Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jul 6, 2024; 12(19): 3936-3941
Published online Jul 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3936
Published online Jul 6, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3936
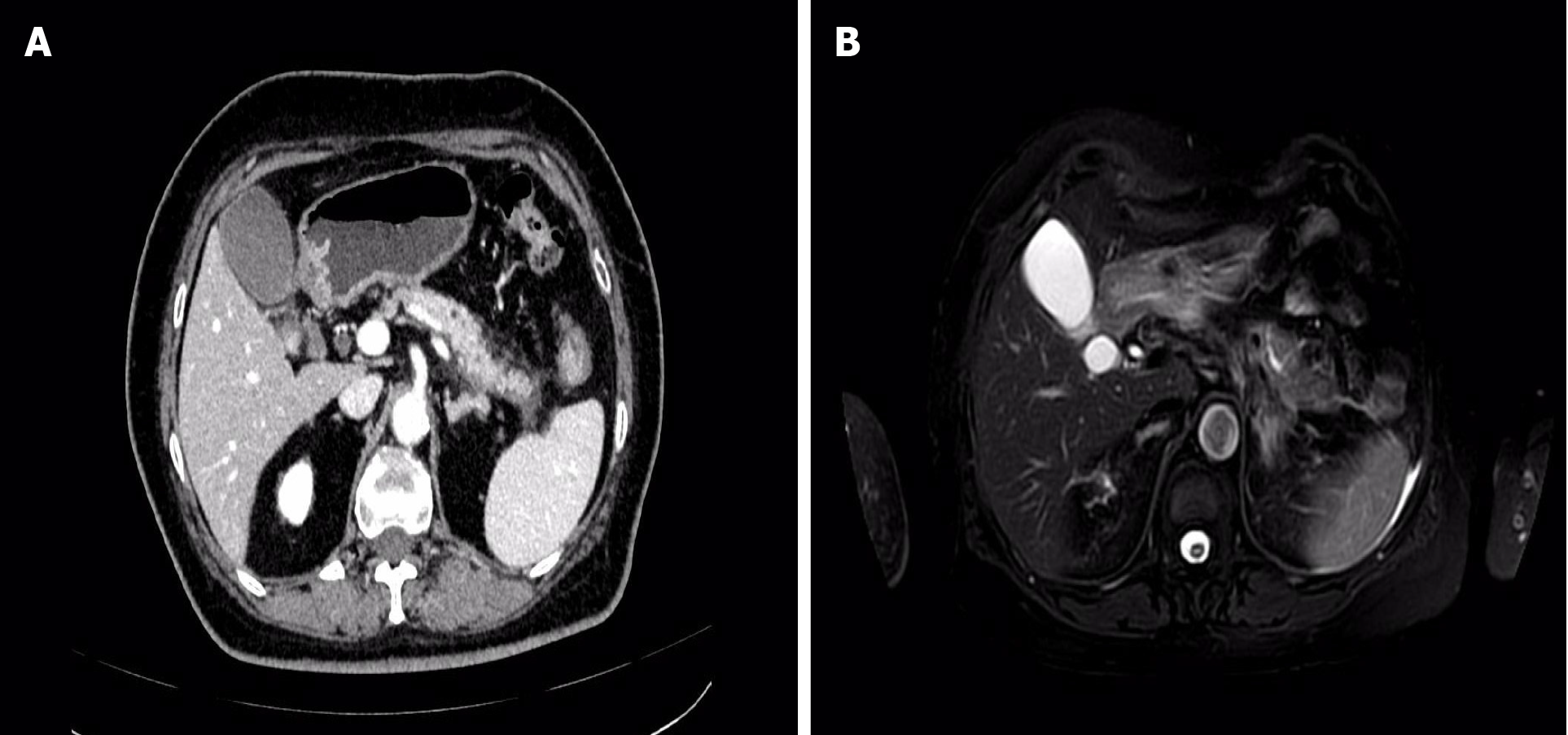
Figure 1 Imaging findings at the time of the patient's first episode of pancreatitis.
A: Enhanced computed tomography image; B: Enhanced magnetic resonance imaging + magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography image.
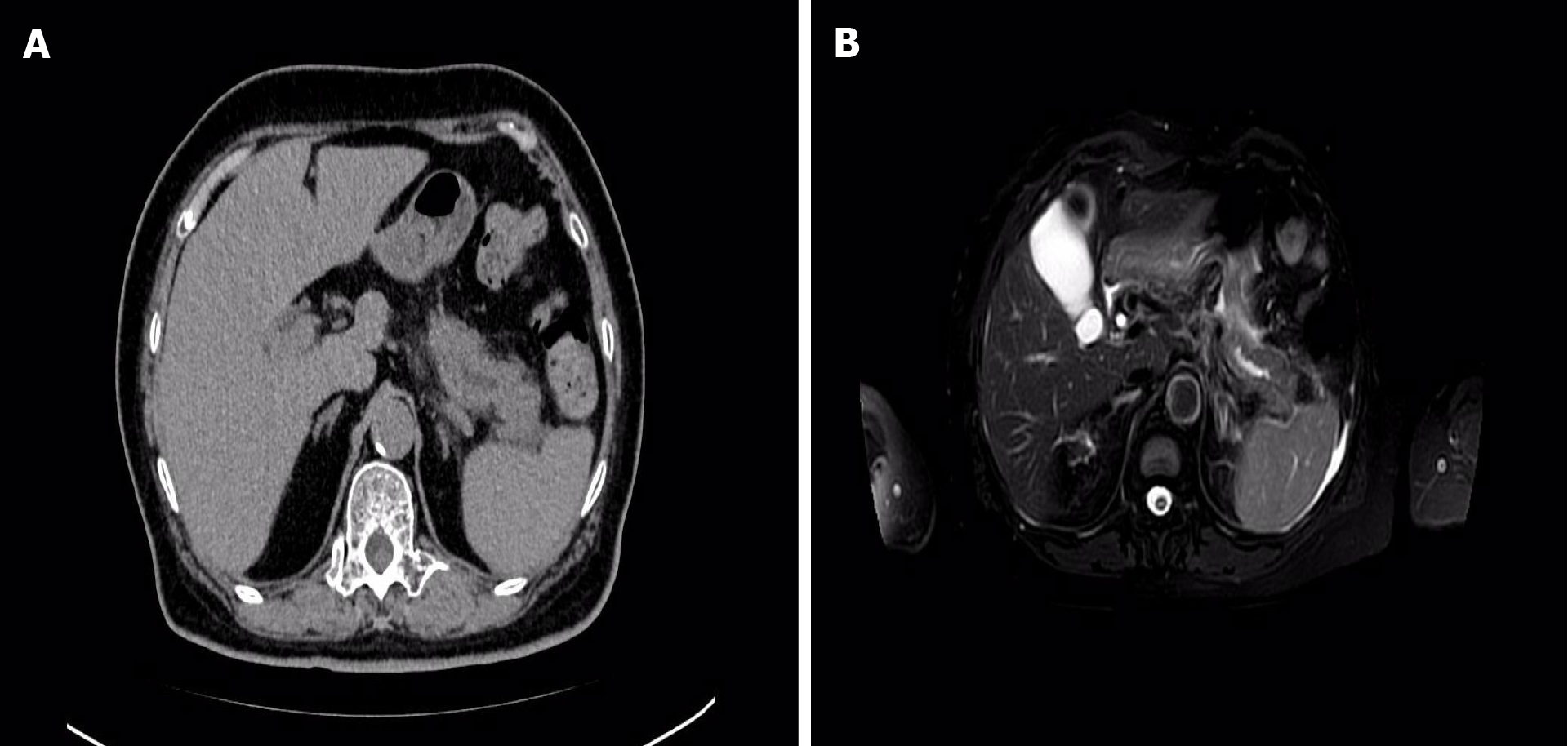
Figure 2 Imaging findings of the patient during another episode of pancreatitis.
A: Plain computed tomography images; B: Enhanced magnetic resonance imaging + magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography image.
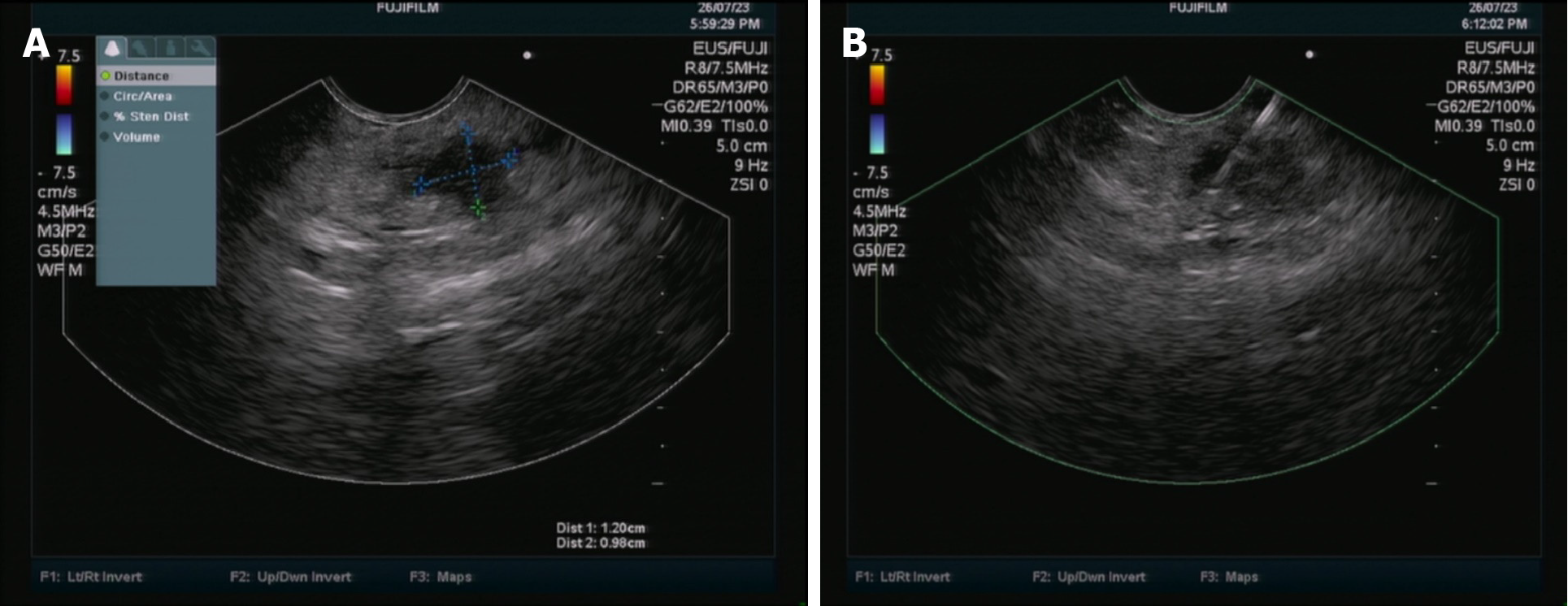
Figure 3 Endoscopic ultrasonography imaging findings of the patient.
A: Hypoechoic pancreatic mass image; B: endoscopic ultrasonography coupled with fine-needle aspiration images.
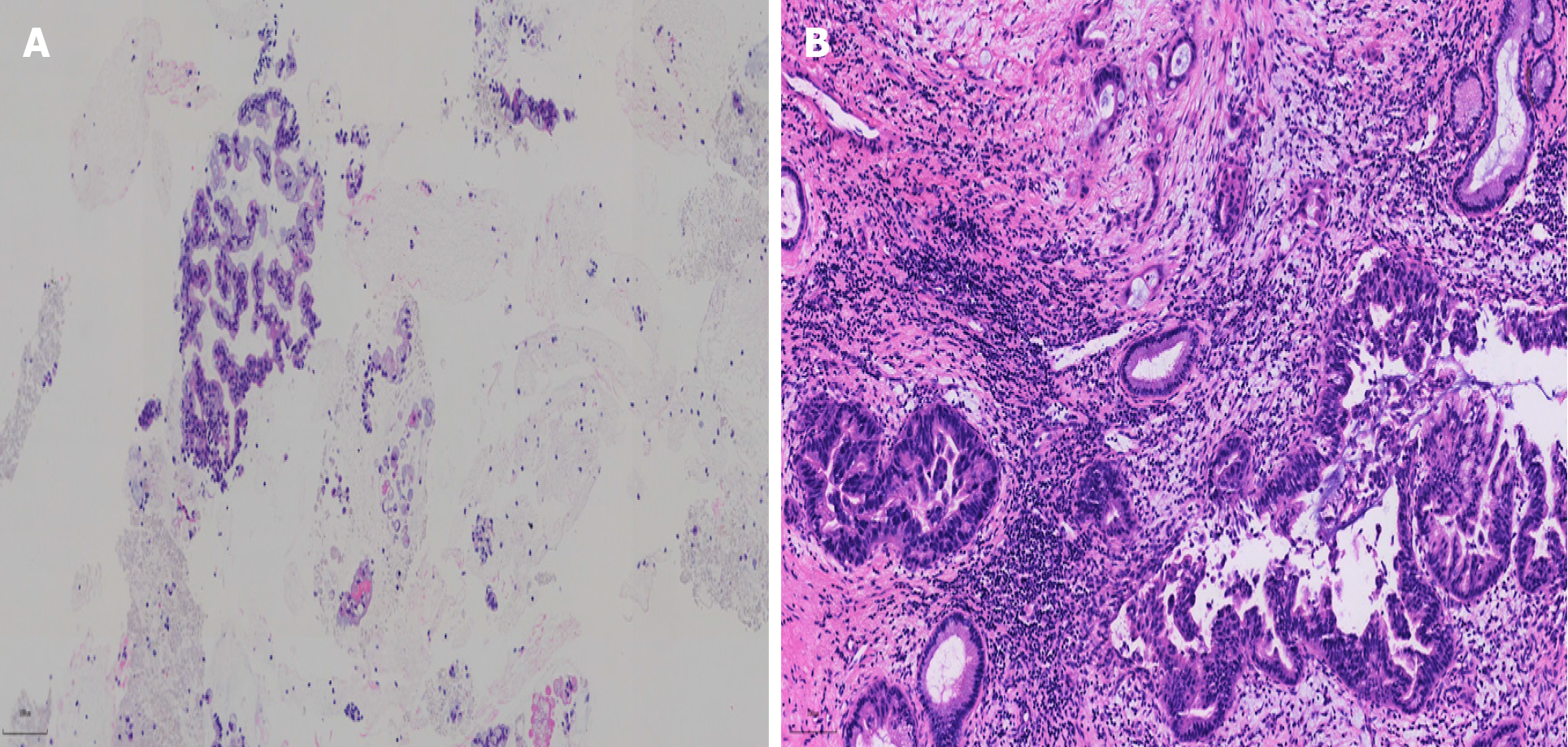
Figure 4 Pathological results of pancreatic masses after puncture and operation.
A: pathological picture of pancreatic mass after endoscopic ultrasonography coupled with fine-needle aspiration (magnification, 20 ×); B: Postoperative pathological picture of pancreatic mass (magnifying, 200 ×).
- Citation: Wei C, Li YC, Jin HT, Li DF, Wang LS, Yao J. Early detection of pancreatic cancer in patients with recurrent pancreatitis: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(19): 3936-3941
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i19/3936.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i19.3936