Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Aug 6, 2024; 12(22): 4983-4991
Published online Aug 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.4983
Published online Aug 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.4983
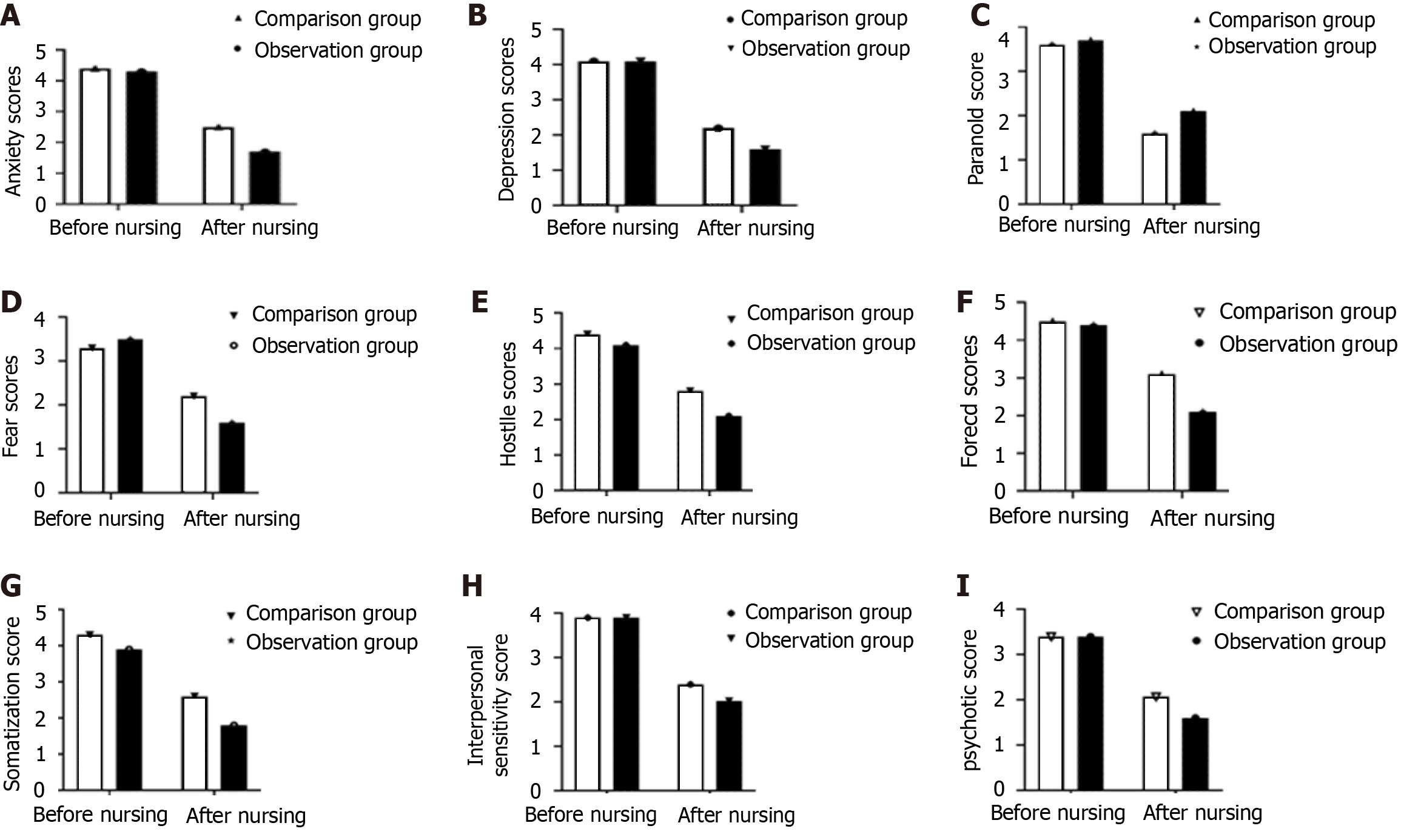
Figure 1 Comparison of negative emotions.
A-I: According to the test standard of α = 0.05, the differences in the Symptom Check List-90 scores of the two groups of patients before nursing were similar, but after nursing, the anxiety score (A), depression score (B), fear score (D), hostility score (E), obsessional score (F), somatization score (G), interpersonal sensitivity score (H), and psychotic score (I) were lower in the observation group than in the control group, while the paranoia score (C) in the observation group was higher than that of the control group. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD, and independent samples t test was used for analysis. The prealbumin (PAB), Tet-responsive element (TRE), and albumin (ALB) in the observation group were lower than those of the control group (P < 0.05).
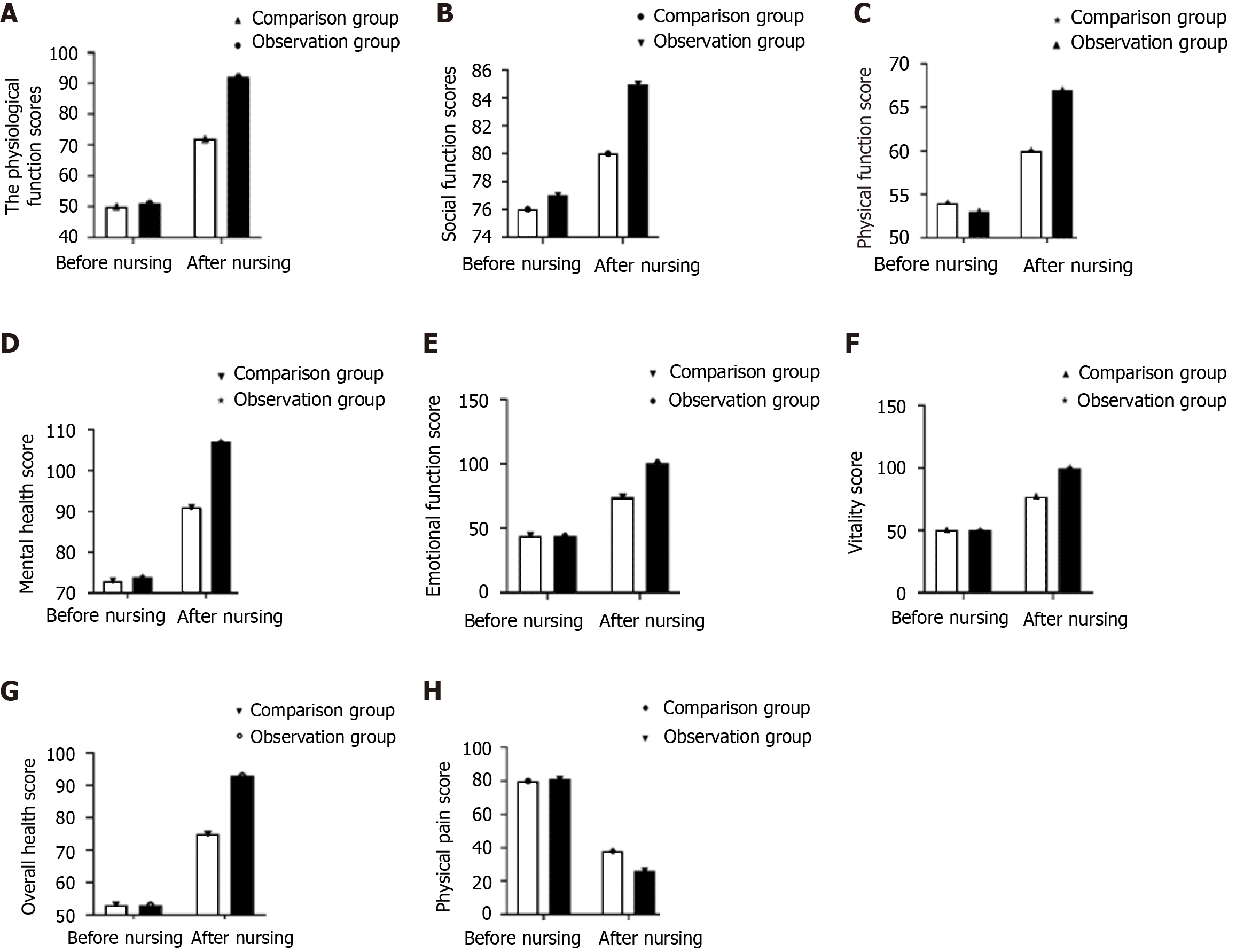
Figure 2 Comparison of quality of life scores.
A-H: According to the test standard of α = 0.05, the difference in the quality of life scores of the two groups before nursing was similar, but after nursing, the physiological function scores (A), social function scores (B), physical function score (C), mental health score (D), emotional function score (E), vitality score (F), and overall health score (G) was significantly higher in the observation group than in the control group, while the physical pain score of the observation group (H) was lower than that of the control group. Values are expressed as the mean ± SD, and independent sample t test was used for analysis. After nursing, the physical function score, social functional score, physical function score, mental health score, emotional function score, vitality score, and overall health score were significantly higher in the observation group than in the control group, while the physical pain score in the observation group was lower than that of the control group (P < 0.05).
- Citation: Li YQ, Liu Y, Peng ZQ, Fang R, Xu HY. Enhanced recovery after surgery-based nursing in older patients with postoperative intestinal obstruction after gastric cancer surgery: A retrospective study. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(22): 4983-4991
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i22/4983.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i22.4983