C: Unweighted pair group method with arithmetic mean (UPGMA) clustering tree of the bacterial community in patient 1; D: UPGMA clustering tree of the bacterial community in patient 2. PLJB: Bacteria in patient 1’s jejunum; PLPB: Bacteria in patient 1’s pancreas; PZJB: Bacteria in patient 2’s jejunum; PZPB: Bacteria in patient 2’s pancreas.
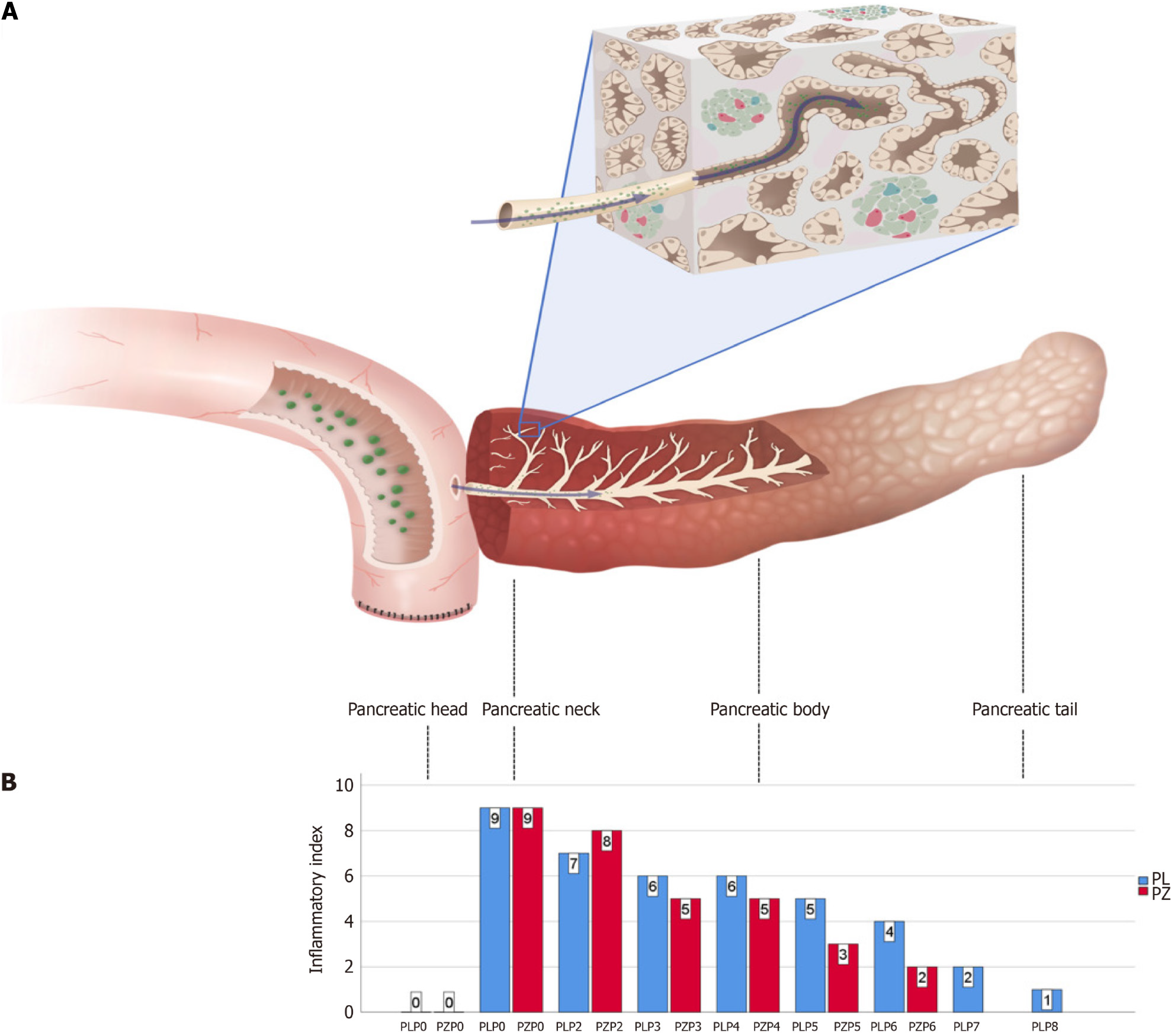
Figure 3 Gradient inflammation and digestive reflux in pancreatic stump after pancreaticoduodenectomy.
A: Schematic representation of digestive reflux in pancreaticojejunostomy. The digestive fluid passes through the anastomosis and reaches deep into the pancreatic ductal system, accompanied by the high-level biochemical activity of the pancreas and mechanical injury, resulting in a gradient of inflammation in the stump; B: Inflammatory index in the pancreatic stump ranges from nine to one. The pancreatic heads are used as controls and labeled as PLP0 and PZP0.
- Citation: Wang TG, Tian L, Zhang XL, Zhang L, Zhao XL, Kong DS. Gradient inflammation in the pancreatic stump after pancreaticoduodenectomy: Two case reports and review of literature. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(9): 1649-1659
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i9/1649.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1649