Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jan 26, 2024; 12(3): 623-629
Published online Jan 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.623
Published online Jan 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.623
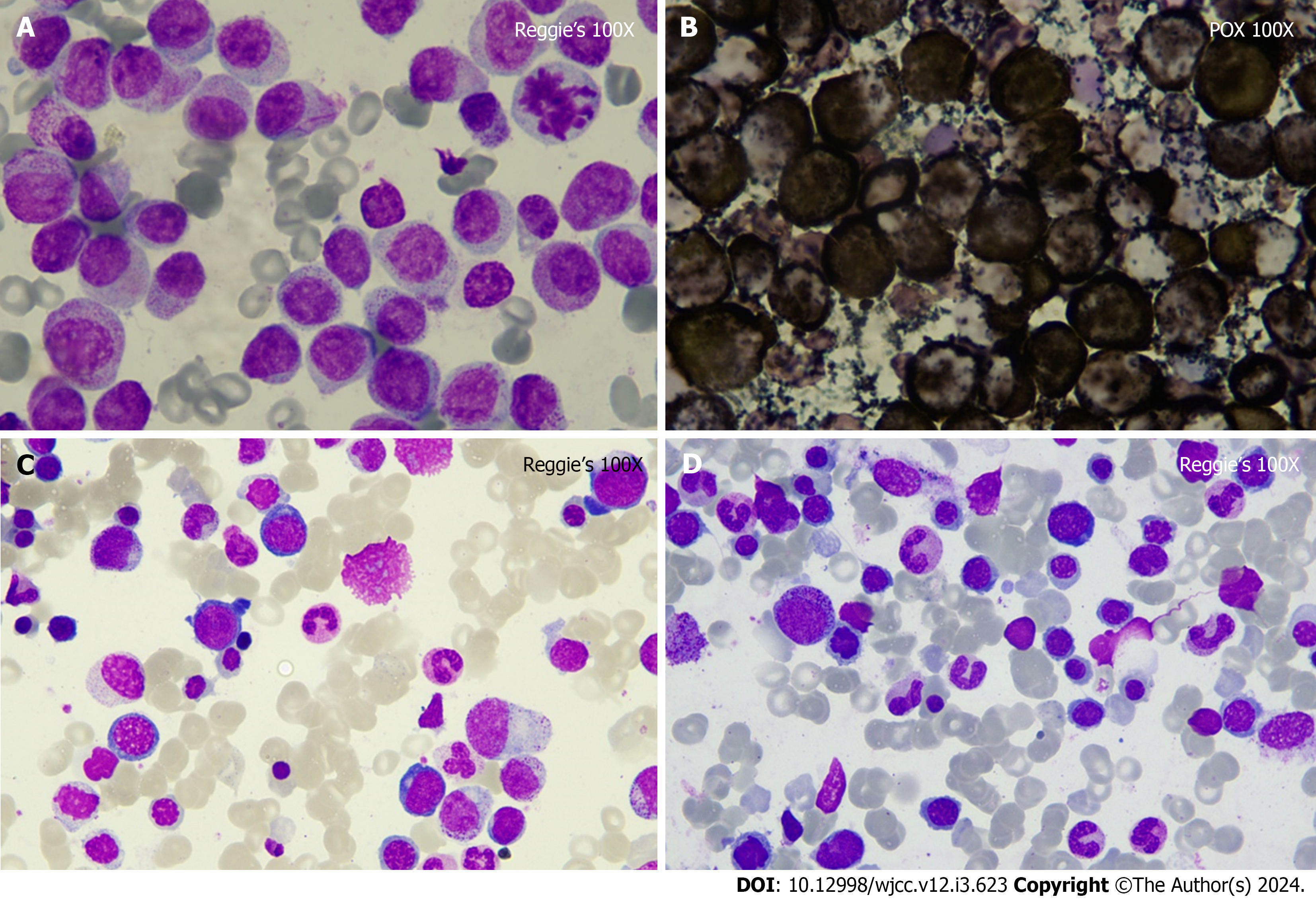
Figure 1 The patient‘s bone marrow smear at high magnification.
A: Reggie’s stain showed promyelocyte accounted for about 55%; B: Peroxidate stain was positivity; C and D: Reggie‘s stain twice showed that the patient achieved clinical complete response after chemotherapy.
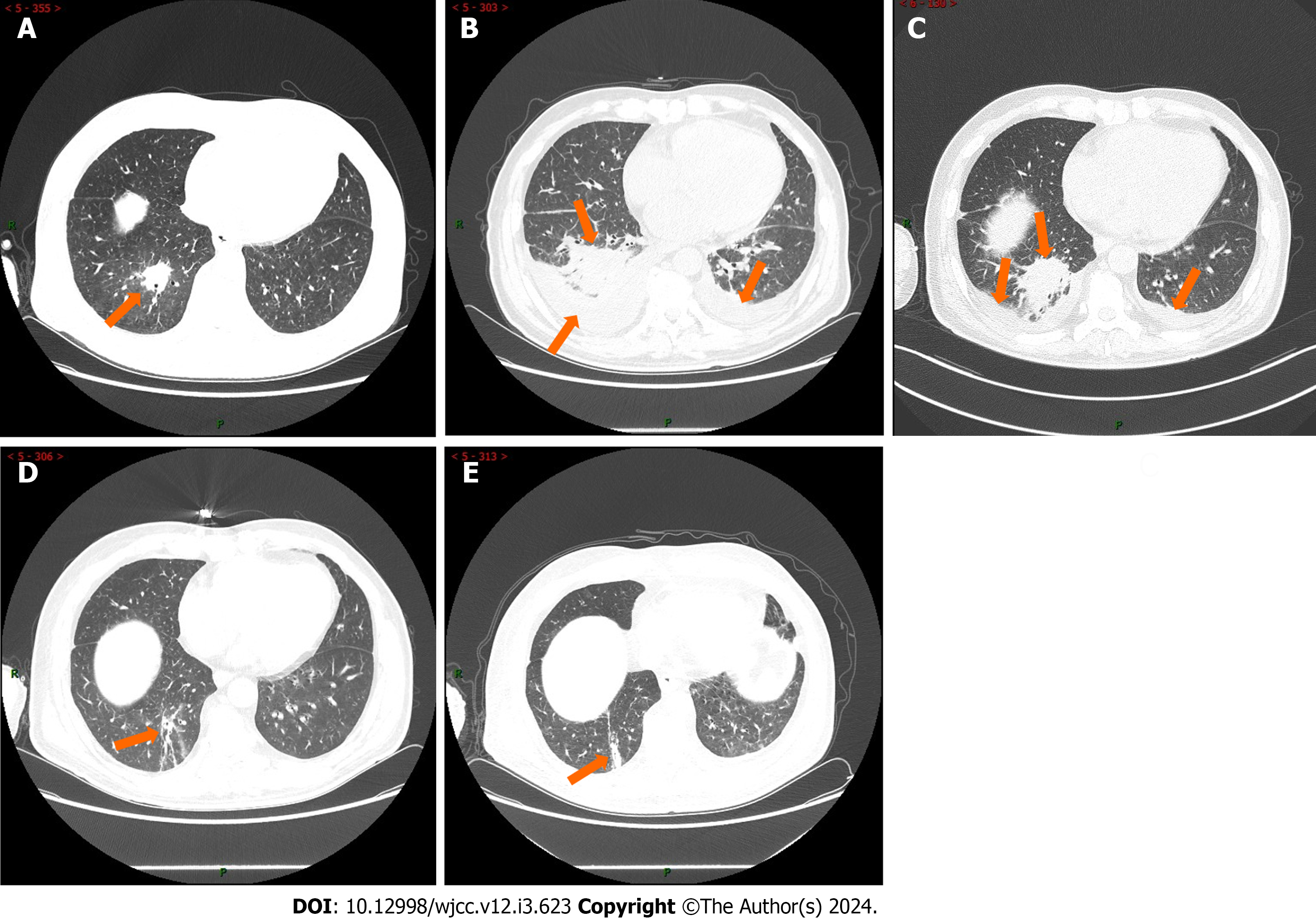
Figure 2 The patient‘s chest computed tomography scan.
A: computed tomography (CT) scan (March 21, 2022) showed consolidation of lung tissue in the right lower lobe (orange arrows) that may be inflammatory in origin; B: CT scan (April 8, 2022) showed the extent of lung consolidation increased in the right lower lobe with bilateral pleural effusion (orange arrows); C: CT scan (April 21, 2022) showed increased lung consolidation in the right lower lobe with decreased bilateral pleural effusion (orange arrows) after routine therapy with antibiotics; D: CT scan (July 20, 2022) showed pneumonitis in the right lower lobe was obvious to get an improvement (arrows) and the pleural effusion disappeared after carrimycin and anti-tuberculous treatment; E: CT scan (November 28, 2022) showed pneumonitis in the right lower lobe had been cured leaving scars (arrows).
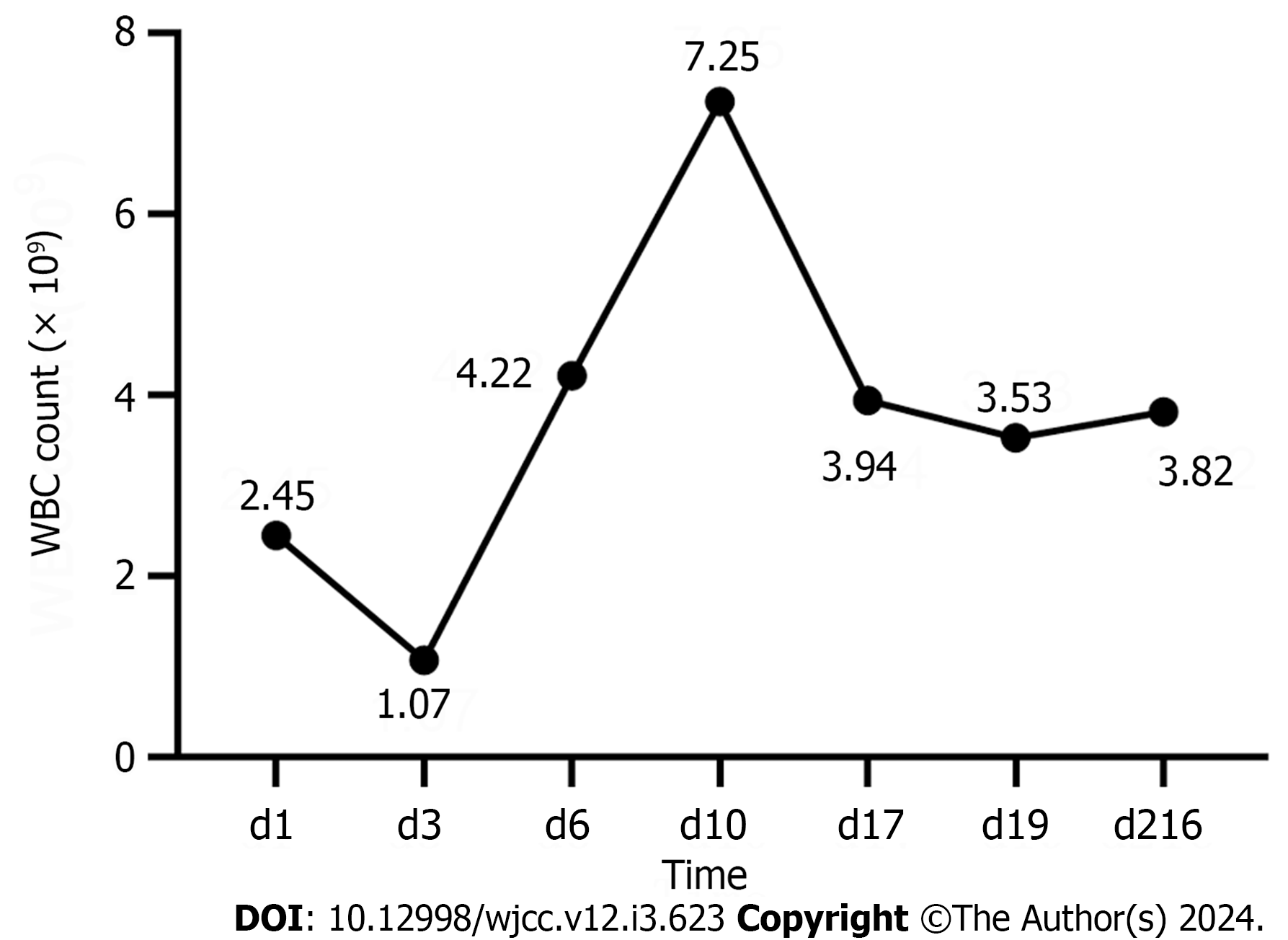
Figure 3 The change of patient‘s white blood cells during treatment.
The patient’s antibiotics uses: d1: Isoniazid 0.3 qd + rifampin 0.45 qd + ethambutol 0.75 qd; d3-d29: Carrimycin 0.4 qd (d10: chemotherapy); d29-d216: He got acute promyelocytic leukemia clinical complete response after chemotherapy and took isoniazid 0.3 qd + rifampin 0.45 qd + ethambutol 0.75 qd.
- Citation: Yang FY, Shao L, Su J, Zhang ZM. Carrimycin in the treatment of acute promyelocytic leukemia combined with pulmonary tuberculosis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(3): 623-629
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i3/623.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i3.623