Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 26, 2024; 12(21): 4527-4535
Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4527
Published online Jul 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4527
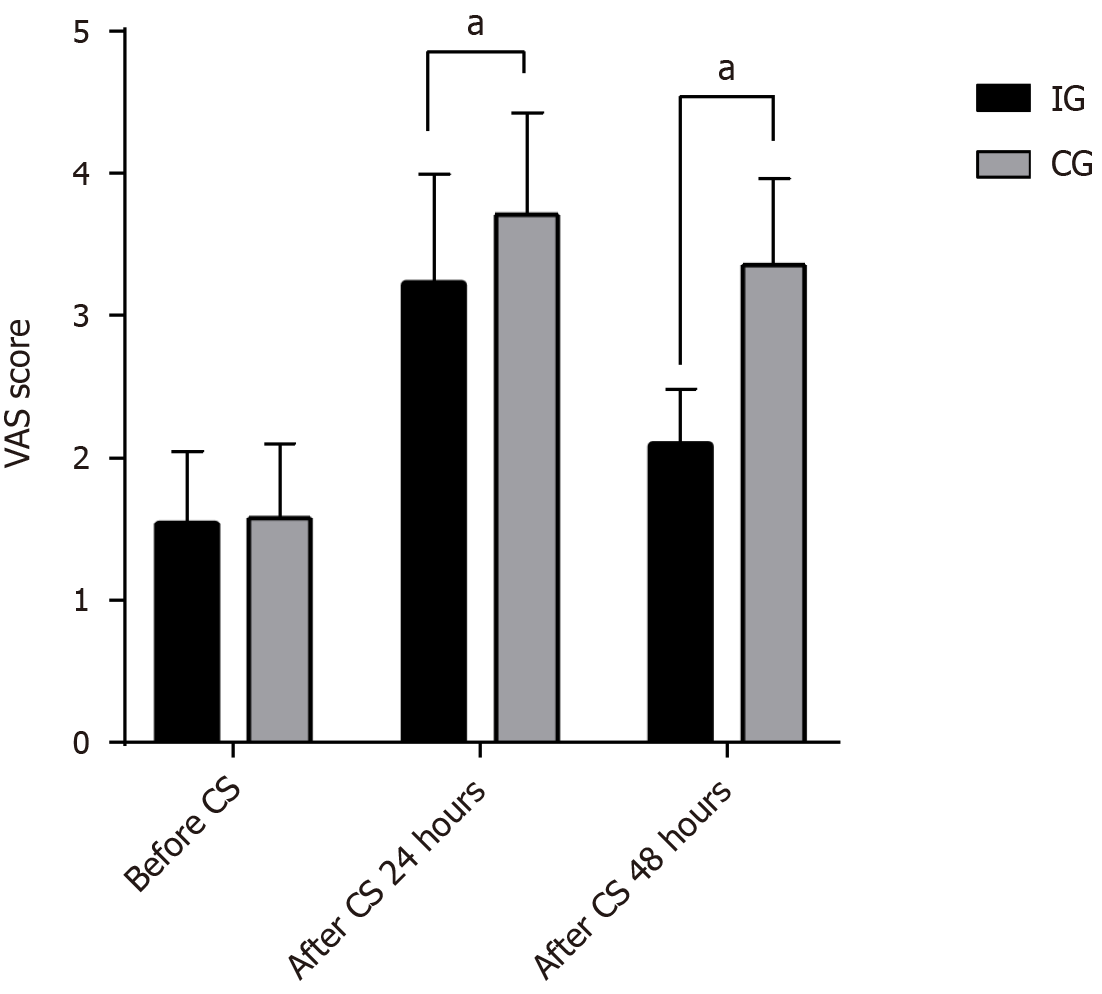
Figure 1 Comparison of the pain visual analogue scale between intervention group and control group.
aAfter cesarean section (CS) of control group with after CS of intervention group. CS: Cesarean section; CG: Control group; IG: Intervention group; VAS: Visual analogue scale.
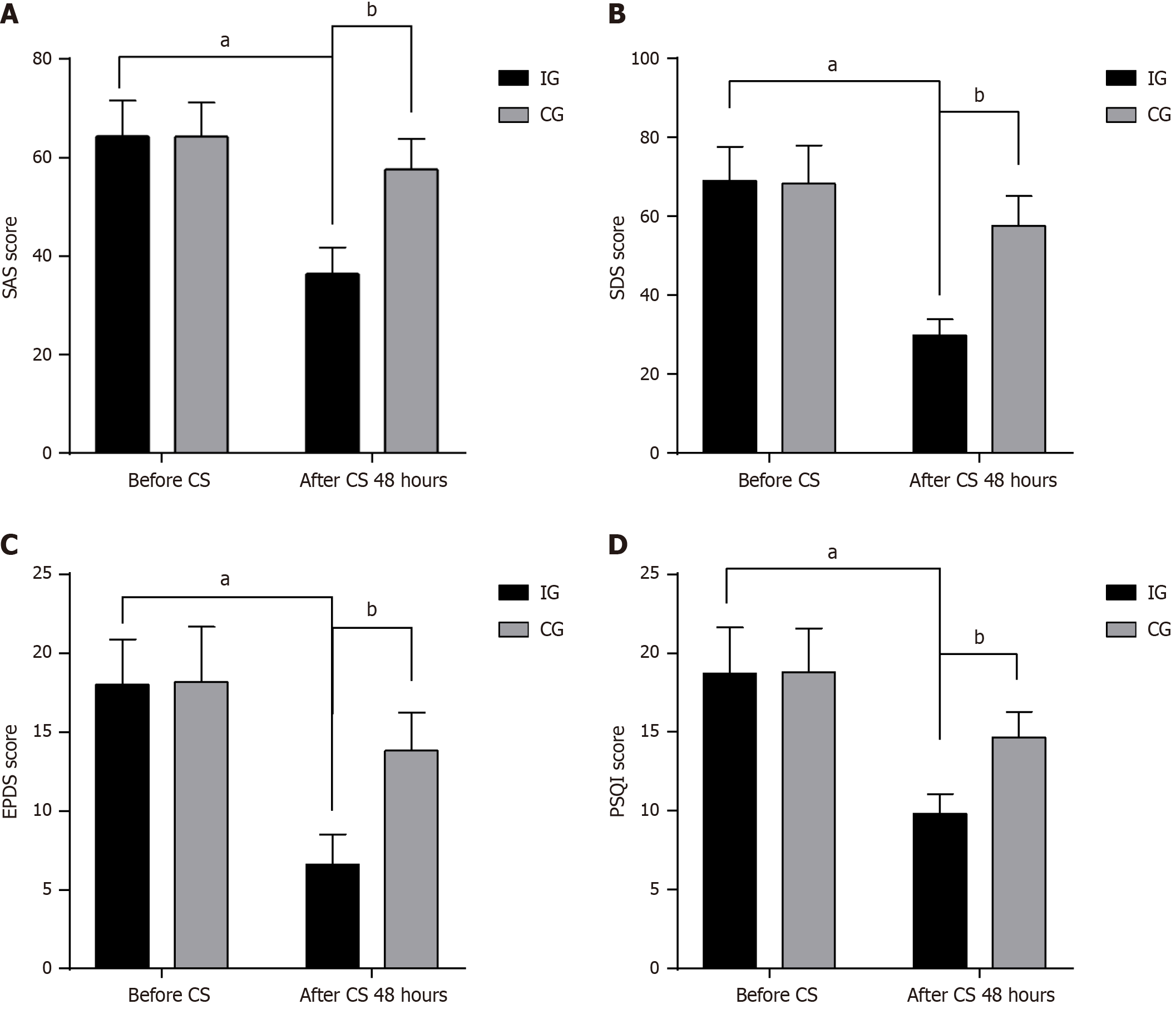
Figure 2 Comparison of postoperative negative emotions and sleeping quality between intervention group and control group.
A: The self-rating anxiety scale; B: The depression self-rating scale; C: The Edinburgh postpartum depression scale; D: The Pittsburgh sleep quality index. aAfter cesarean section (CS) of control group (CG) with After CS of intervention group (IG). bAfter CS of IG with before CS of IG. CS: Cesarean section; CG: Control group; IG: Intervention group; SAS: Self-rating anxiety scale; SDS: Self-rating depression scale; EPDS: Edinburgh postpartum depression scale; PSQI: Pittsburgh sleep quality index.
- Citation: Liu XY, Chen XB, Wen YL, Guo XP, Zhou XB. Effect of psychological nursing intervention combined with acupressure on postoperative recovery of women after cesarean section. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(21): 4527-4535
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i21/4527.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i21.4527