Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2024; 12(7): 1326-1332
Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1326
Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1326
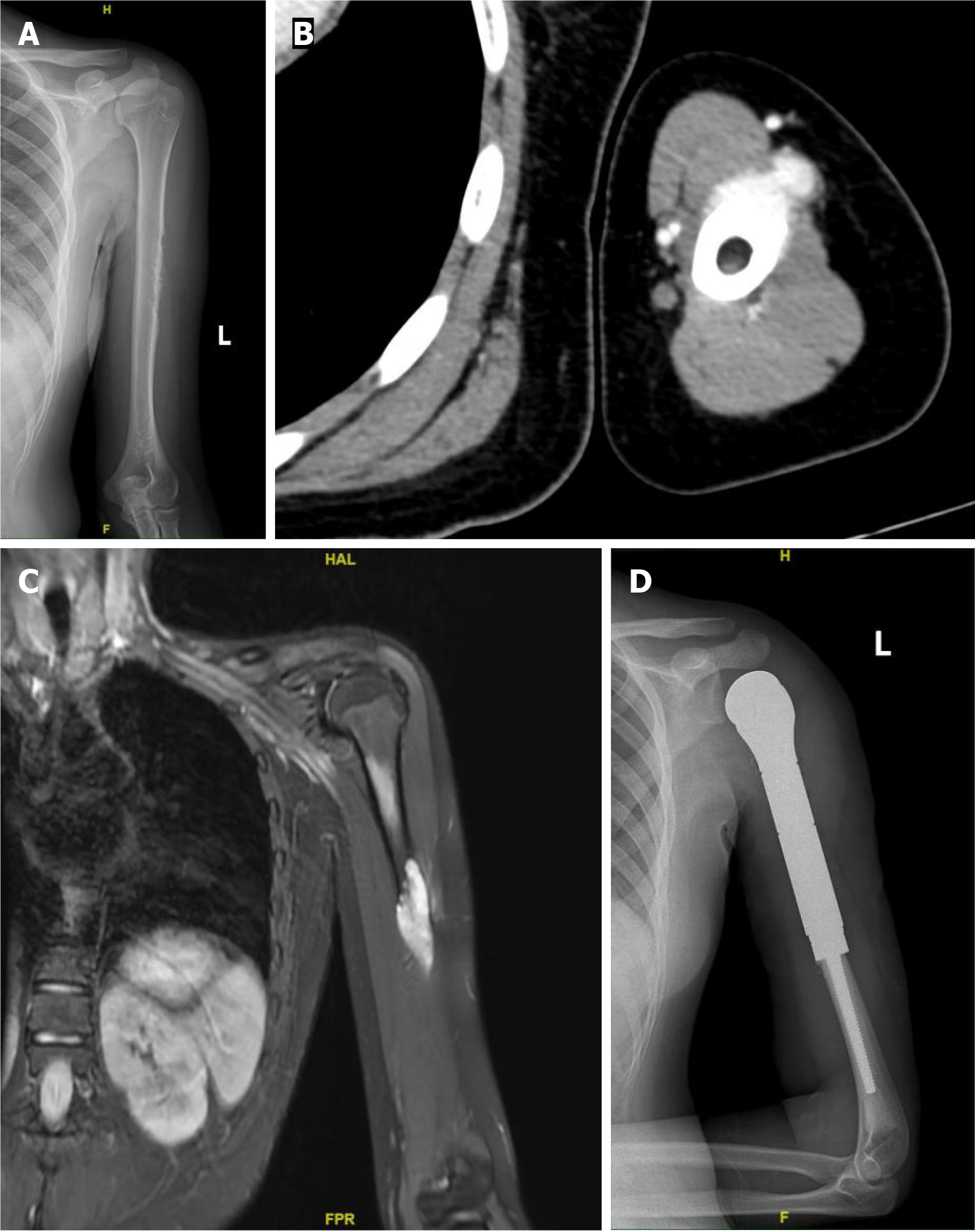
Figure 1 Imaging findings of the lesion.
A: X-ray reveals bone destruction and thinning of the corresponding segment of the cortical bone in the midshaft of the left femur; B: Computed tomography scan reveals roughness of the cortical bone in the middle segment of the left humerus, with surrounding soft tissue masses exhibiting a nodular morphology; C: Magnetic resonance imaging reveals a soft tissue mass surrounding the left humerus, which appears as a high signal on diffusion-weighted imaging; D: The postoperative X-ray indicates the presence of metallic internal fixation material in the surgical area of the left humerus.
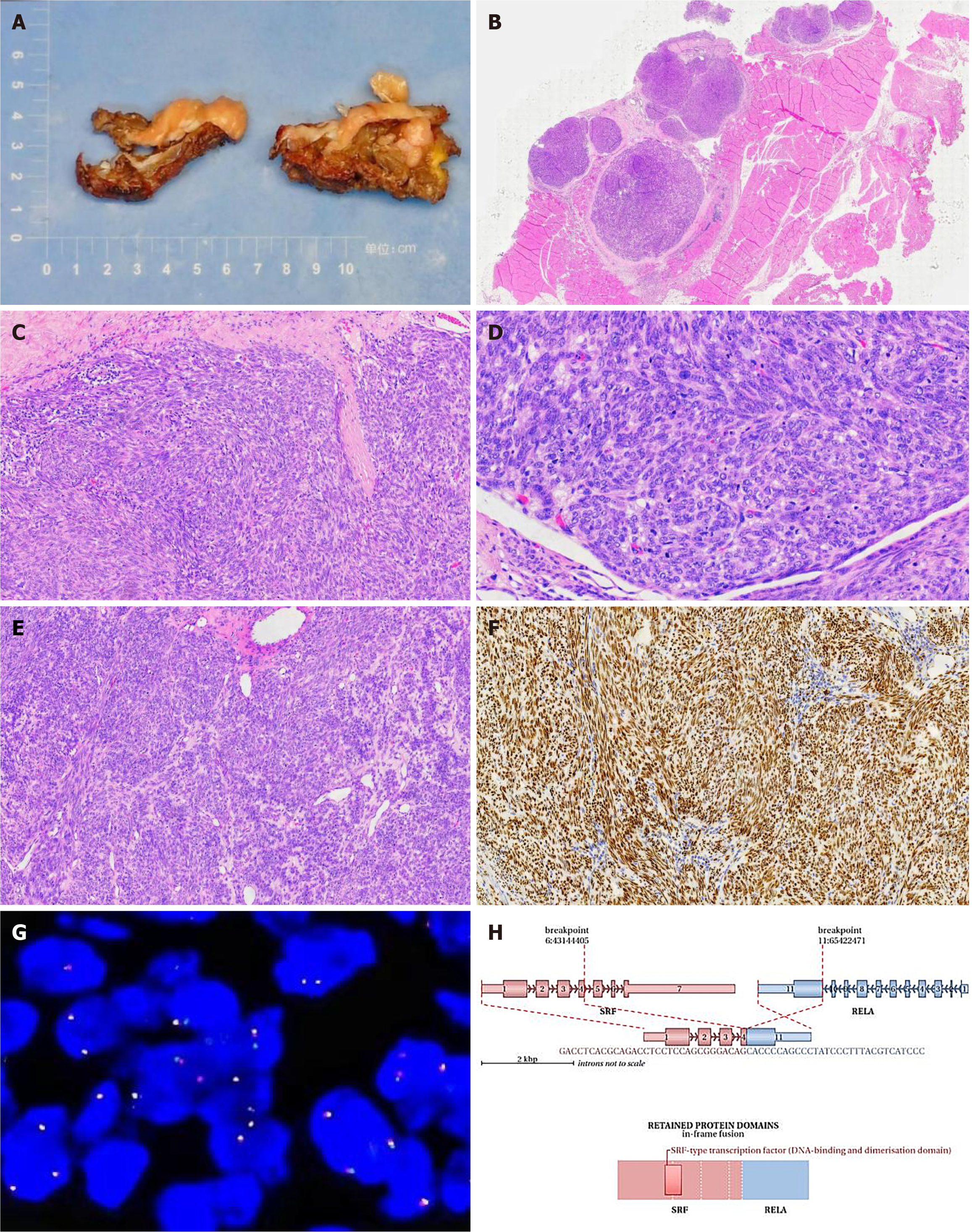
Figure 2 Integrated analysis of specimen photograph, histopathological findings, fluorescence in situ hybridization testing, and next-generation sequencing testing results.
A: The tumor appears multi-nodular, measuring 5 cm × 4.5 cm × 2 cm, with individual nodules ranging from 1.5 to 2 cm in diameter. The cut surface is solid, slightly firm, and grayish-yellow; B: Nodular distribution of the tumor within fibromuscular tissue, hematoxylin and eosin (HE) stain, low magnification; C: Cells exhibiting oval and spindle shapes, densely packed, arranged in bundles or whirls, HE stain, medium magnification; D: Average of approximately 10 mitotic figures per 10 high-power fields (HPF) with evident focal mitotic figures (approximately 20 per 10 HPF), HE stain, high magnification; E: Tumor cell nuclei are relatively plump, enlarged, and indicate certain dysplasia, HE stain, medium magnification; F: Diffuse strong positive expression of TLE1 in tumor cells, envision method, medium magnification; G: Negative result for SS18 gene probe dual-color break-apart fluorescence in situ hybridization assay, high magnification; H: Gene second-generation sequencing results revealing an SRF-RELA fusion variant.
- Citation: Zhou Y, Sun YW, Liu XY, Shen DH. Misdiagnosis of synovial sarcoma - cellular myofibroma with SRF-RELA gene fusion: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(7): 1326-1332
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i7/1326.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1326