Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 16, 2024; 12(23): 5354-5365
Published online Aug 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i23.5354
Published online Aug 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i23.5354
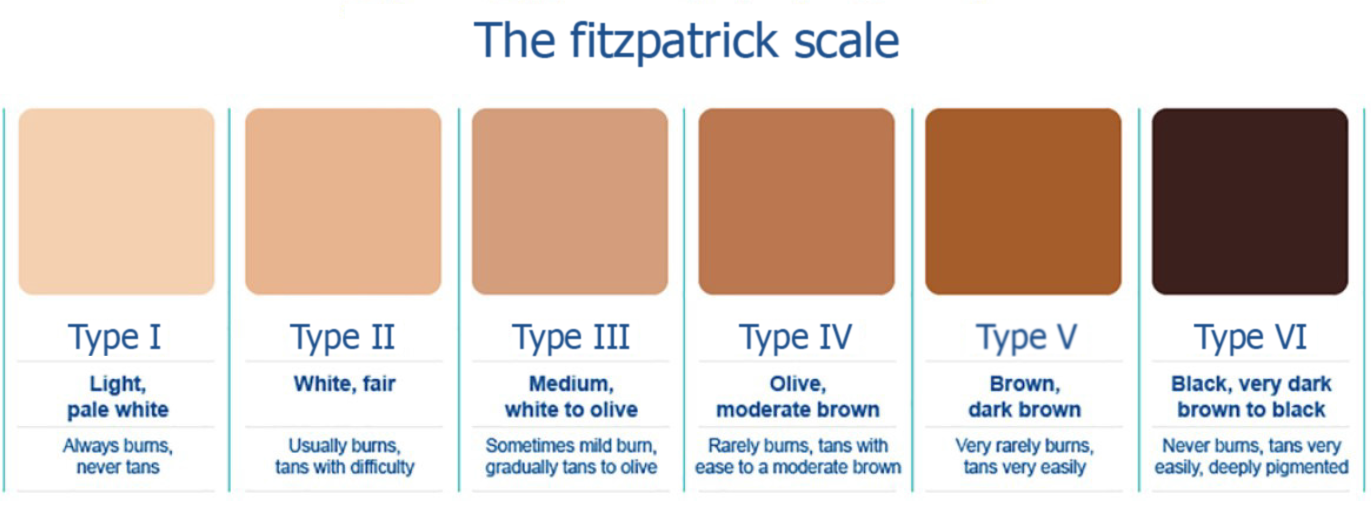
Figure 1
Fitzpatrick scale.
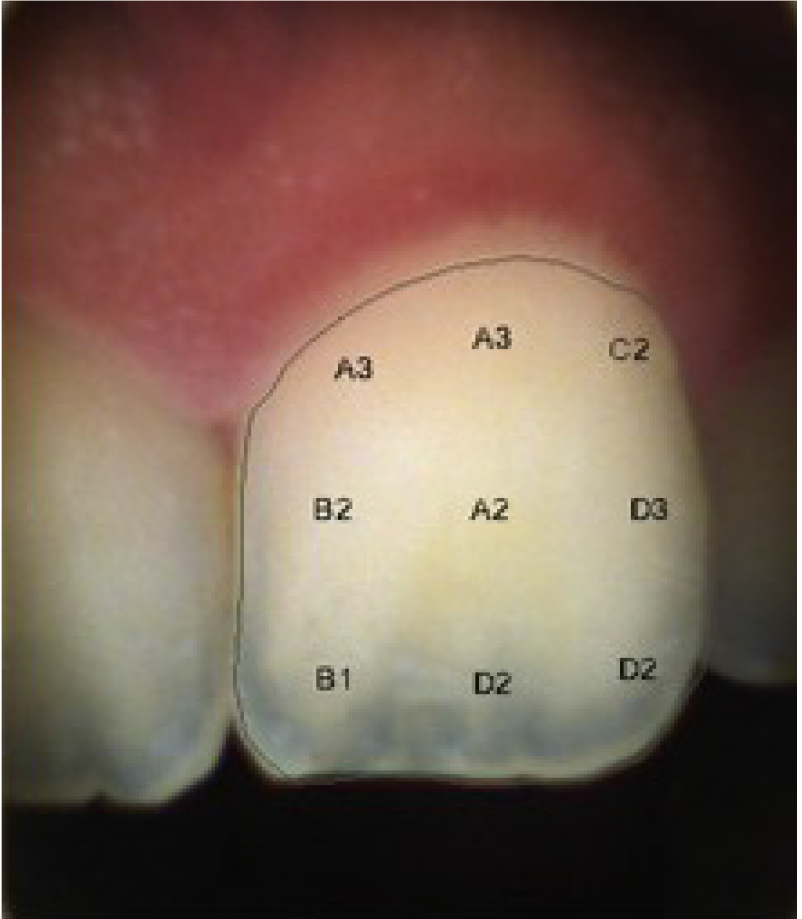
Figure 2
Representative image for digital shade mapping using digital shade detector “Ray Plicker”.
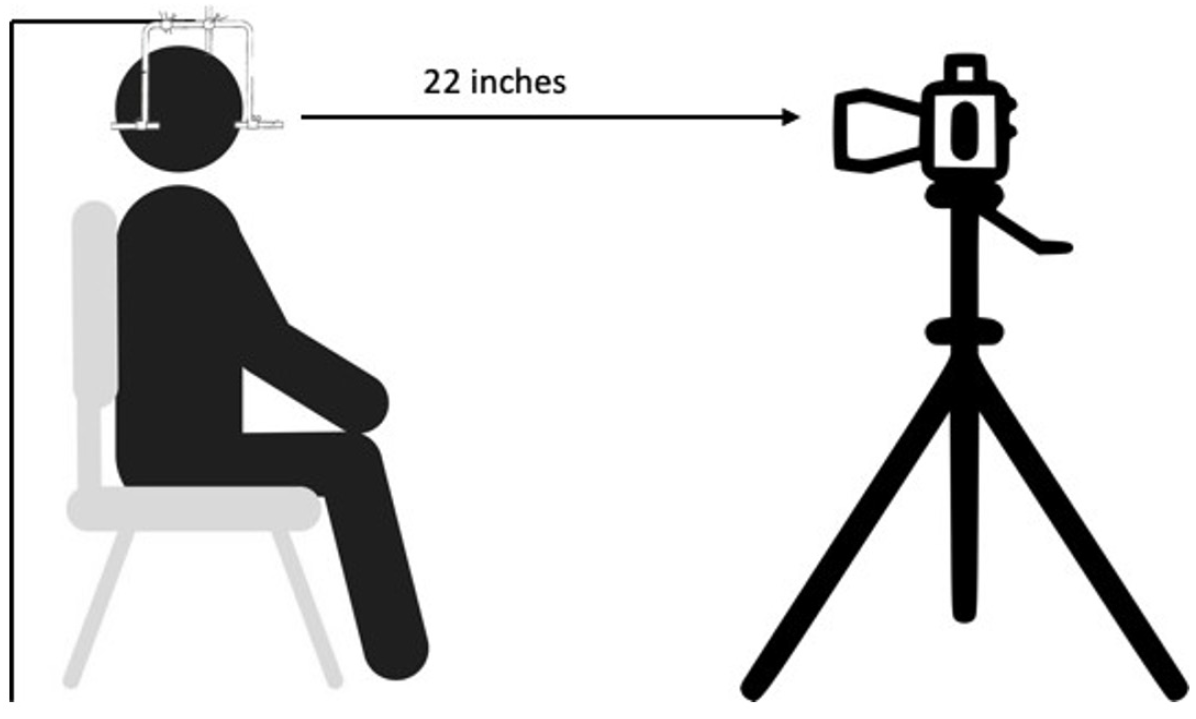
Figure 3
Patient position in reference to camera.
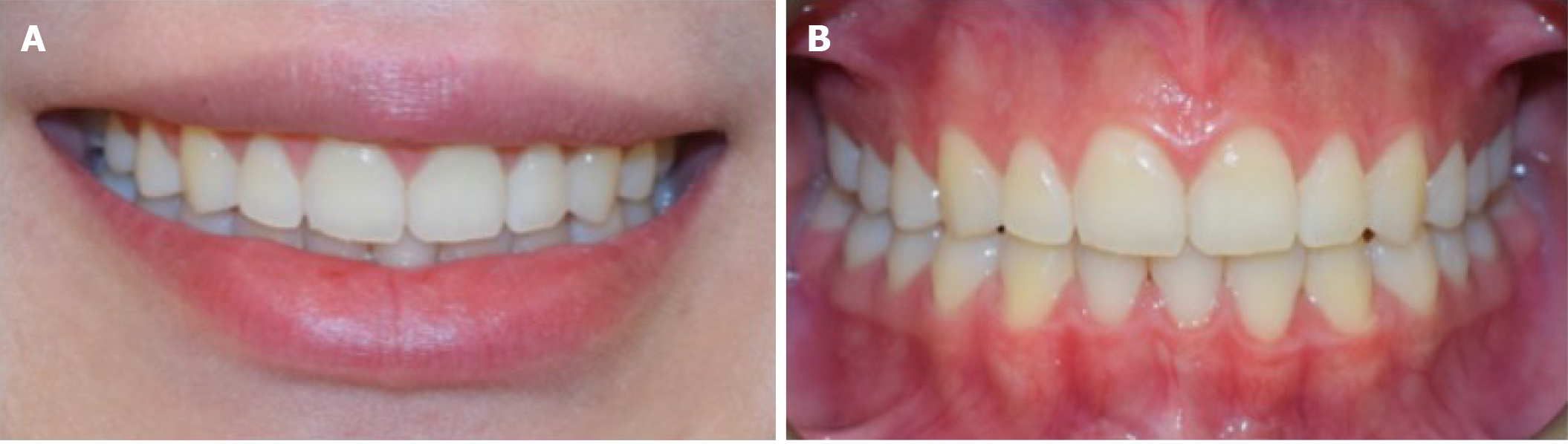
Figure 4 Frontal views.
A: Smiling with lips; B: Smiling with retracted lips.
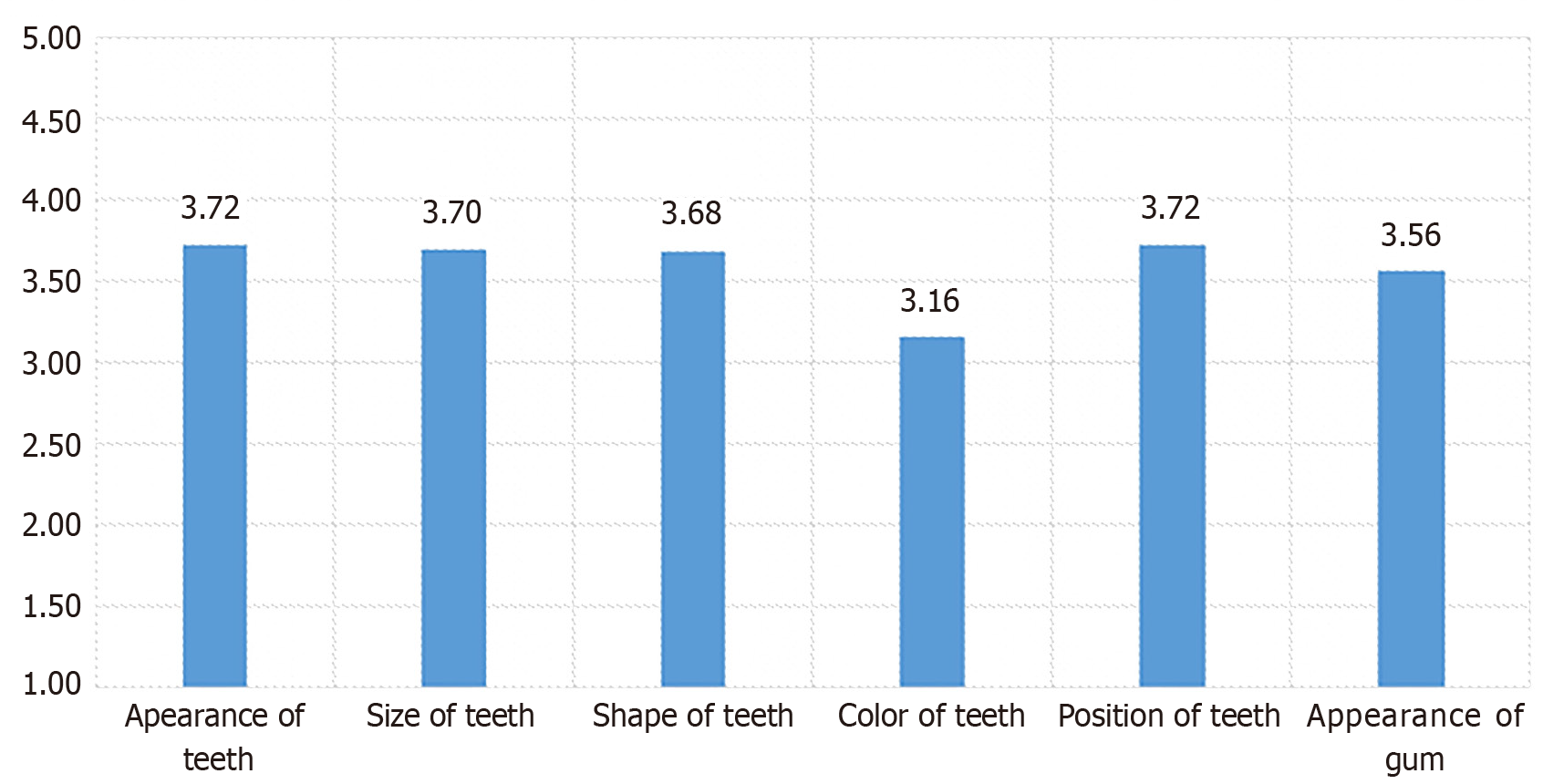
Figure 5
Patients' mean response scores for satisfaction about dental appearance.
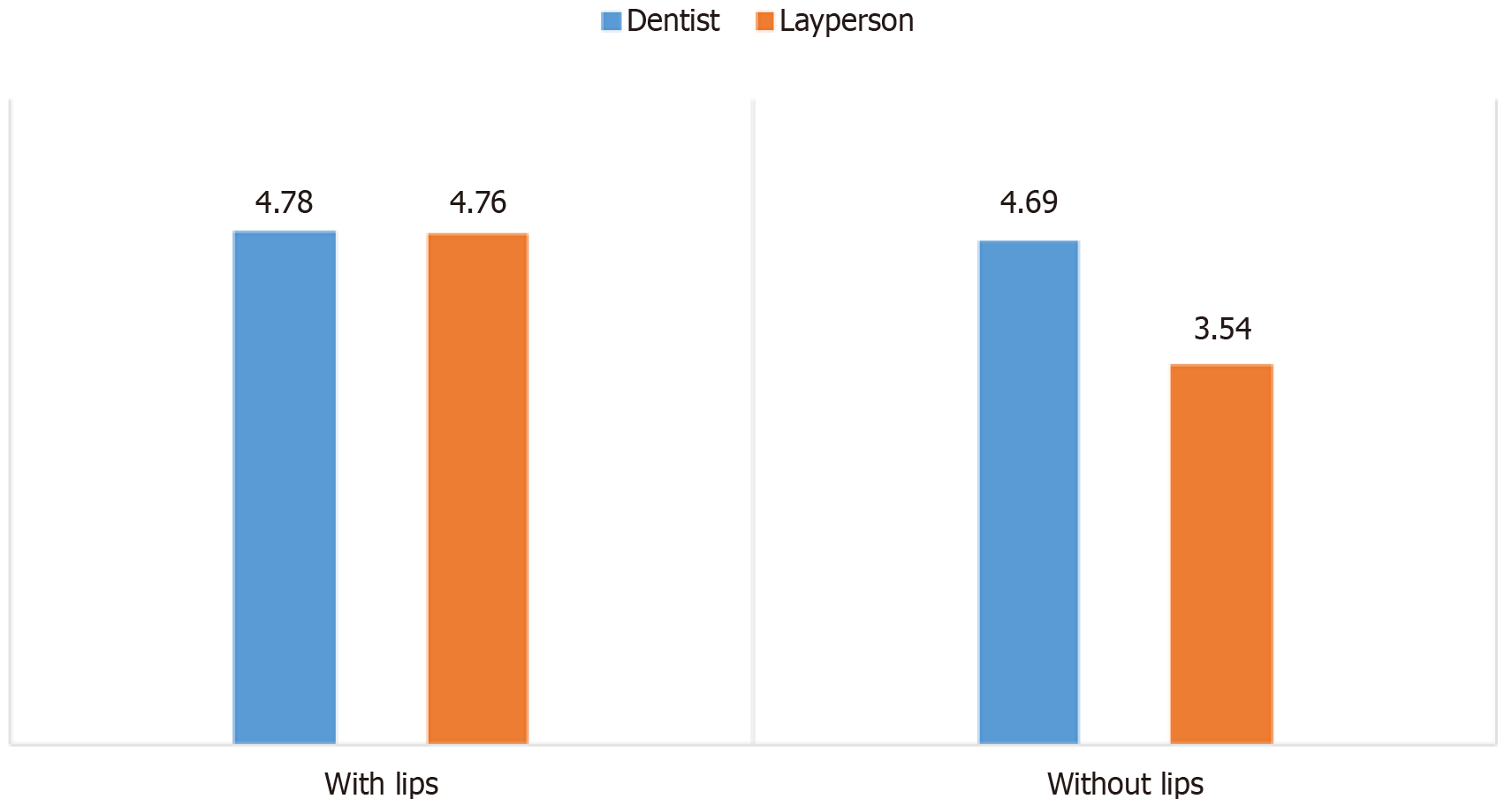
Figure 6
Comparison between dentist and laypersons mean score for pictures with lips and without lips.
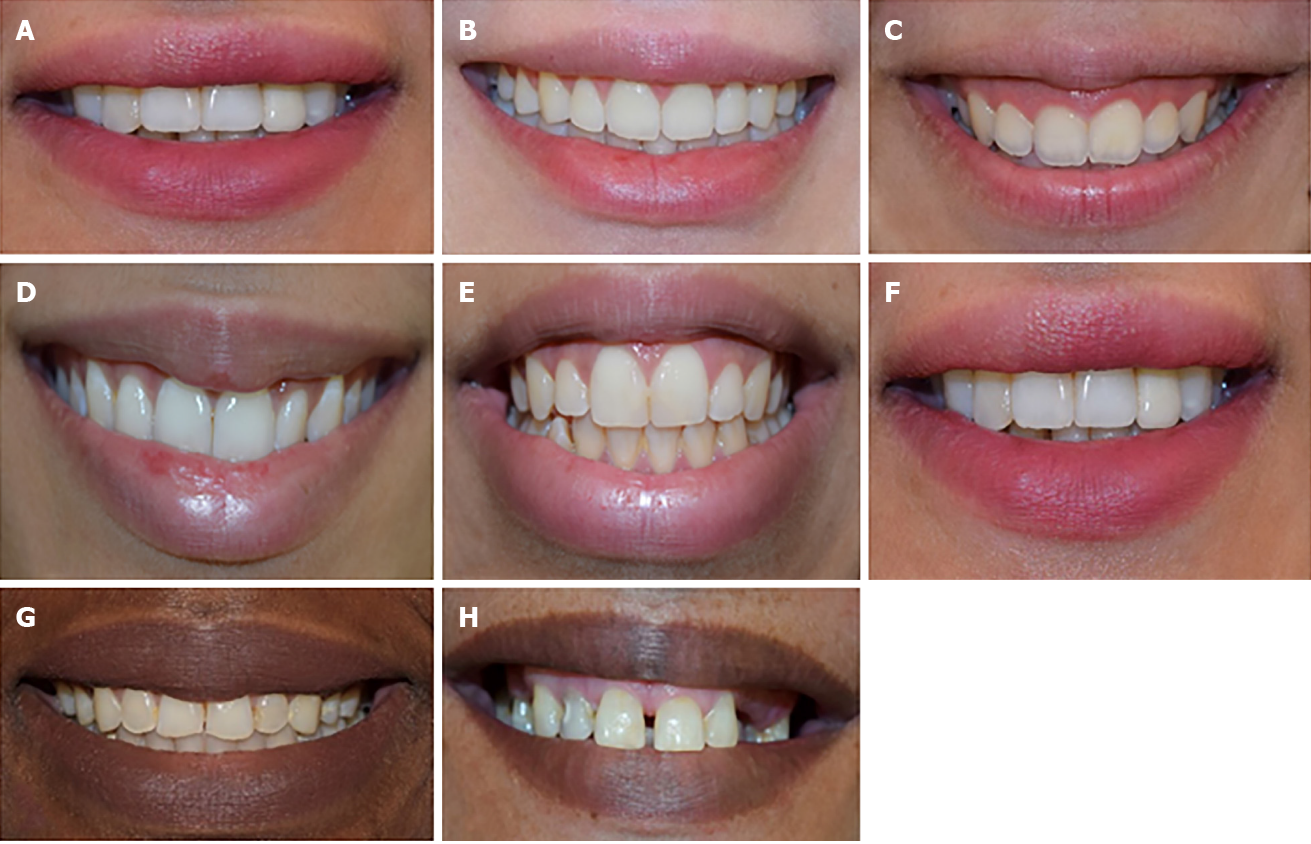
Figure 7 Extra-oral photograph.
A: Average upper lip position, straight upper lip curvature, coincident between upper inter-incisal line and midline, normal buccal corridor, occlusal plane parallel to the commissural line; B: Low upper lip position, straight smile arc, narrow smile line width; C: High upper lip position, the bottom line of the upper teeth formed a consistent curve with the lower lip; D: Upward upper lip curvature; E: Downward upper lip curvature, midline discrepancy to the right, intermediate smile line width; F: Midline discrepancy to the left; G: Proper dental midline coincidence, the bottom line of the upper teeth does not form a consistent curve with the lower lip, wide smile line width; H: Diastema between their central incisors.
- Citation: Aldegheishem A, Alfayadh HM, AlDossary M, Asaad S, Eldwakhly E, AL Refaei NAH, Alsenan D, Soliman M. Perception of dental appearance and aesthetic analysis among patients, laypersons and dentists. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(23): 5354-5365
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i23/5354.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i23.5354