Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 16, 2024; 12(20): 4180-4190
Published online Jul 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4180
Published online Jul 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4180
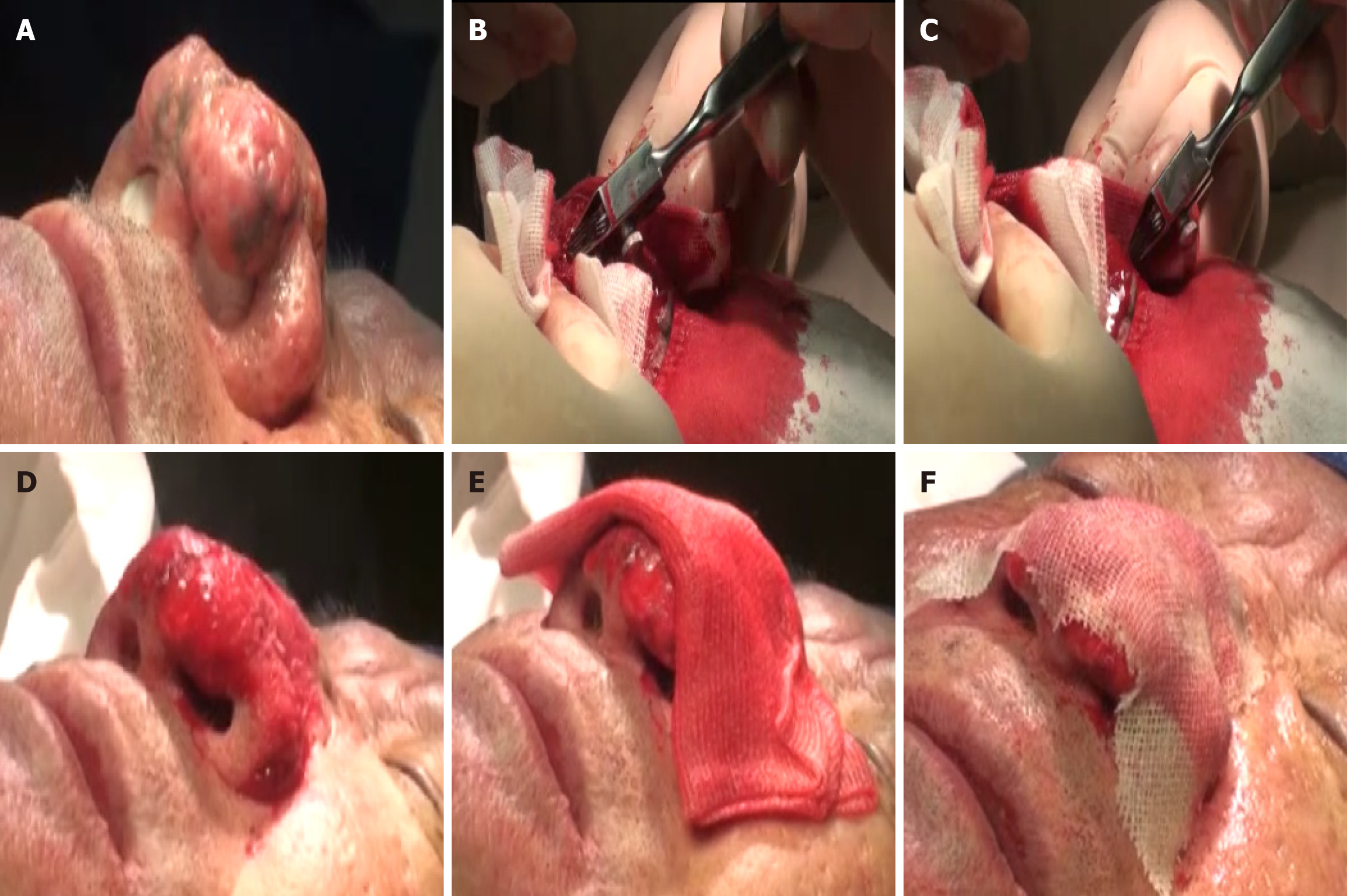
Figure 1 Surgical procedure.
A: Dry cotton balls were used to plug the nostrils to prevent blood from flowing into them; B and C: Performing criss-cross scratching using a five-blade scratcher; D: The final wound surface resembled that of a strawberry; E: Ice saline coverage; F: Covering the wound with petrolatum gauze.
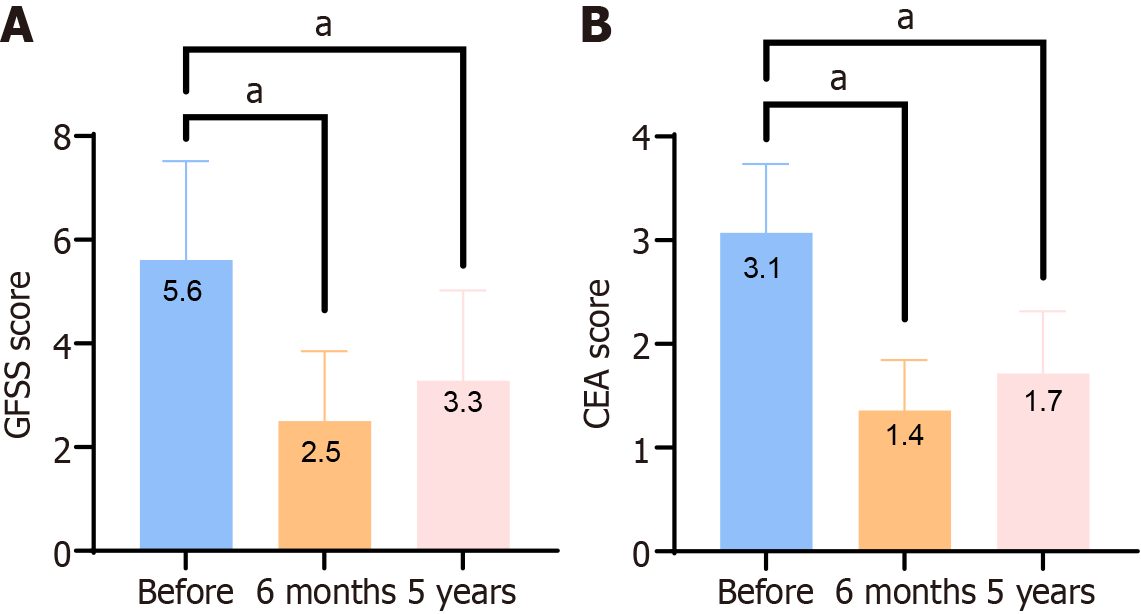
Figure 2 Evaluation of therapeutic effect.
A: Changes in mean Global Flushing Severity Score (GFSS) scores before and after five-blade scratcher treatment; B: Changes in mean GFSS scores before and after five-blade scratcher treatment. GFSS and Clinician Erythema Assessment scores significantly decreased at 6 months and 5 years postoperatively. aP < 0.001, the difference was statistically significant. GFSS: Global Flushing Severity Score; CEA: Clinician Erythema Assessment.
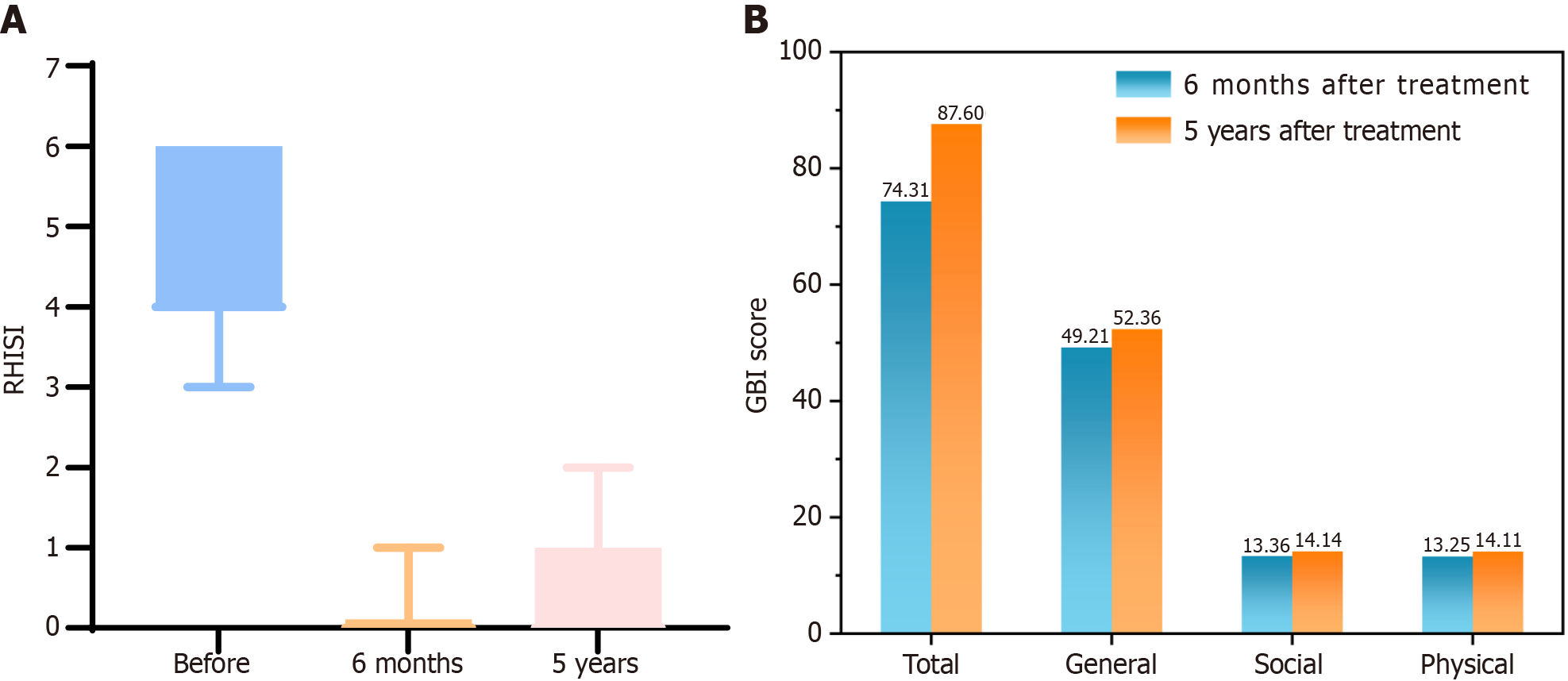
Figure 3 Evaluation of Rhinophyma Severity Index and Glasgow Benefit Inventory scores.
A: Changes in Rhinophyma Severity Index (RHISI) scores after five-blade scratcher treatment; B: Changes in Glasgow Benefit Inventory scores after five-blade scratcher treatment. The RHISI scores at 6 months and 5 years postoperatively were significantly lower than before. Concurrently, five-blade scratcher treatment can benefit patients, and the benefit is more obvious 5 years postoperatively. RHISI: Rhinophyma Severity Index; GBI: Glasgow Benefit Inventory.
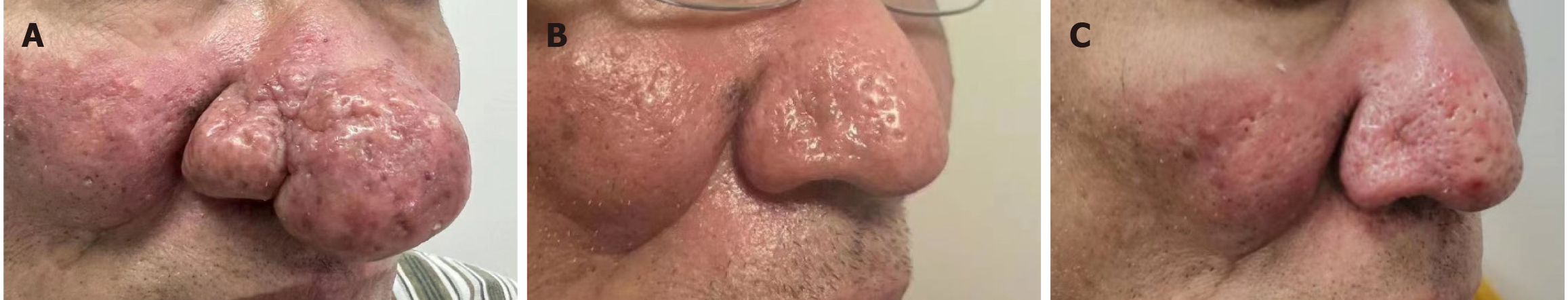
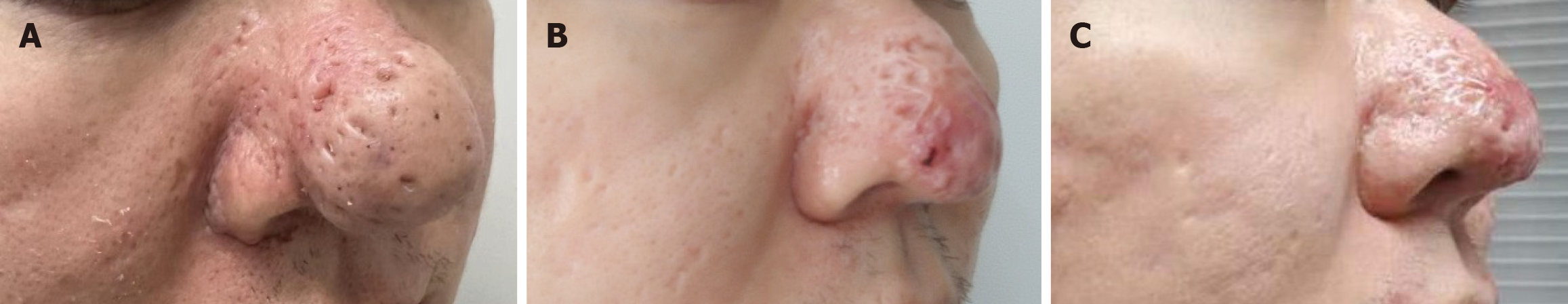
Figure 4 A 63-year-old male patient with severe rhinophyma with a 15-year course.
A: Preoperative photograph, taken on October 13, 2016; B: April 15, 2017, which is 6 months postoperatively; C: October 8, 2021, with a significant improvement observed.
Figure 5 A 33-year-old male patient with severe rhinophyma with a 10-year course.
A: Preoperative photograph, taken on December 20, 2016, B: June 18, 2017, which is 6 months postoperatively; C: December 20, 2021, with a marked improvement postoperatively.
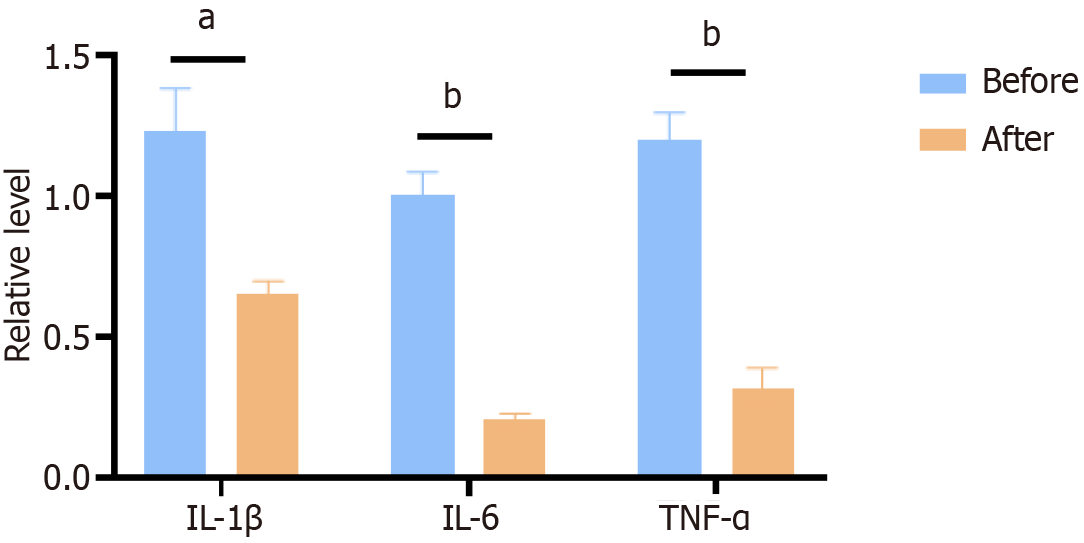
Figure 6 The level of inflammatory factors.
The level of IL-1β, IL-6 and TNF-α were detected in serum from before and after surgery groups by ELISA. The difference was statistically significant. aP < 0.05, bP < 0.001.
- Citation: Zheng YP, He XF, Zhang YF, Geng LX, Zhang HM, Wan H, He X. Five-blade scratcher for treating severe rhinophyma: A retrospective study. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(20): 4180-4190
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i20/4180.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i20.4180