Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 26, 2024; 12(9): 1560-1568
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1560
Published online Mar 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1560
Figure 1 Treatment process (right knee) for Patient 1.
A: Anteroposterior X-ray before revision; B: Lateral X-ray before revision; C: Surgical opening before revision; D: Incision for revision; E: The incision healed well after revision.
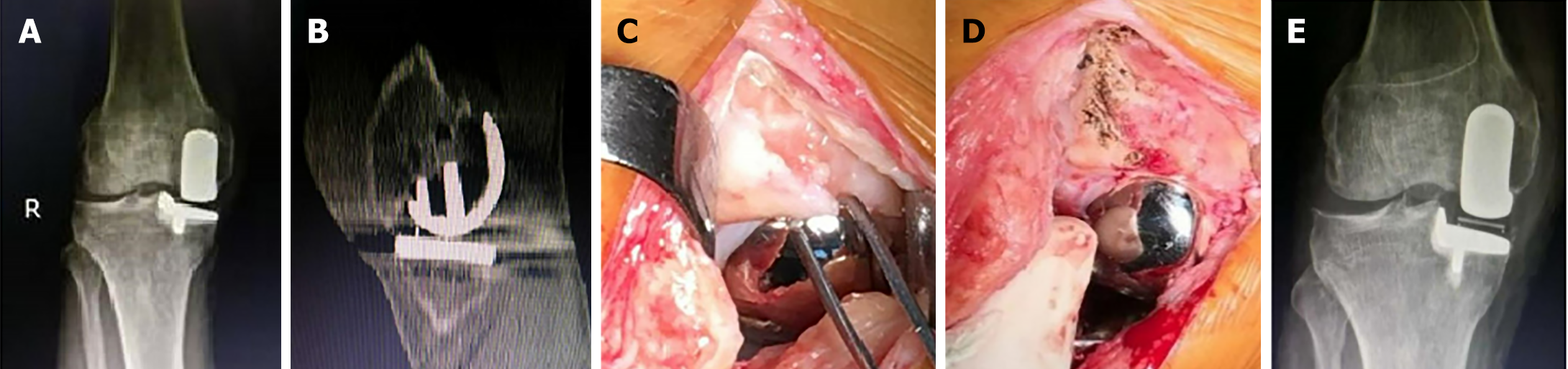
Figure 2 Treatment process (right knee) for Patient 3.
A: Anteroposterior X-ray before revision; B: Dual computed tomography image showing osteophytes in front of the femoral prosthesis; C: Osteophytes in front of the femoral prosthesis; D: Excision of osteophytes; E: Anteroposterior X-ray after revision.
Figure 3 Treatment process (left knee) for Patient 5.
A: Dual computed tomography image showing that there was a bone-free body between the tibial prosthesis and the femoral prosthesis; B: Residual bone cement was found during arthroscopic exploration.
Figure 4 Treatment process (right knee) for Patient 6.
A: Anteroposterior X-ray before revision; B: Lateral X-ray before revision; C: The tibial prosthesis was loose; D: The tibial prosthesis was easily removed during revision; E: The femoral prosthesis was removed and modified for total knee arthroplasty.
Figure 5 Treatment process (right knee) for Patient 8.
A: A large amount of inflammatory synovium in the suprapatellar bursa was observed during revision; B: The lateral femoral condyle cartilage was injured; C: Synovial tissue; D: Oxford movable platform single condyle prosthesis.
Figure 6 Treatment process (right knee) for Patient 9.
A: Lateral X-ray before unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA); B: Lateral X-ray in the weight-bearing position after UKA.
Figure 7 Treatment process (left knee) for Patient 12.
A: Before revision, X-ray showed that the gasket was dislocated; B: The spacer was moved forward under extreme knee flexion; C: The centre of the femoral prosthesis was inwards; D: Prosthesis displacement; E: X-ray after revision.
Figure 8 Treatment process (left knee) for Patient 13.
A: X-ray image showing genu valgus after Unicompartmental knee arthroplasty (UKA); B: X-ray showing residual bone cement after UKA; C: Repair of the medial collateral ligament; D: X-ray anteroposterior films after revision.
- Citation: Zhao JL, Jin X, Huang HT, Yang WY, Li JH, Luo MH, Liu J, Pan JK. Analysis of the causes of primary revision after unicompartmental knee arthroplasty: A case series. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(9): 1560-1568
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i9/1560.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i9.1560