Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2024; 12(19): 4010-4015
Published online Jul 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.4010
Published online Jul 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.4010
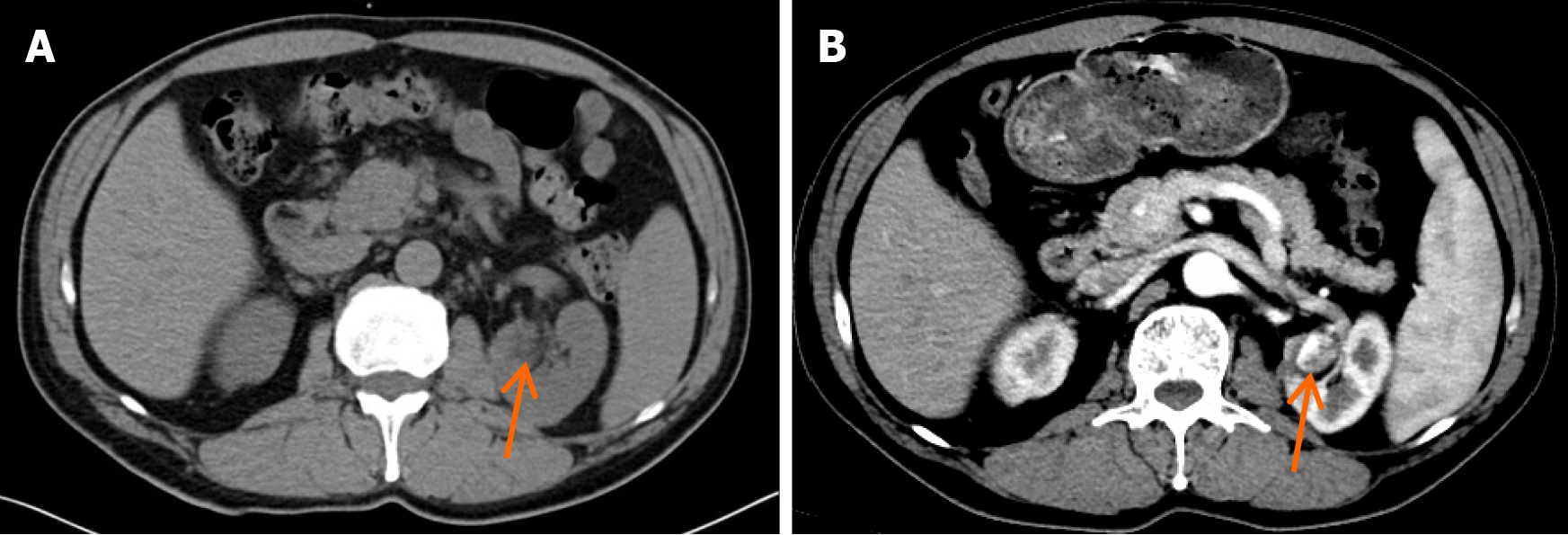
Figure 1 Computed tomography images of anastomosing hemangioma in the left kidney.
A: Conventional computed tomography (CT) revealed a low-density nodule (arrow) in the left kidney; B: Contrast-enhanced CT showed an unevenly enhanced nodule in the left kidney.
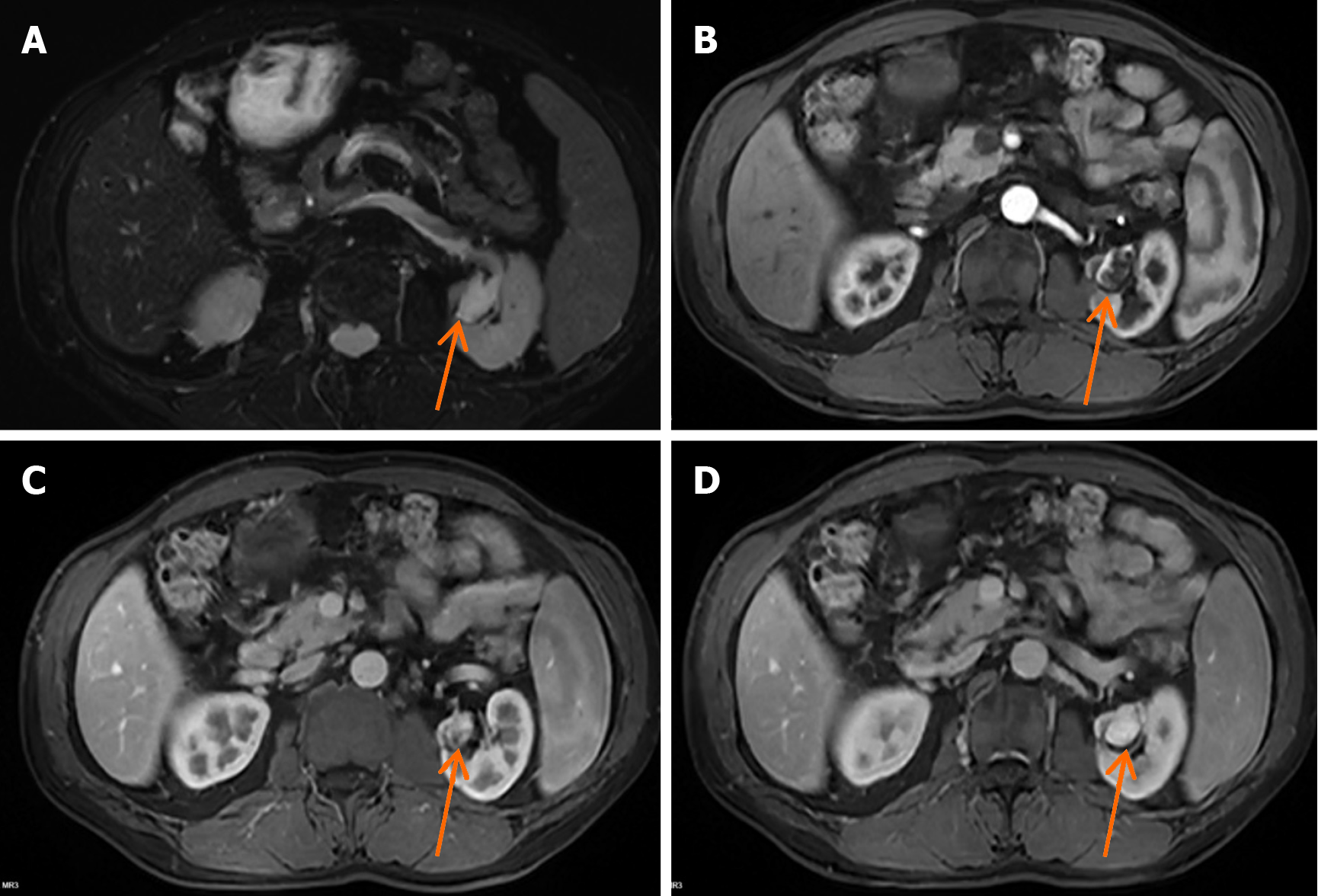
Figure 2 Magnetic resonance imaging images of the anastomosing hemangioma in the left kidney.
A: A renal lesion (arrow) presented with high signal intensity on T2-weighted imaging; B: Arterial phase image of the left renal nodule (arrow) on contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance imaging (MRI); C: Venous phase image of the left renal nodule (arrow) on contrast-enhanced MRI; D: Delayed phase contrast-enhanced MRI image of the left renal nodule (arrow).
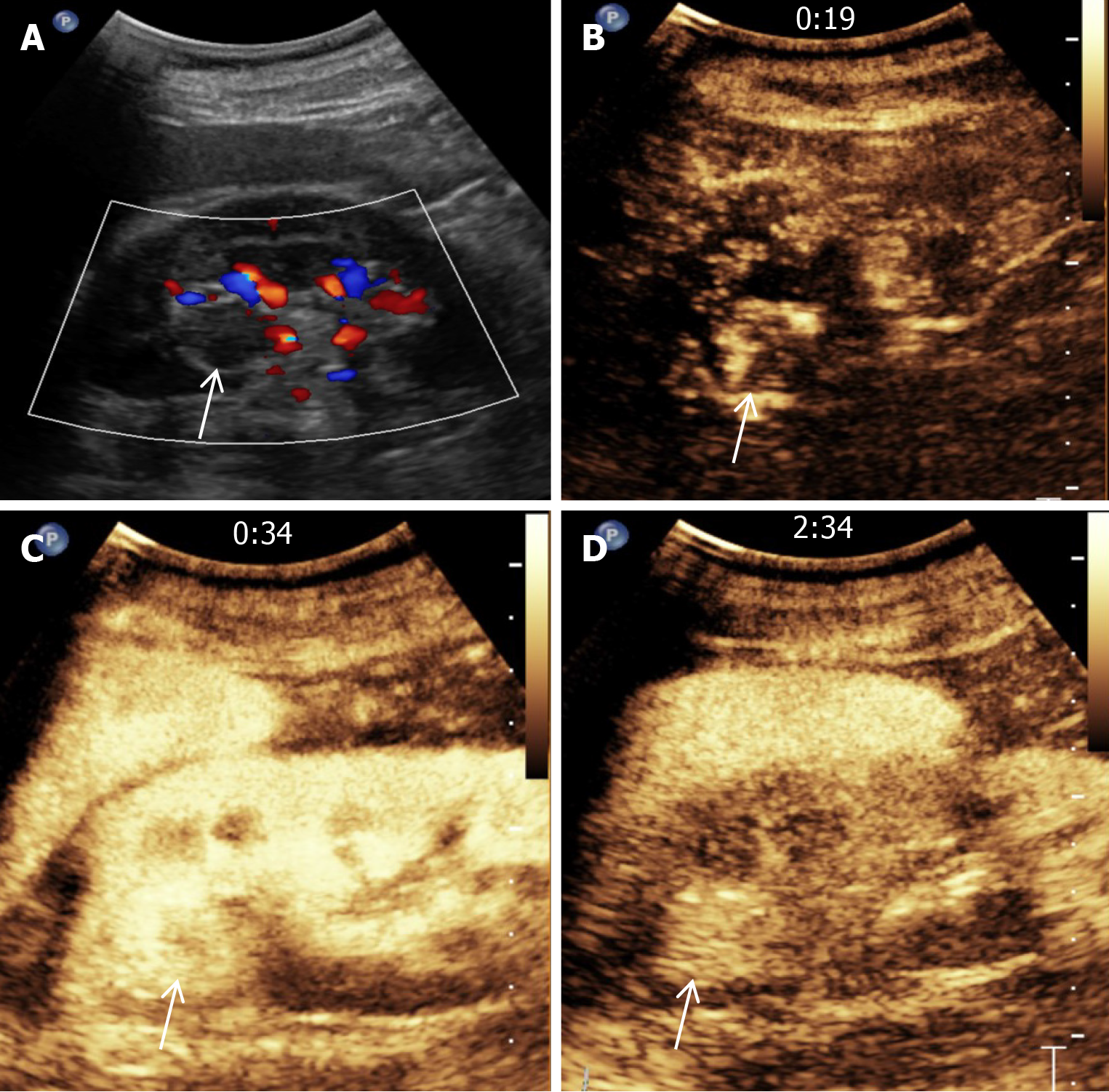
Figure 3 Ultrasonography images of the anastomosing hemangioma in the left kidney.
A: Color doppler flow imaging finding of the renal lesion (arrow); B: Ultrasound image of the left renal nodule at the 19 second after the injection of contrast agent; C: Ultrasound image of the left renal nodule at 34 s after the injection of the contrast agent; D: Ultrasound image of the left renal nodule at 2 min and 34 s after the injection of contrast agent.
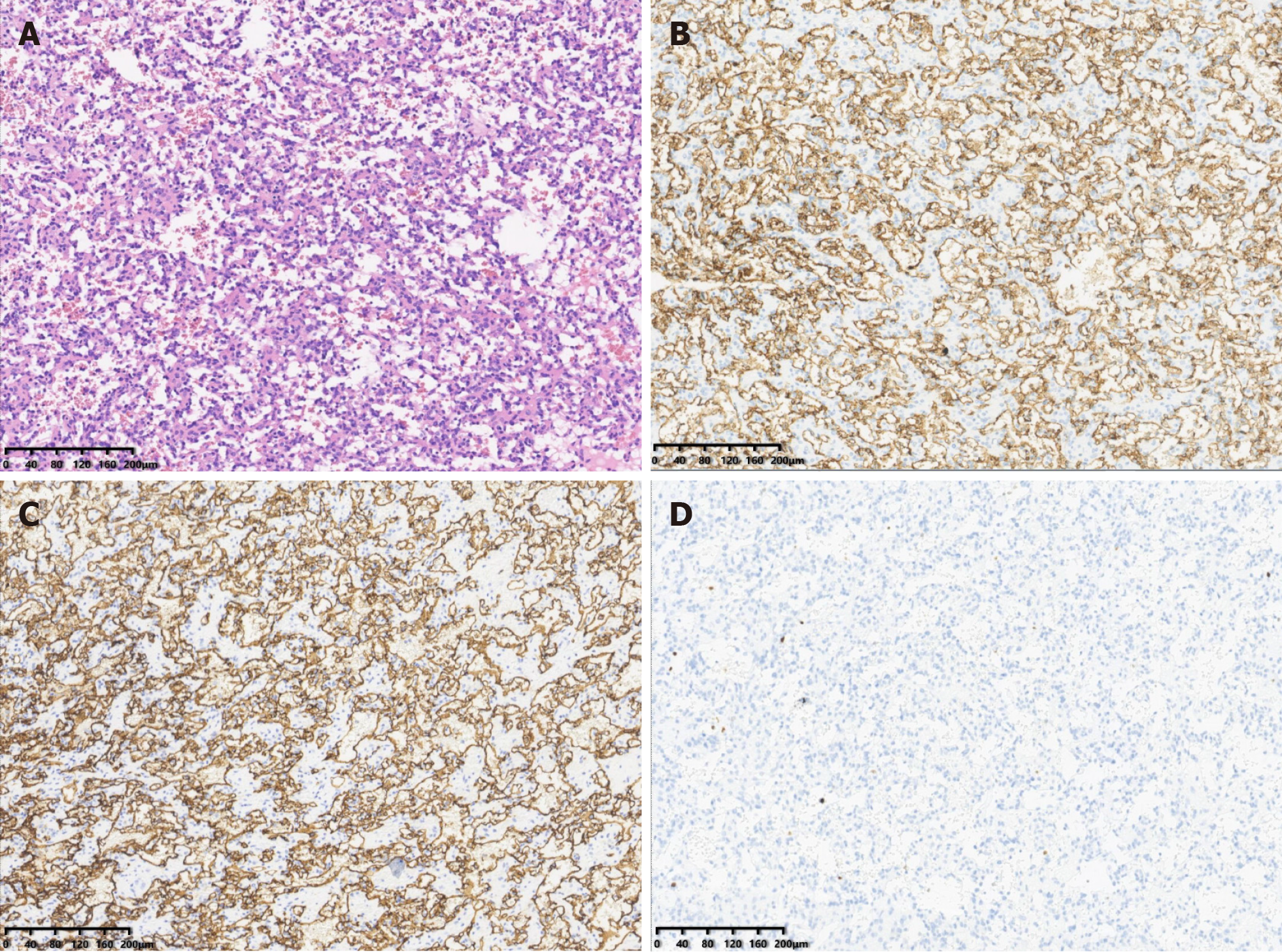
Figure 4 Pathological findings of the anastomosing hemangioma in the left kidney.
A: Histopathological section (hematoxylin and eosin staining); B: Immunohistochemistry results showing the expression of CD31; C: Immunohistochemistry results showing the expression of CD34; D: Immunohistochemistry results showing the expression of Ki-67.
- Citation: Chen J, Cai DM. Renal anastomosing hemangioma following partial nephrectomy for renal cell carcinoma: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(19): 4010-4015
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i19/4010.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.4010