Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2024; 12(22): 5016-5023
Published online Aug 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5016
Published online Aug 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5016
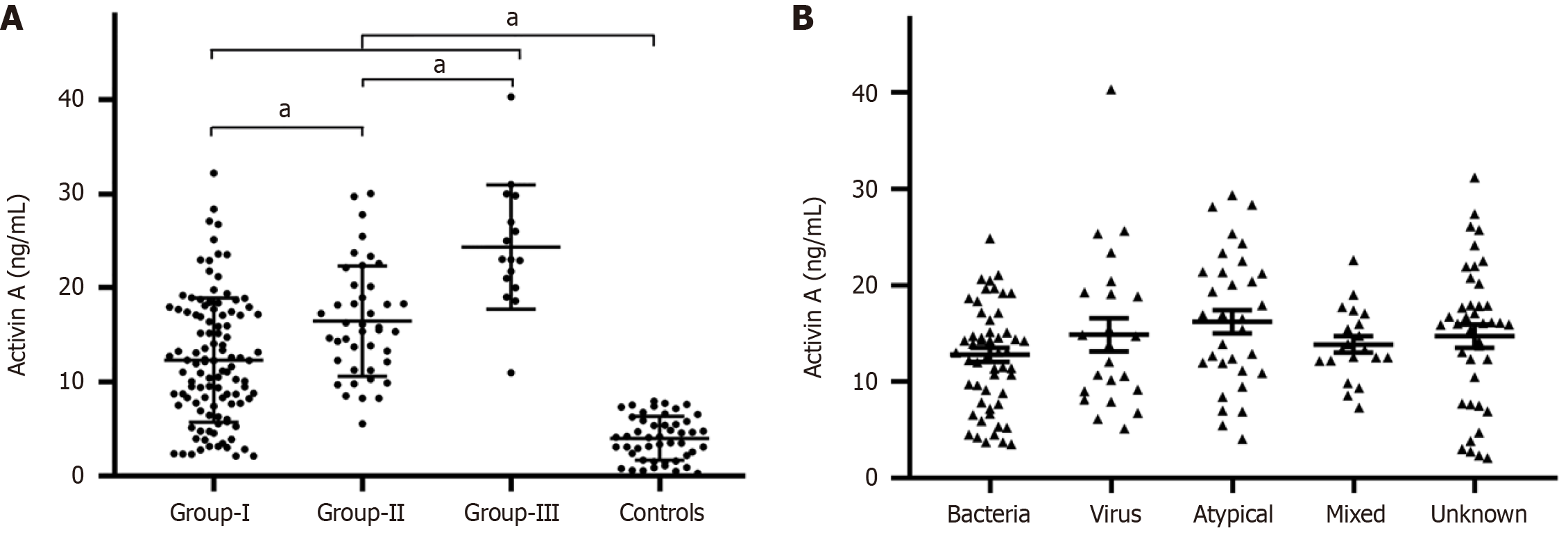
Figure 1 Serum levels of activin A in enrolled individuals.
A: Serum activin A level distribution in different multiple groups and healthy volunteers, aP < 0.05; B: Serum activin A level distribution in different causative etiologies of community-acquired pneumonia in the study patients.
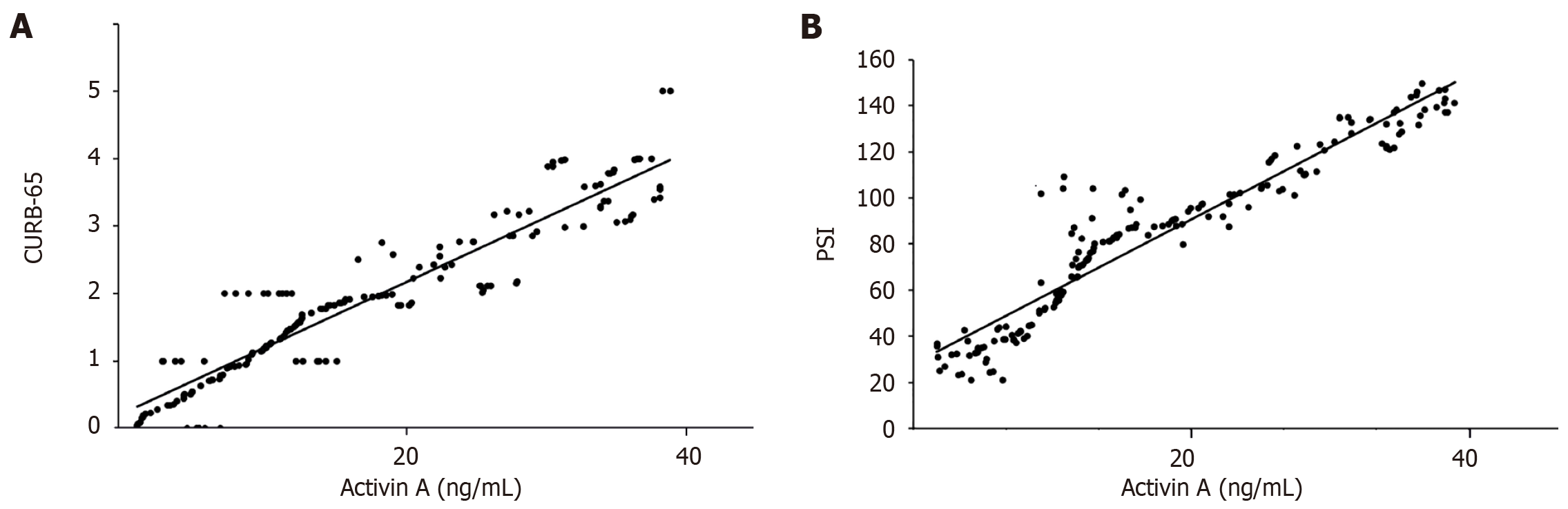
Figure 2 Correlation between serum activin A levels and biomarkers in different groups of community-acquired pneumonia.
A: Positive correlation between activin A and CURB-65 scores in patients; B: Positive correlation between activin A and Pneumonia Severity Index scores in patients.
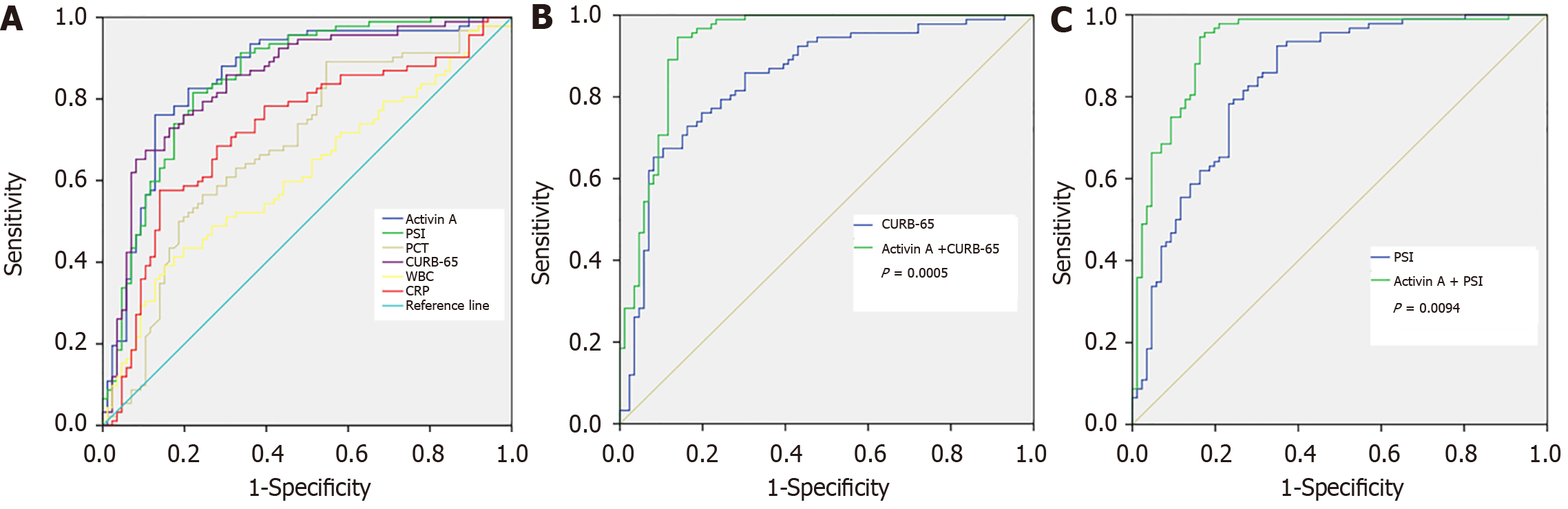
Figure 3 Receiver operating curve analysis for serum activin A concentrations to predict hospital mortality.
A: Area under the receiver operating curve [areas under the curve (AUC)] for the biomarkers evaluated in this study; B: AUC of combination of activin A and CURB-65 or CURB-65 alone, P = 0.0005; C: AUC of combination of activin A and Pneumonia Severity Index (PSI) or PSI alone, P = 0.0094.
- Citation: Wang YT, Liu Y, Zhou GH, Liu K, Fen Y, Ding H. Serum activin A as a prognostic biomarker for community acquired pneumonia. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(22): 5016-5023
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i22/5016.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.5016