Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Dec 26, 2024; 12(36): 6905-6915
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6905
Published online Dec 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6905
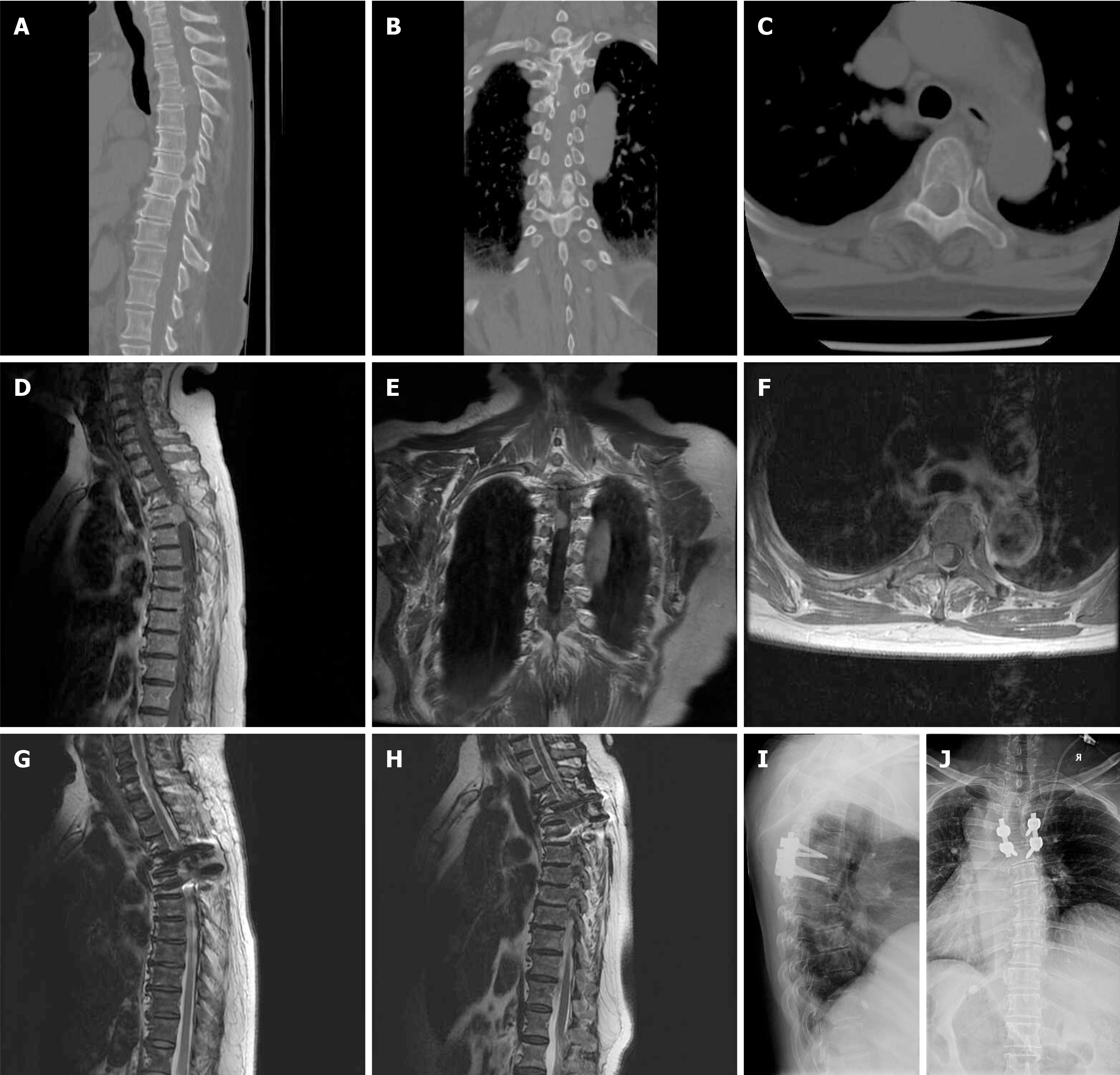
Figure 1 Imaging finding in case 1.
A: Sagittal; B: Coronal; C: Axial 3-dimensional CT images revealed calcification within the tumor; D: Subsequent sagittal; E: Coronal; F: Axial magnetic resonance imaging T1-weighted post-contrast-enhanced images demonstrated homogeneous contrast enhancement of the tumor, which was located in the thoracic spine with ventrolateral dural attachment; G: Sagittal magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T2-weighted image displayed gross-total resection of the tumor; H: Sagittal MRI T2-weighted image displayed no recurrence of the tumor observed 3 years after surgery; I: Lateral; J: Anteroposterior X-ray images depicted pedicle screw fixation and posterolateral bone graft fusion procedures that were conducted to stabilize the spine.
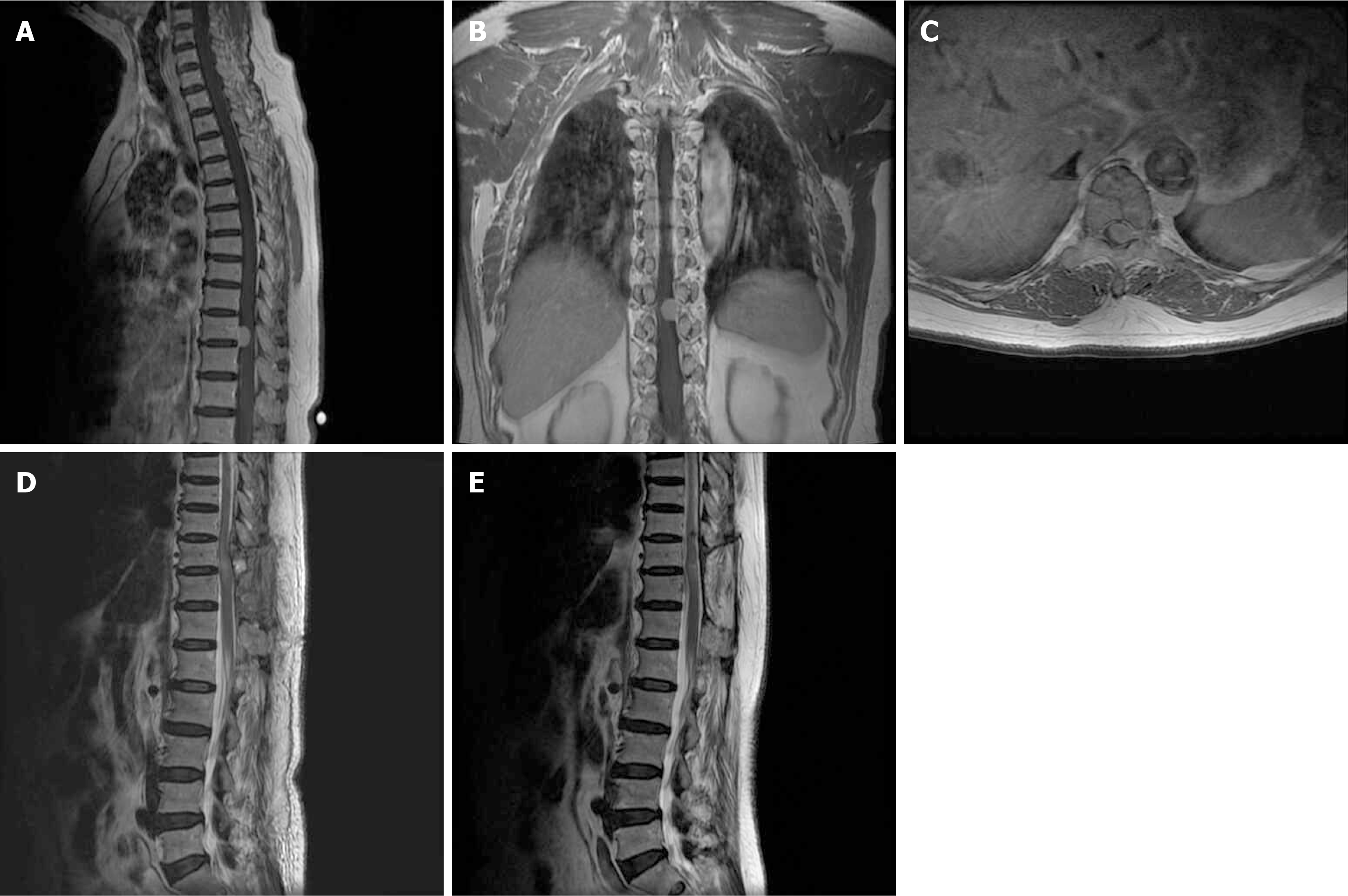
Figure 2 Imaging finding in Case 2.
A: Sagittal; B: Coronal; C: Axial magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) T1-weighted post-contrast-enhanced images revealed a homogeneously contrast-enhanced tumor located in the thoracic spine with ventrolateral dural attachment; D: Sagittal MRI T2-weighted image indicated gross-total resection of the tumor; E: Sagittal MRI T2-weighted image indicated no recurrence of the tumor observed 2 years after surgery.
- Citation: Chen H, Fu YN, Fu CD. Safety and efficacy of posterior approach for resection of spinal meningioma: Impact of dural attachment location. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(36): 6905-6915
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i36/6905.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i36.6905