Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2024; 12(23): 5422-5430
Published online Aug 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i23.5422
Published online Aug 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i23.5422
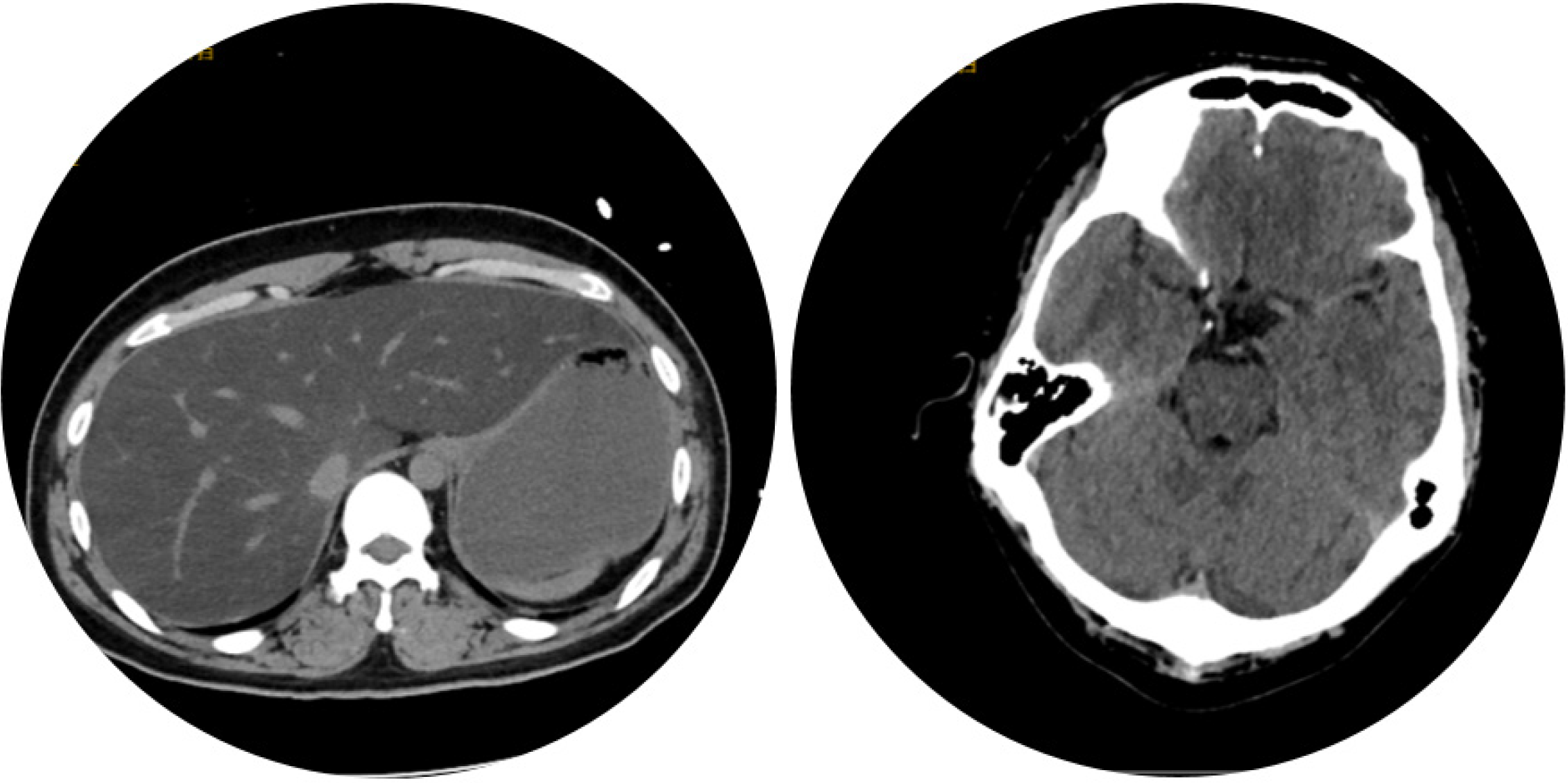
Figure 1
Computer tomography indicted severe fatty liver and sallow cerebral sulci.
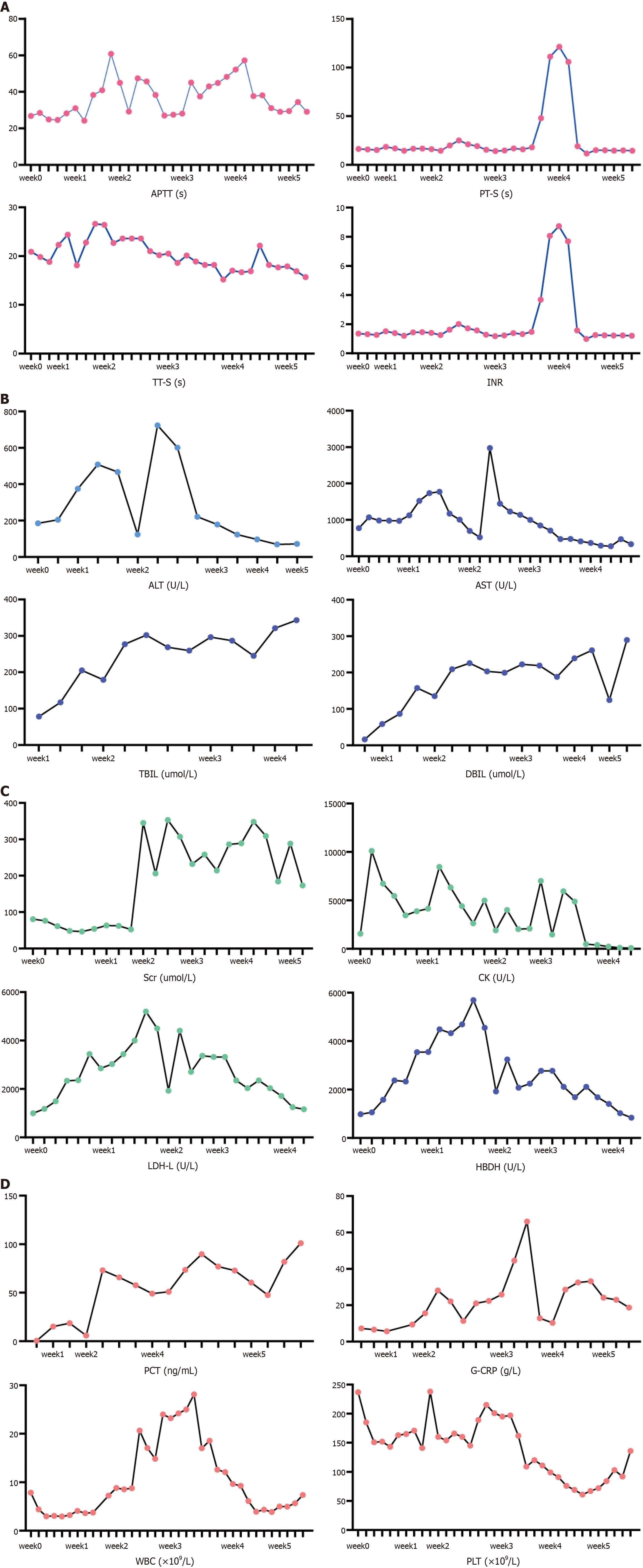
Figure 2 Changes of clinical biochemistry after treatment.
A: Coagulation system: levels of thromboplastin time (APTT), thrombin time (TT), prothrombin time (PT) and international normalized ratio (INR); B: Liver function: levels of alanine transaminase (ALT), aspartic transaminase (AST), direct bilirubin (DBIL), indirect bilirubin (IBIL); C: Kidney function and myolysis: levels of serum creatinine (Scr), creatine kinase (CK), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH-L), hydroxybutyrate dehydrogenase (HBDH); D: Infection indicators: levels of procalcitonin (PCT), high sensitive C-reactive protein (CRP), white blood cells (WBC), platelets (PLT).
- Citation: Li XX, Yang XN, Pan HD, Liu L. Fatal multiple acyl-CoA dehydrogenase deficiency caused by ETFDH gene mutation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(23): 5422-5430
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i23/5422.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i23.5422