Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 26, 2024; 12(24): 5589-5595
Published online Aug 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i24.5589
Published online Aug 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i24.5589
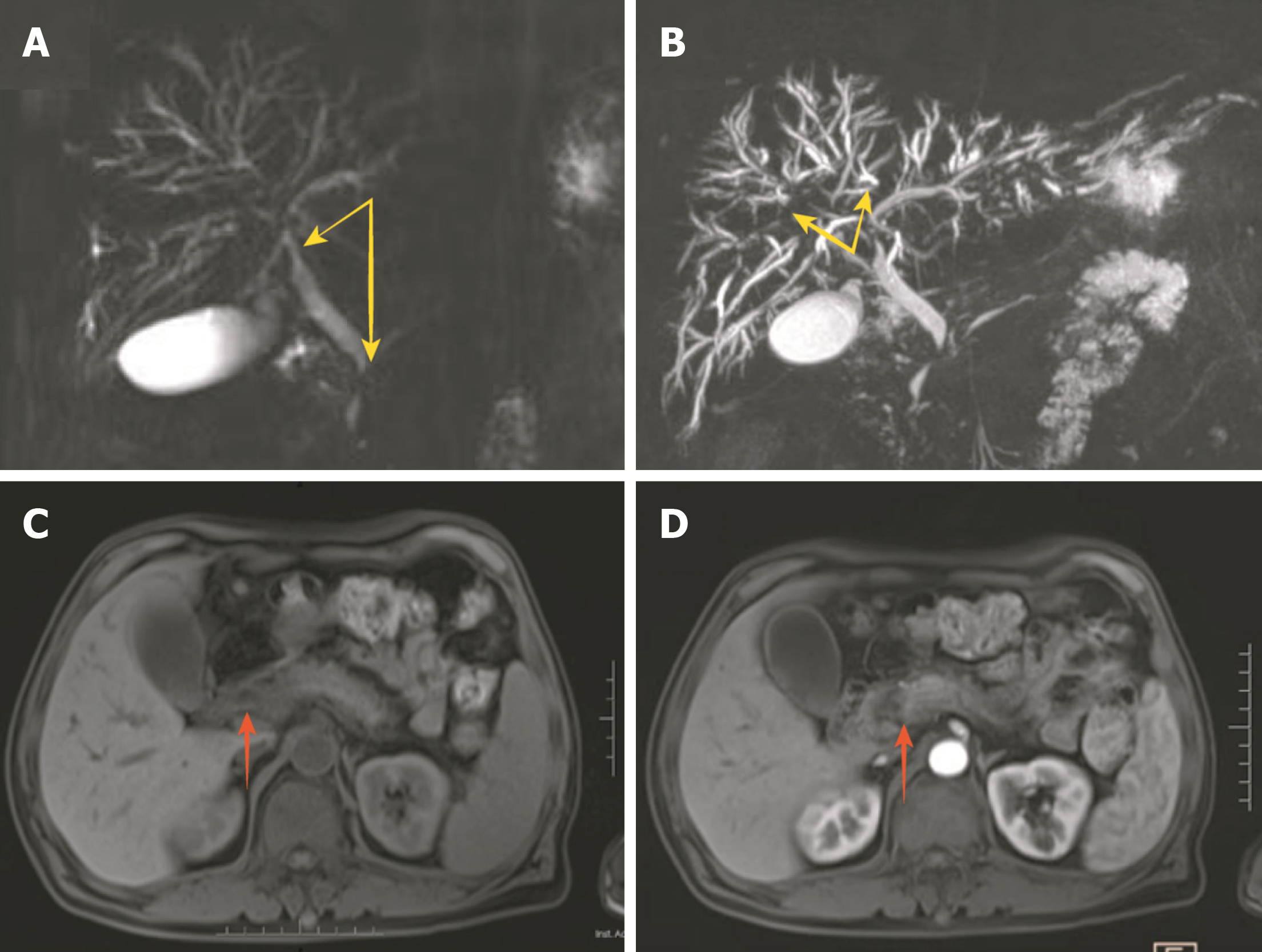
Figure 1 Magnetic resonance imaging of the bile ducts.
A and B: Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography revealed dilation of the intrahepatic bile duct and local narrowing in the bilateral hepatic duct, common hepatic duct, and lower segment of the common bile duct (yellow arrows); C and D: Plain and enhanced magnetic resonance imaging showed an enlarged pancreatic head. Possible local inflammation was, but there was no delayed enhancement (red arrows).
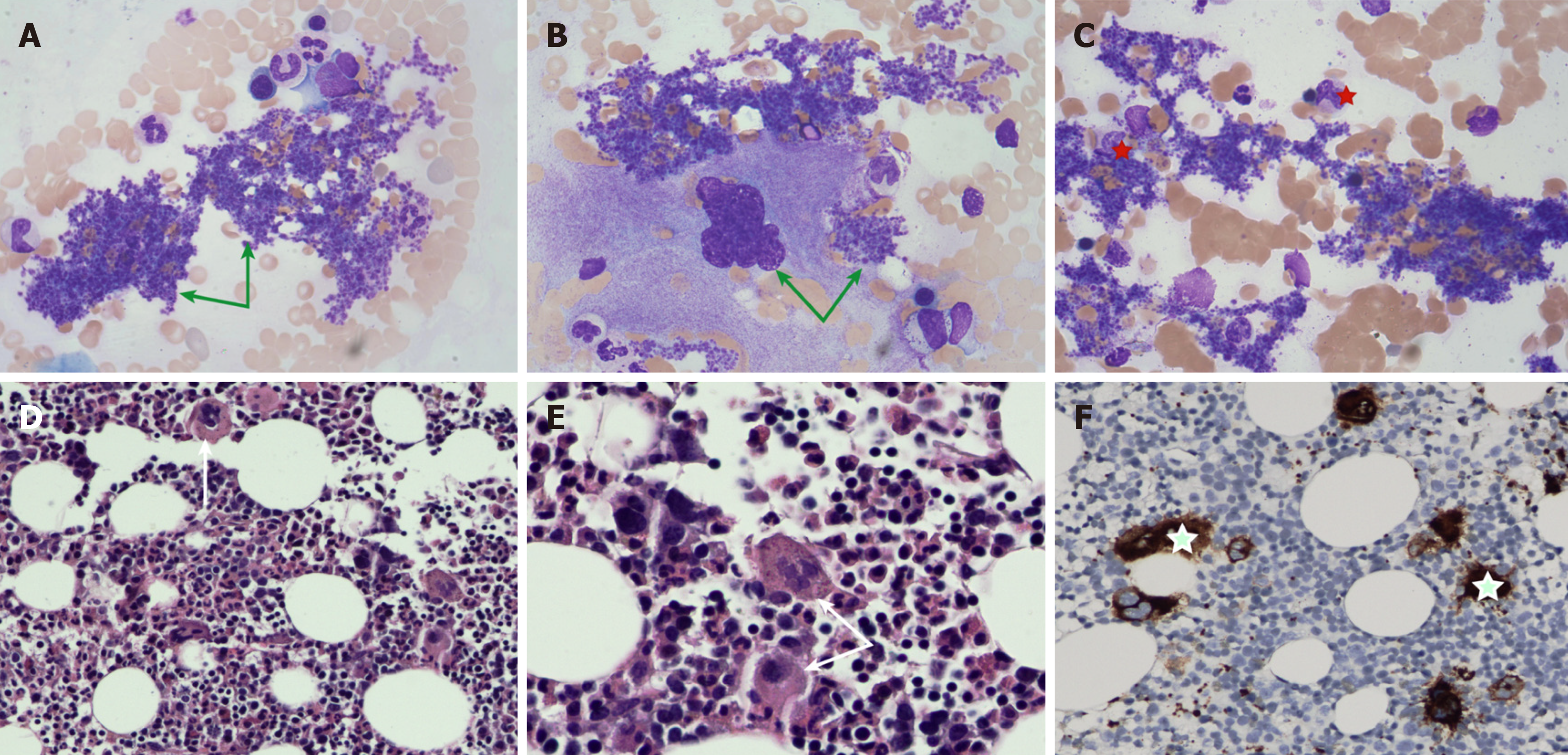
Figure 2 Bone marrow examination.
A and B: Platelets existed in the form of piles and pieces in the peripheral blood smear and bone marrow smear (green arrows); C: Proplatelet-producing megakaryocytes were markedly increased in the bone marrow smear (red five-pointed star); D and E: The number of megakaryocytes was significantly elevated, especially megakaryocytes with large cell bodies and hyperlobated nuclei, and they were isolated or arranged in dense clusters (reticular fibrosis grade of MF-1) (Hematoxylin-eosin staining: 200 times, 400 times) (white arrows); F: CD61 immunohistochemistry was also positive on megakaryocytes (green five-pointed star).
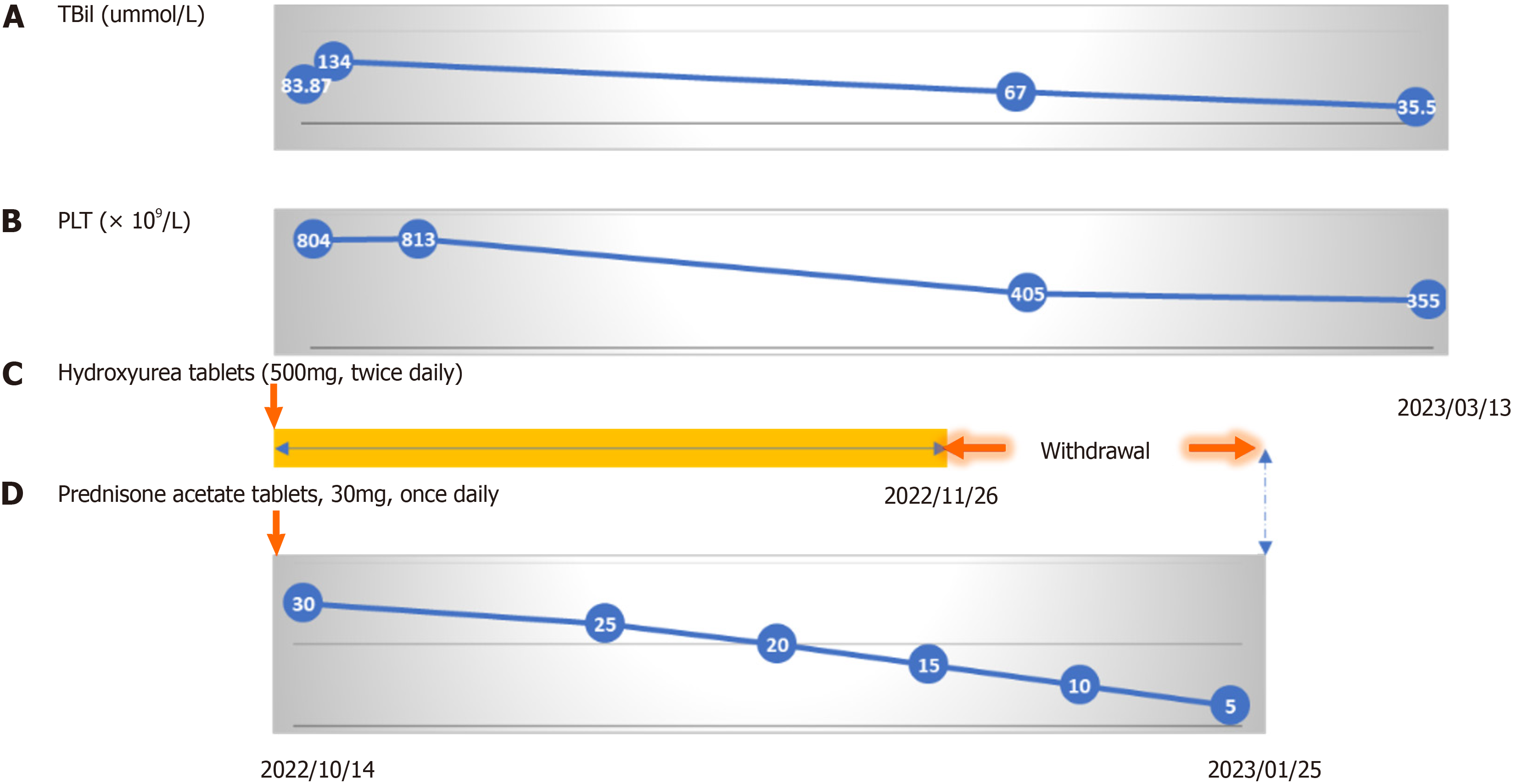
Figure 3 Follow-up procedure.
A and B: Changes in total bilirubin (TBIL) and platelets (PLT) in the patient during the treatment process; C: Hydroxyurea (500 mg 2/d) was self-discontinued after 1 mo; D: Acetate prednisone tablets were reduced by 5 mg after the first 2 wk, followed by a weekly reduction of 5 mg. The patient self-discontinued the medication after 3 mo of use.
- Citation: Wu ZN, JI R, Xiao Y, Wang YD, Zhao CY. IgG4-related sclerosing cholangitis associated with essential thrombocythemia: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(24): 5589-5595
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i24/5589.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i24.5589