Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 16, 2024; 12(8): 1487-1496
Published online Mar 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1487
Published online Mar 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1487
Figure 1 Computed tomography revealed a 5-mm round cyst in the pancreatic tail (arrow) but with no solid mass, atrophy, or fatty change in the pancreas.
A: Pancreatic parenchymal phase; B: Equilibrium phase.
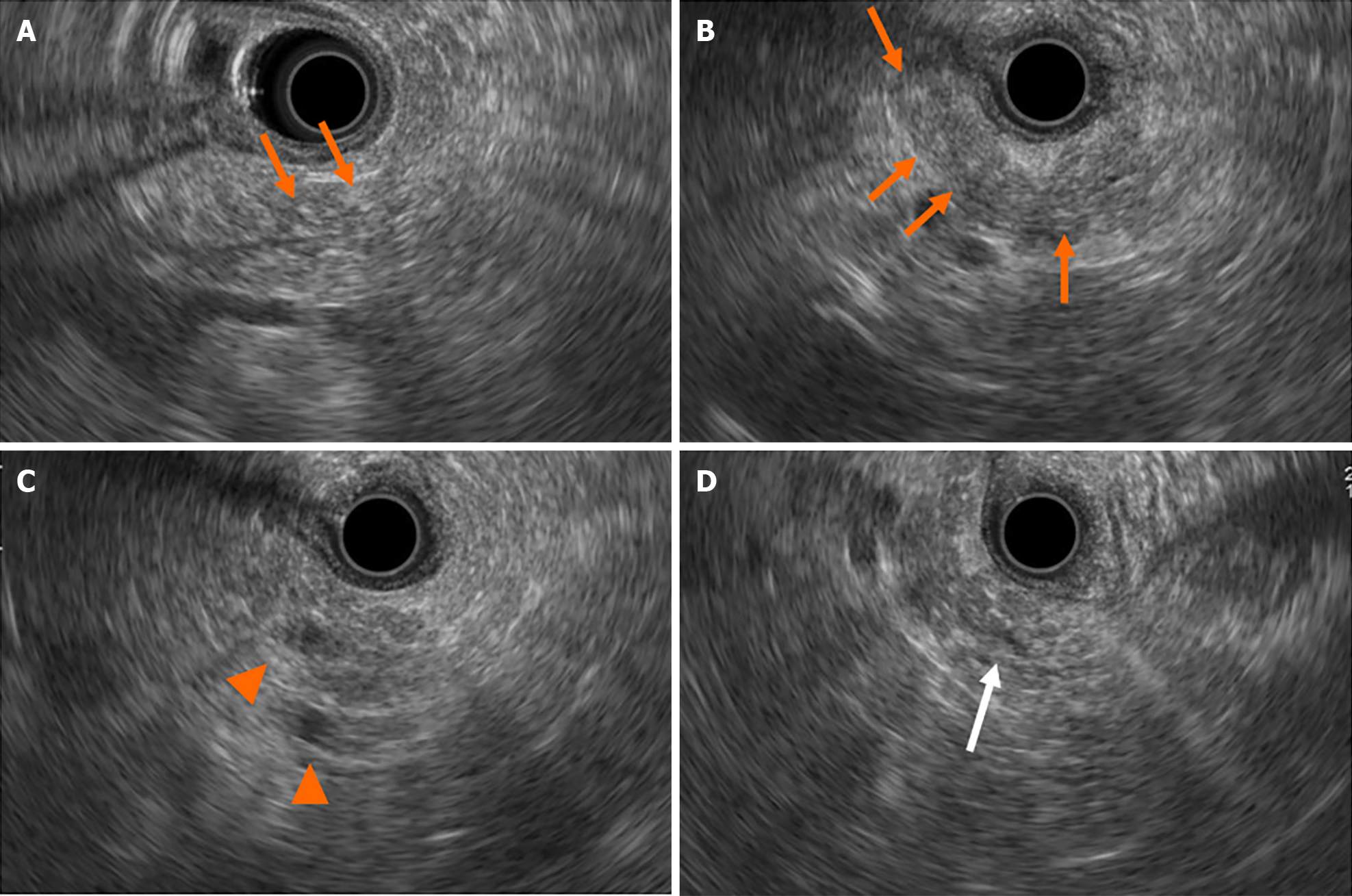
Figure 2 Findings of endoscopic ultrasonography at first visit to our institute.
A and B: There were diffuse high echoic spots (orange arrows) in the whole pancreas, indicating early chronic pancreatitis; C: Small round cysts (arrowheads) were found in the pancreatic tail; D: There was no caudal main pancreatic duct dilatation in the pancreatic tail (white arrow).
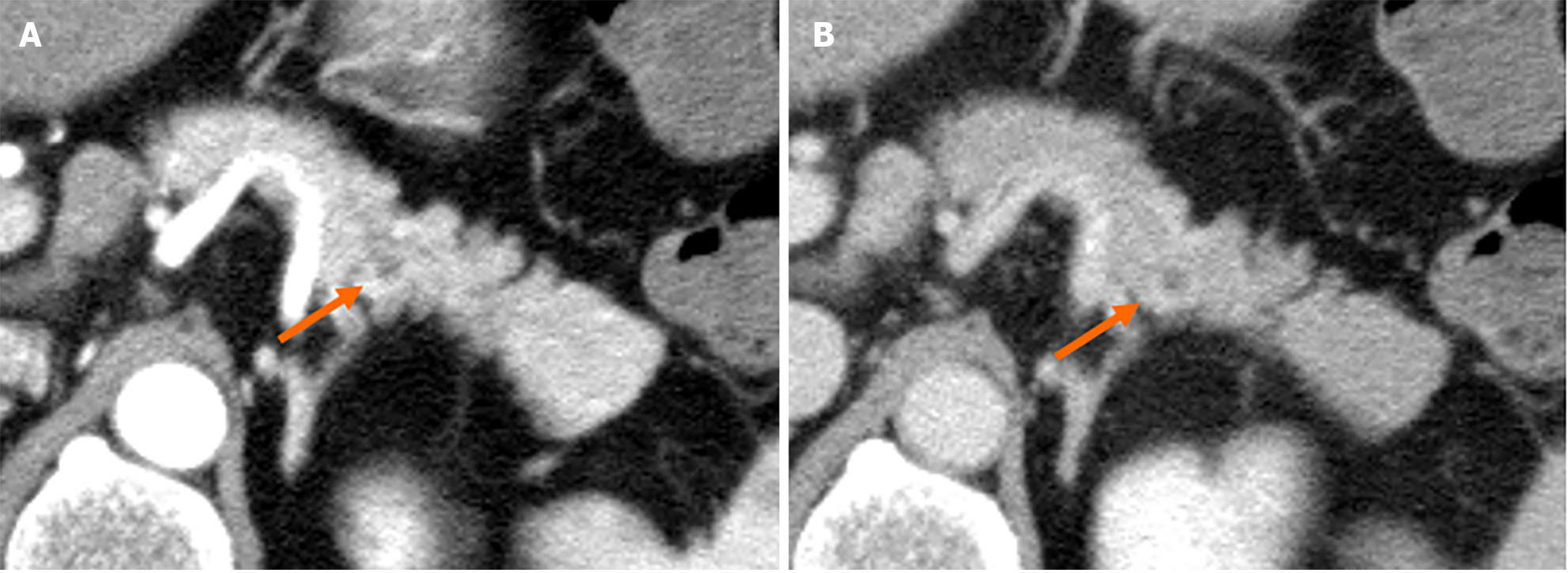
Figure 3 Findings of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography at first visit to our institute.
A: The main pancreatic duct (MPD) had poor description in a 20-mm range (arrows) at the pancreatic body/tail, but there was no dilation of the caudal MPD; B: Other sequence of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed irregular MPD in the same position (arrowheads).
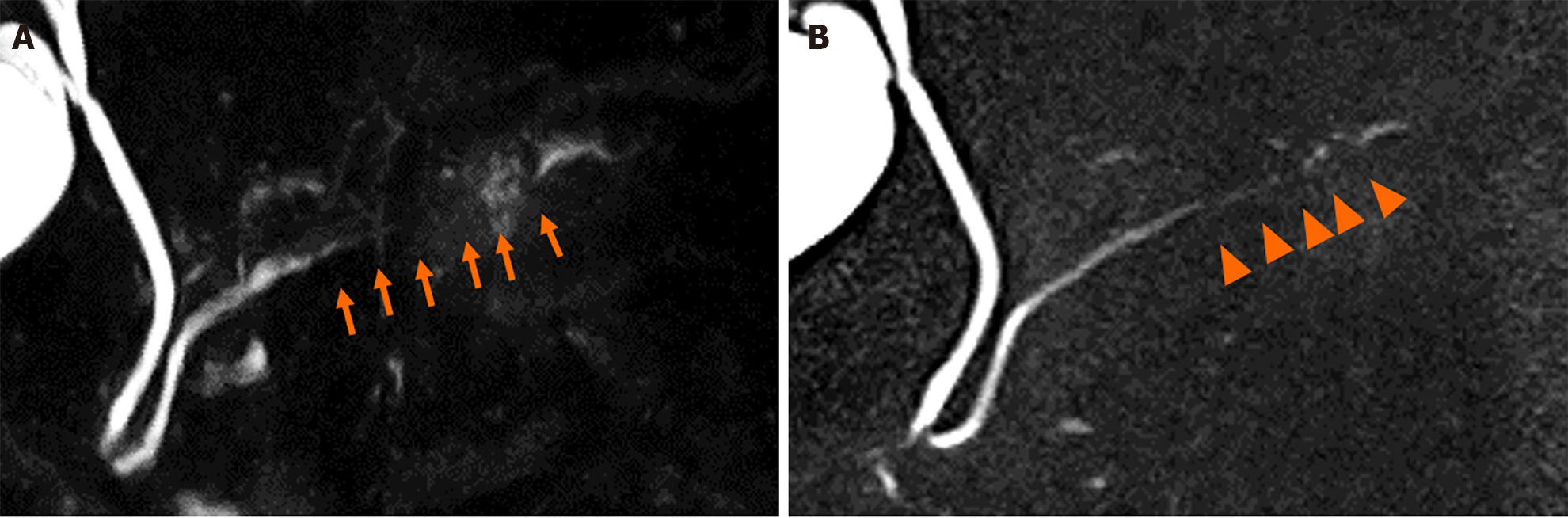
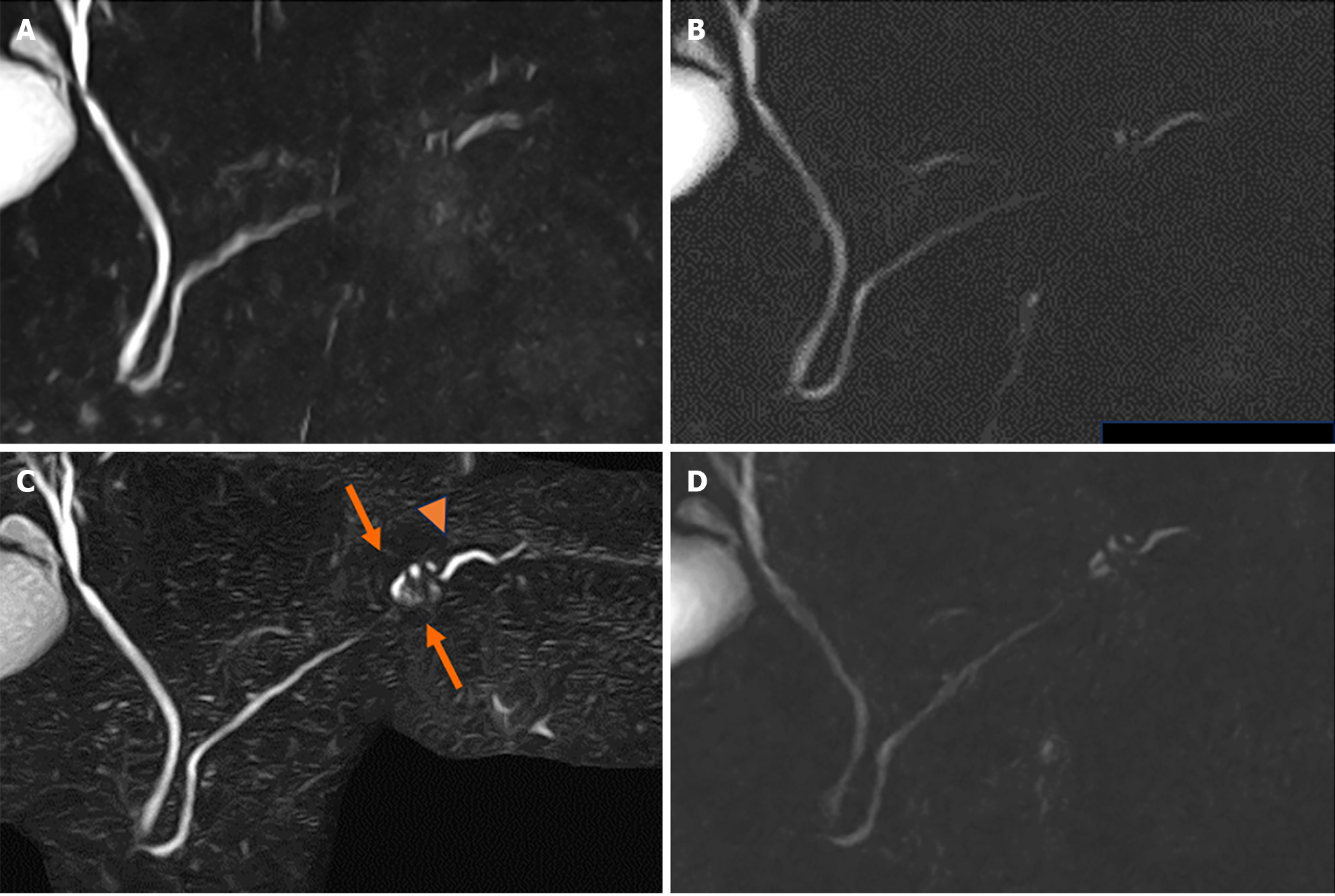
Figure 4 Changes of magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography findings.
A: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (MRCP) findings demonstrated no change at 6 months; B: Other MRCP sequence at 6 months; C: Caudal cyst has grown (arrows) and caudal main pancreatic duct caliber has slightly increased (arrowhead) at 24 months; D: Other MRCP sequence at 24 months.
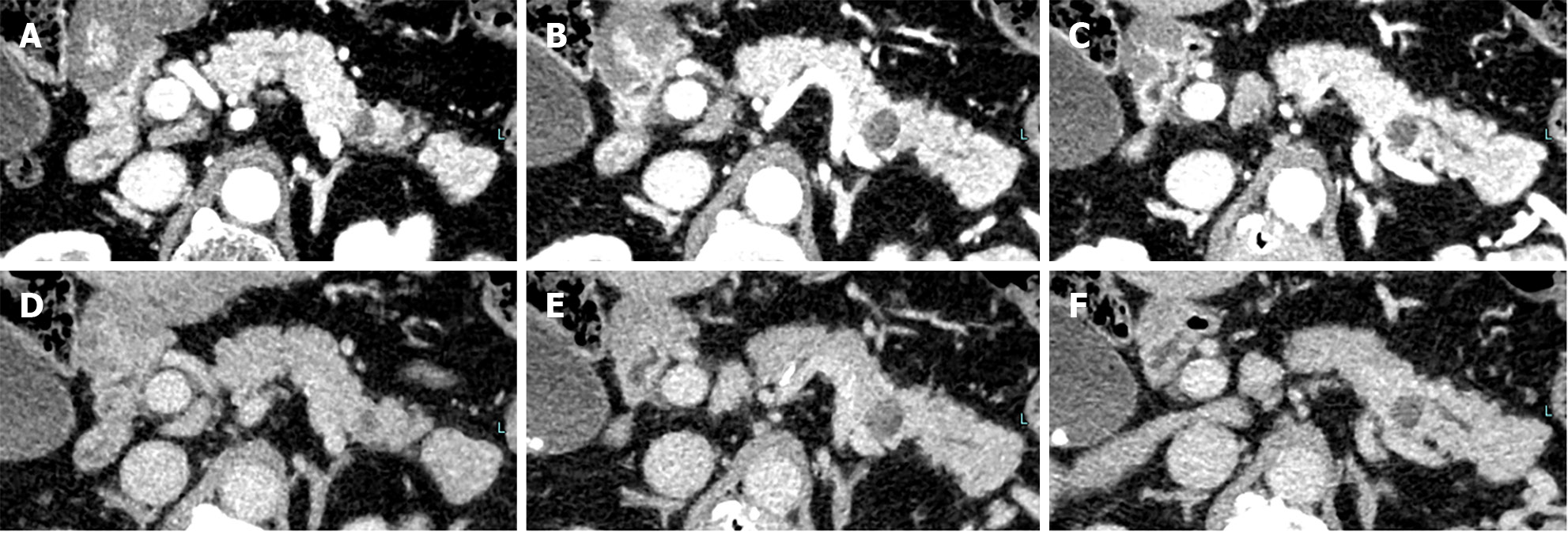
Figure 5 Computed tomography at 24 months revealed no solid space-occupying lesion but the pancreatic tail cyst has grown to 10 mm and the caudal main pancreatic duct was slightly dilated.
A-C: Pancreatic parenchymal phase; D-F: Equilibrium phase.
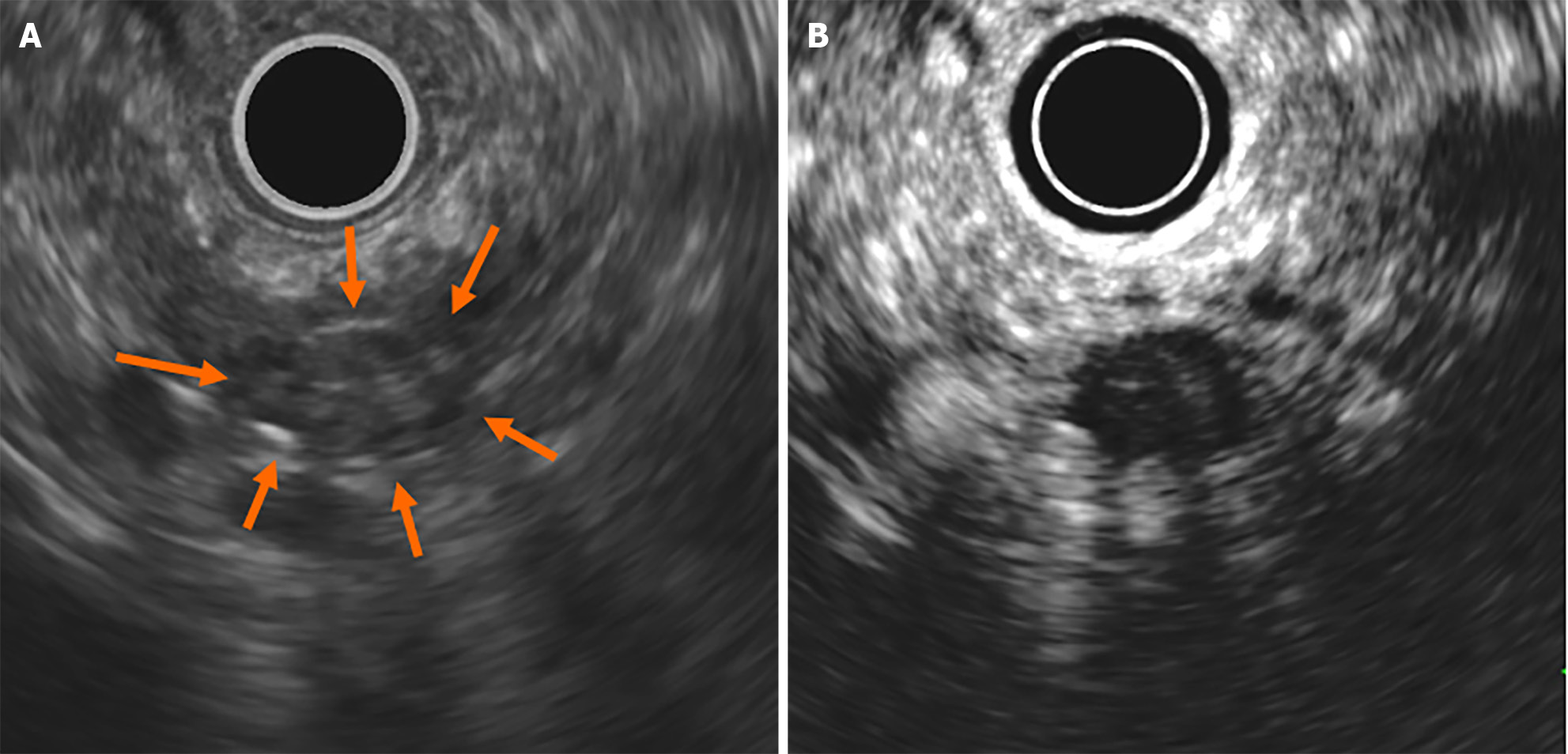
Figure 6 Findings of endoscopic ultrasonography at 24 months.
A: On endoscopic ultrasonography (EUS), the cyst was described like a solid mass (arrows); B: Contrast-enhanced EUS using Sonazoid showed the mass as a round cyst.
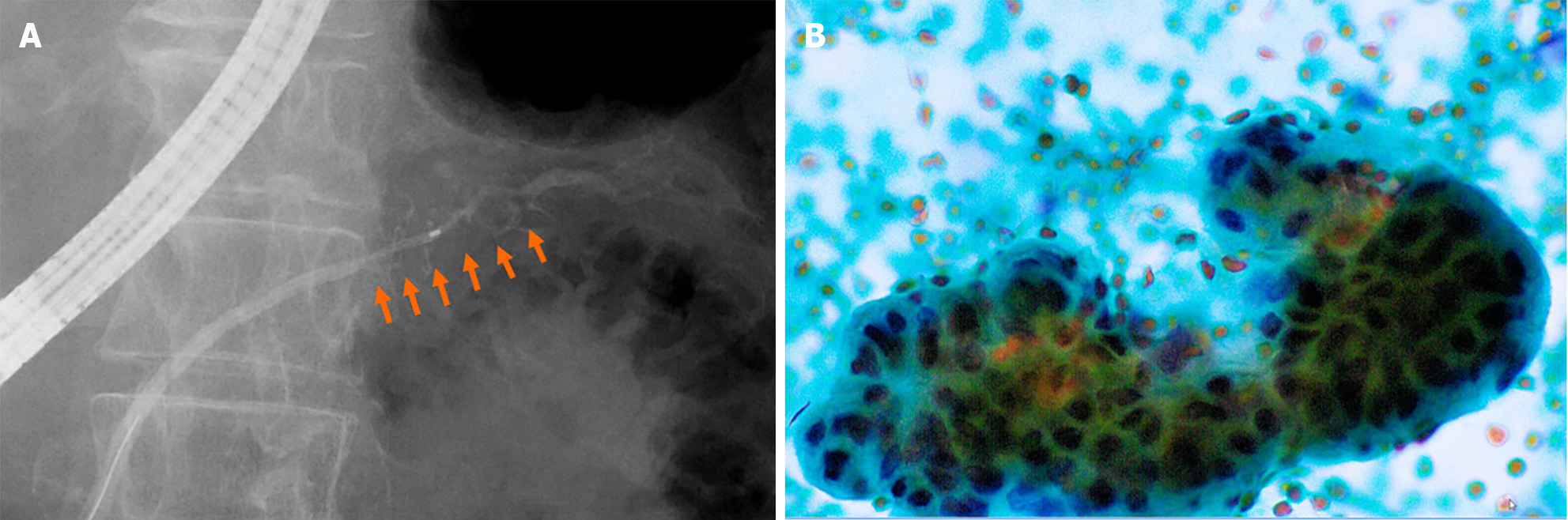
Figure 7 Findings of endoscopic retrograde pancreatography.
A: Endoscopic retrograde pancreatography revealed that the main pancreatic duct (MPD) in the pancreatic tail was irregularly narrowing (arrows) in a 20-mm range and the caudal MPD was slightly dilated; B: Serial pancreatic juice aspiration cytology examination revealed atypical cells consistent with adenocarcinoma.
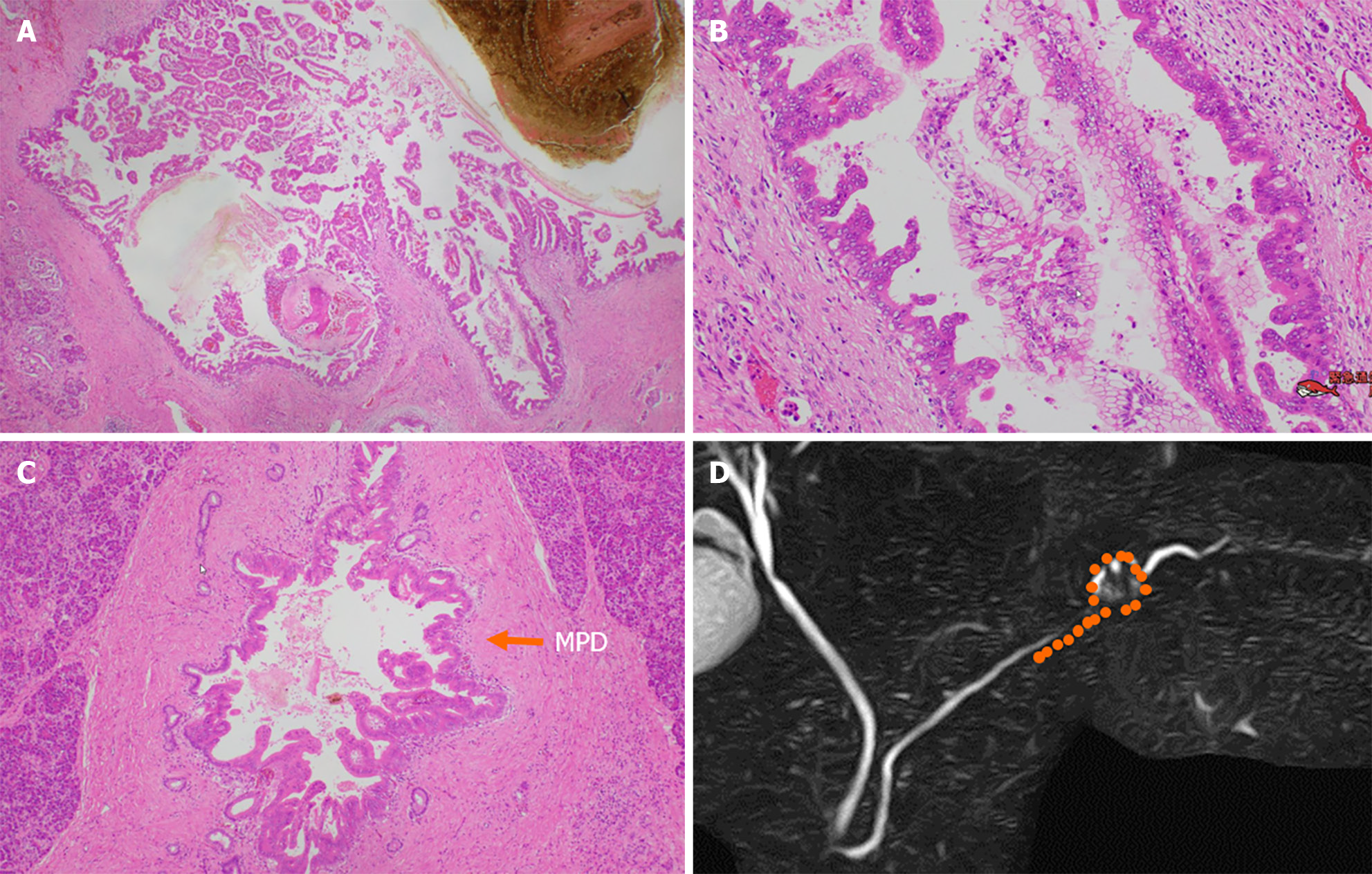
Figure 8 Pathological findings.
A and B: Low-papillary and pseudopapillary adenocarcinoma cells were spread in the cyst wall; C: Malignant cells spread to the main pancreatic duct (arrow) and branch duct, in a 20-mm range toward the pancreatic body; D: Distribution of high-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia (orange points). MPD: Main pancreatic duct.
- Citation: Furuya N, Yamaguchi A, Kato N, Sugata S, Hamada T, Mizumoto T, Tamaru Y, Kusunoki R, Kuwai T, Kouno H, Kuraoka K, Shibata Y, Tazuma S, Sudo T, Kohno H, Oka S. High-grade pancreatic intraepithelial neoplasia diagnosed based on changes in magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography findings: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(8): 1487-1496
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i8/1487.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i8.1487