Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Mar 6, 2024; 12(7): 1272-1283
Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1272
Published online Mar 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1272
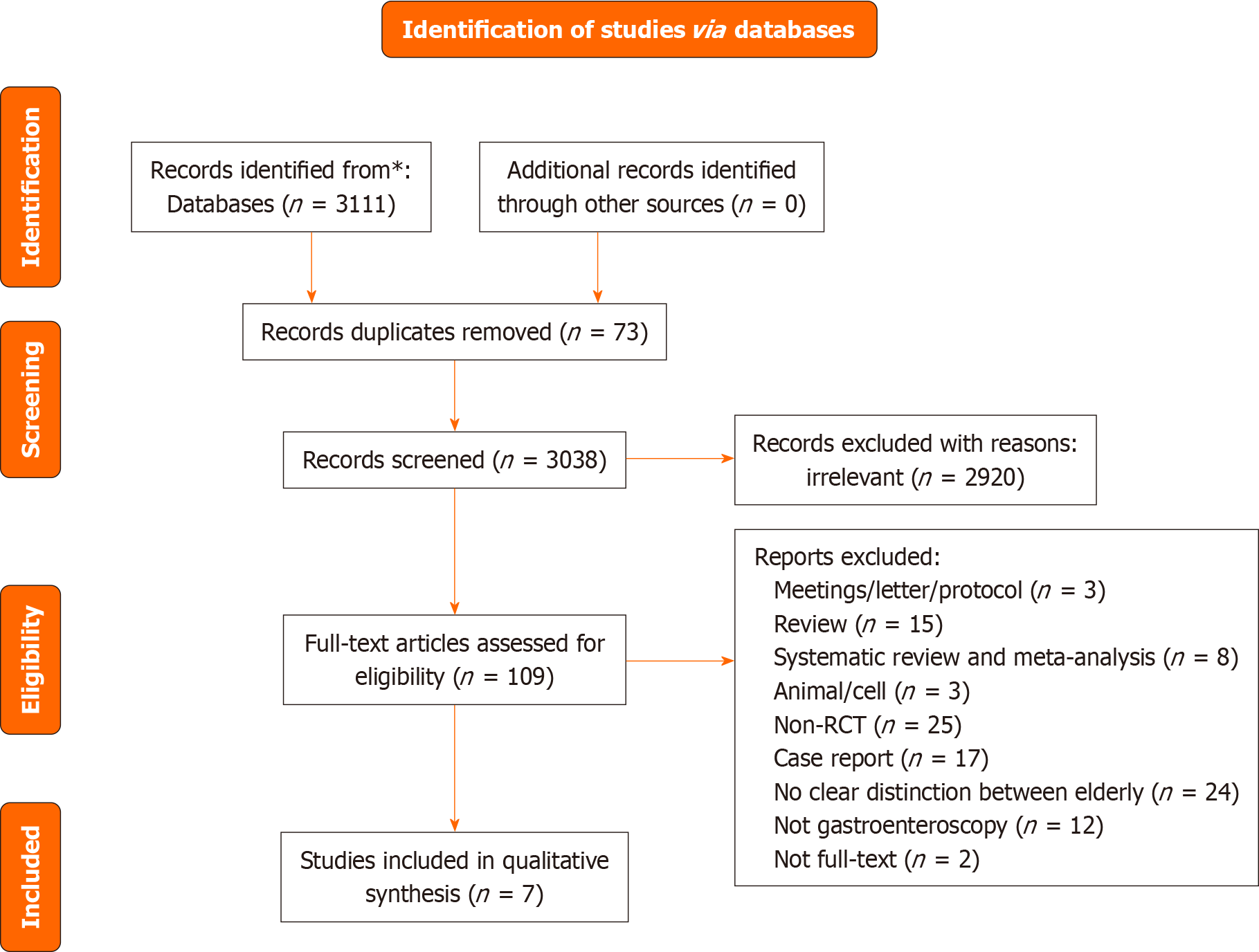
Figure 1 The selection of literature for the included studies.
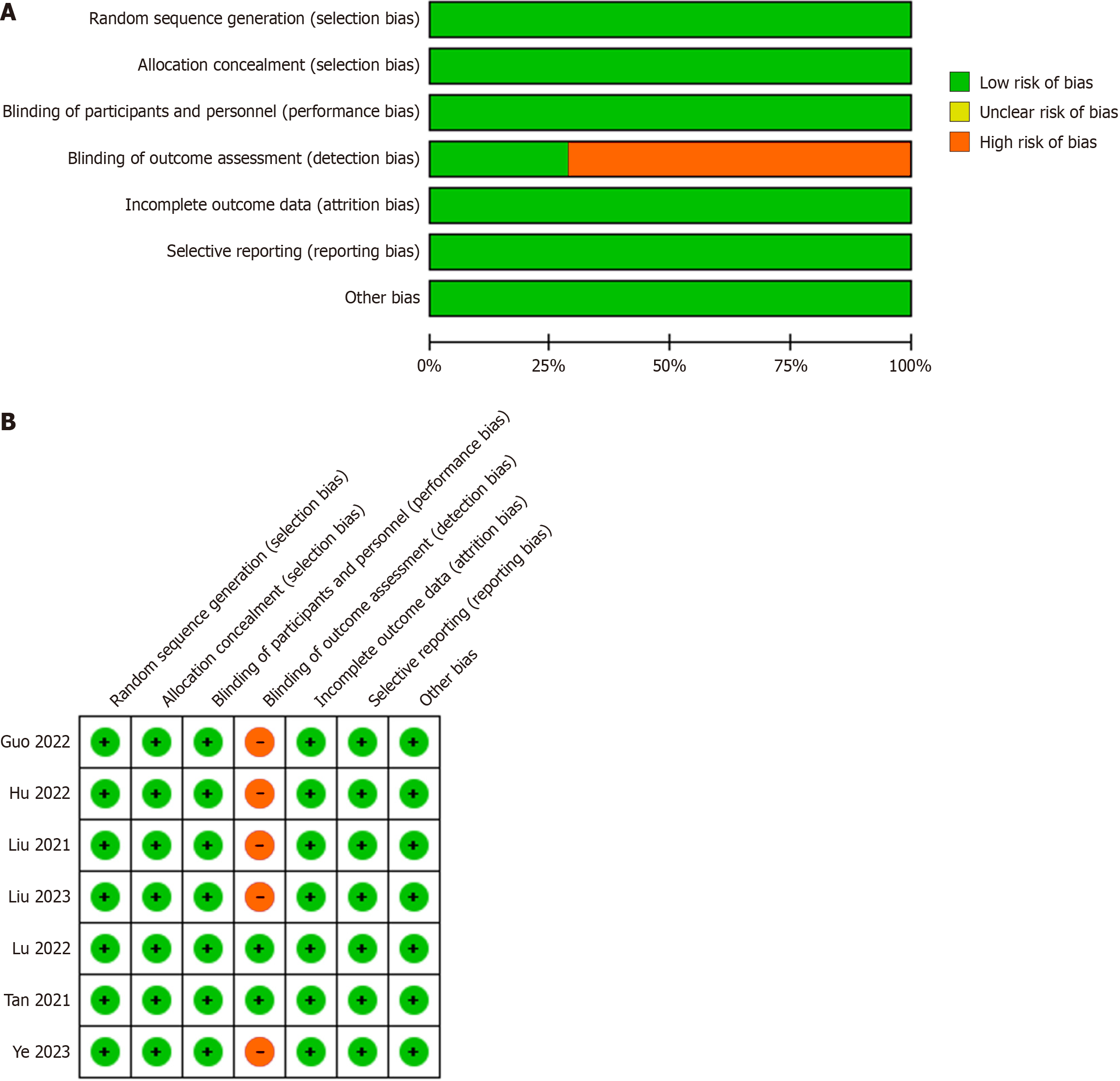
Figure 2 The graph (A) and summary (B) of risk bias of randomized controlled trials.
The seven studies showed a low bias risk for they assessed randomized sequence generation (100%), blinding of participants (100%), blinding of outcome (25%), selective reporting (100%), and others (100%).
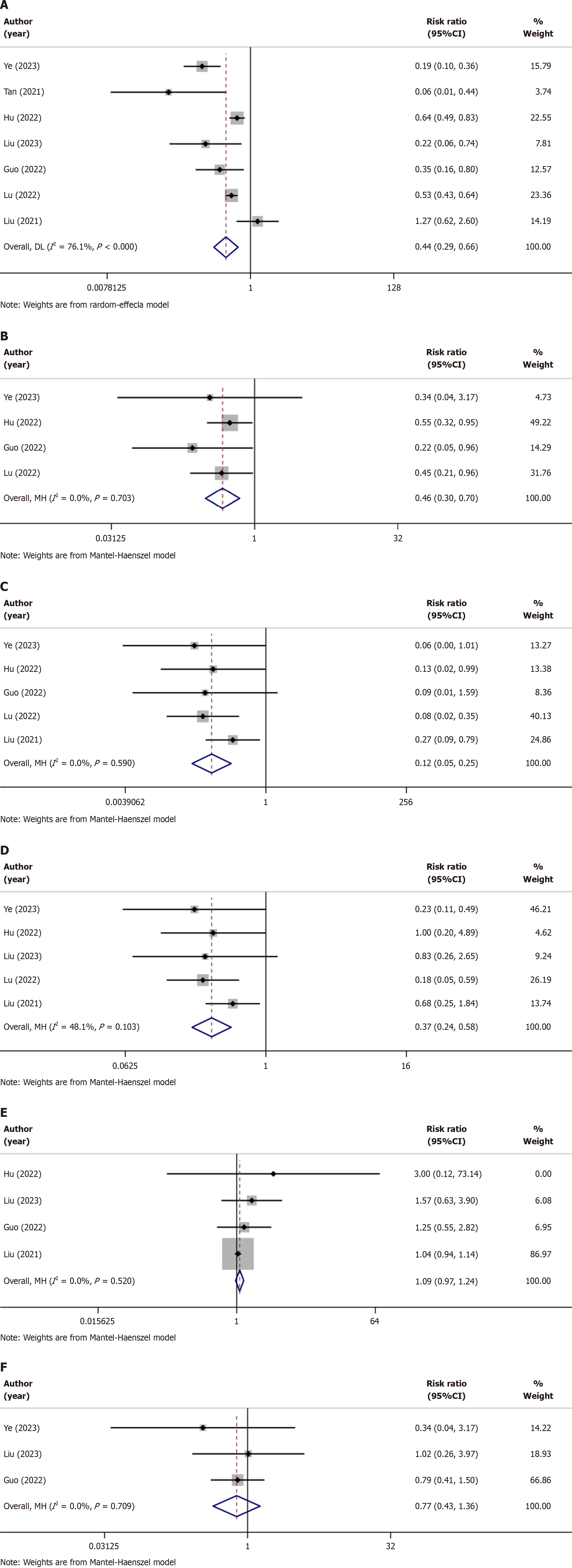
Figure 3 Forest plots of adverse events after administration of remimazolam or propofol.
A: Hypotension; Seven cohort studies reported that the hypotension after administration of remimazolam or propofol the overall estimated prevalence was 44%; B: Respiratory depression; In terms of respiratory depression, four reported that the overall estimated prevalence was 46%; C: Injection pain; Five studies provided comprehensive information regarding the injection pain after administration, with a pooled prevalence of 12%; D: Bradycardia; A total of five cohort studies investigated bradycardia after the two sedatives, with a pooled prevalence of 37%; E: Postoperative nausea and vomiting; In terms of postoperative nausea and vomiting reported in four limited studies, it showed that hat there was no significant difference between the injection of the two drugs; F: Dizziness; A total of three studies investigated dizziness, with a pooled prevalence of 77%.
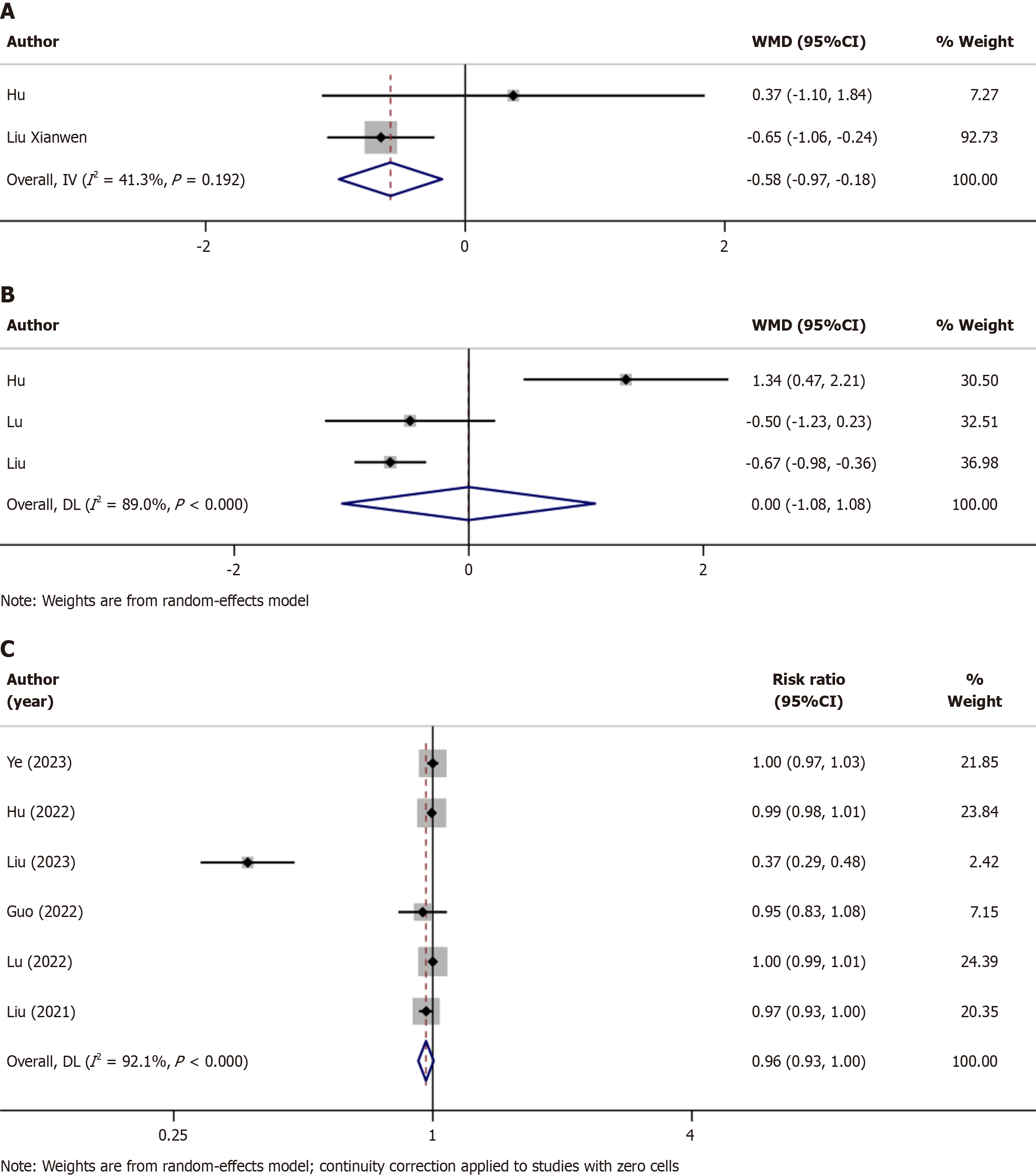
Figure 4 Forest plots of secondary outcomes after administration of remimazolam or propofol.
A: The forest plot of the time to discharge after administration of remimazolam or propofol. Only two studies provided comprehensive information regarding the time to discharge, we found that compared to propofol group, elderly patients who were injected with remimazolam have the shorter discharge time, weighted mean difference equals -0.58; B: The forest plot of the time to fully alert after administration of remimazolam or propofol. A total of three cohort studies investigated which revealed that the time for patients to be fully alert after remimazolam sedation and that after propofol sedation without statistical significance P = 0.998; C: The forest plot of the successful sedation rate after administration of remimazolam or propofol. A total of six cohort studies investigated the successful sedation rate, and pooled analysis showed 96%.
- Citation: Li FZ, Zhao C, Tang YX, Liu JT. Safety and efficacy comparison of remimazolam and propofol for intravenous anesthesia during gastroenteroscopic surgery of older patients: A meta-analysis. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(7): 1272-1283
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i7/1272.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i7.1272