Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2024; 12(18): 3368-3377
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i18.3368
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i18.3368
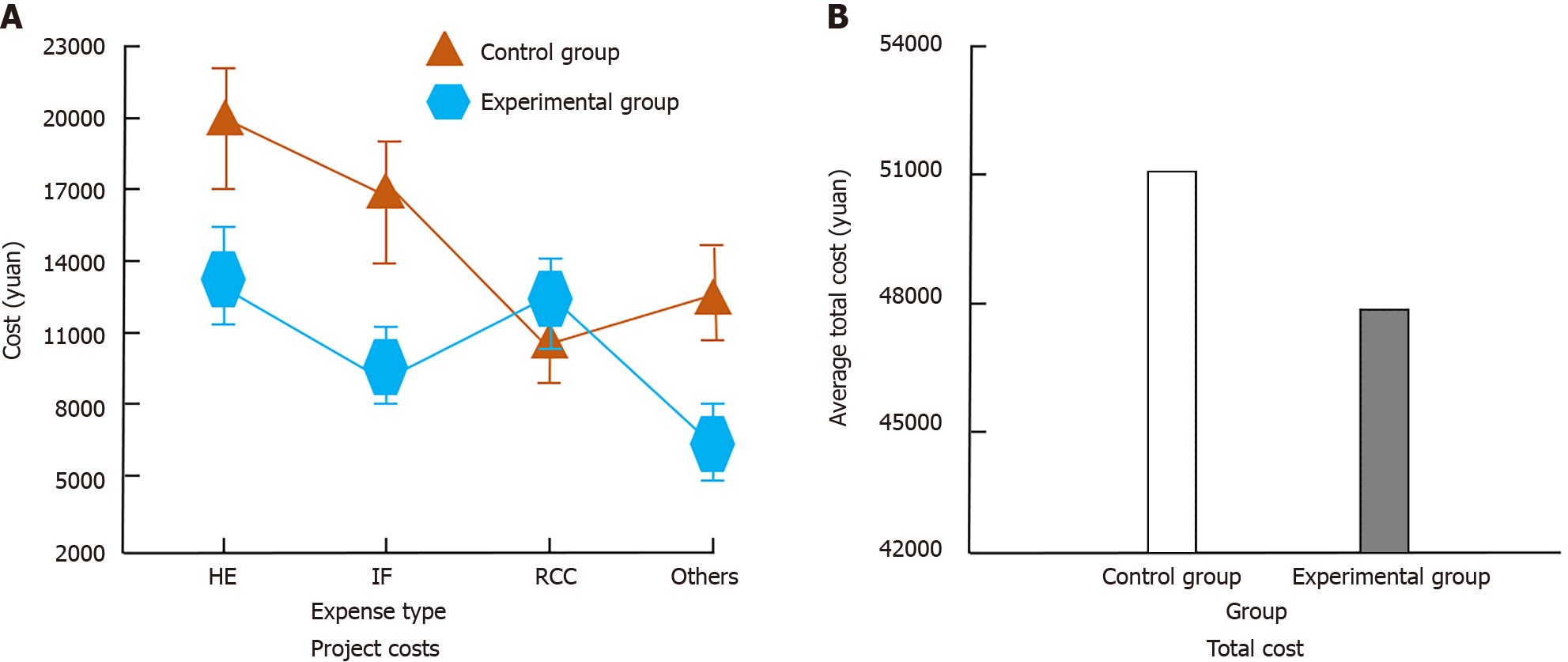
Figure 1 Patient treatment related expenses.
A: The cost of different projects for patients during treatment; B: The total cost of treatment for the patient. HE: Hematoxylin and eosin staining; IF: Immunofluorescence; RCC: Renal cell carcinoma.
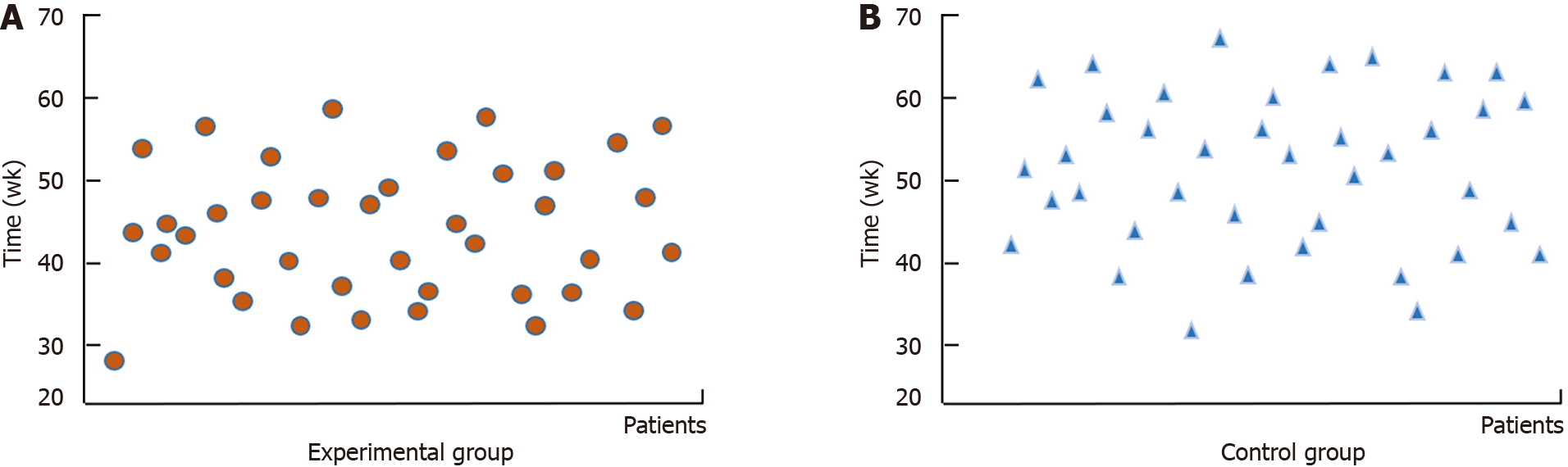
Figure 2 Patient recovery time.
A: The recovery time of the experimental group patients during treatment; B: The recovery time of the control group patients during treatment.
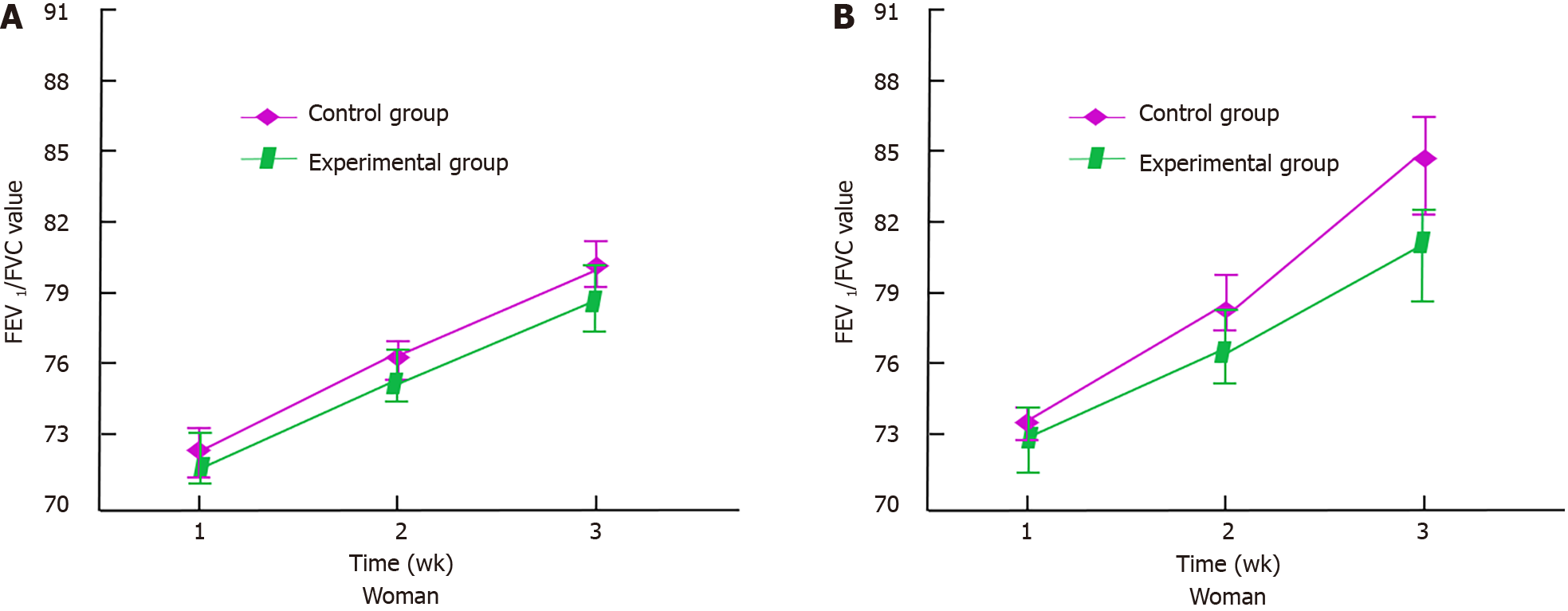
Figure 3 Patient Forced Expiratory Volume in the first second/Forced Vital Capacity value changes.
A: The changes in Forced Expiratory Volume in the first second/Forced Vital Capacity (FEV1/FVC) values of female patients during treatment; B: The changes in FEV1/FVC values of male patients during treatment. FEV1/FVC: Forced Expiratory Volume in the first second/Forced Vital Capacity.
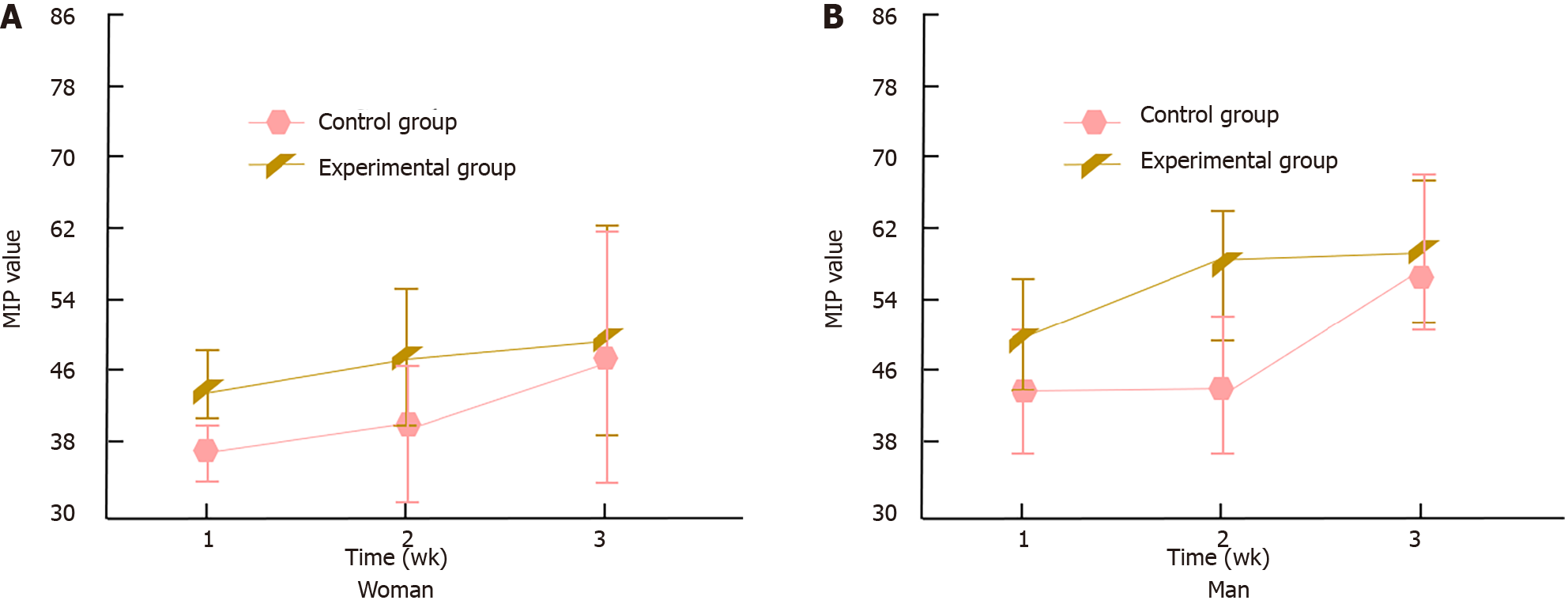
Figure 4 Changes in patient maximum inspiratory pressure values.
A: The changes in maximum inspiratory pressure (MIP) values of female patients during treatment; B: The changes in MIP values of male patients during treatment. MIP: Maximum inspiratory pressure.
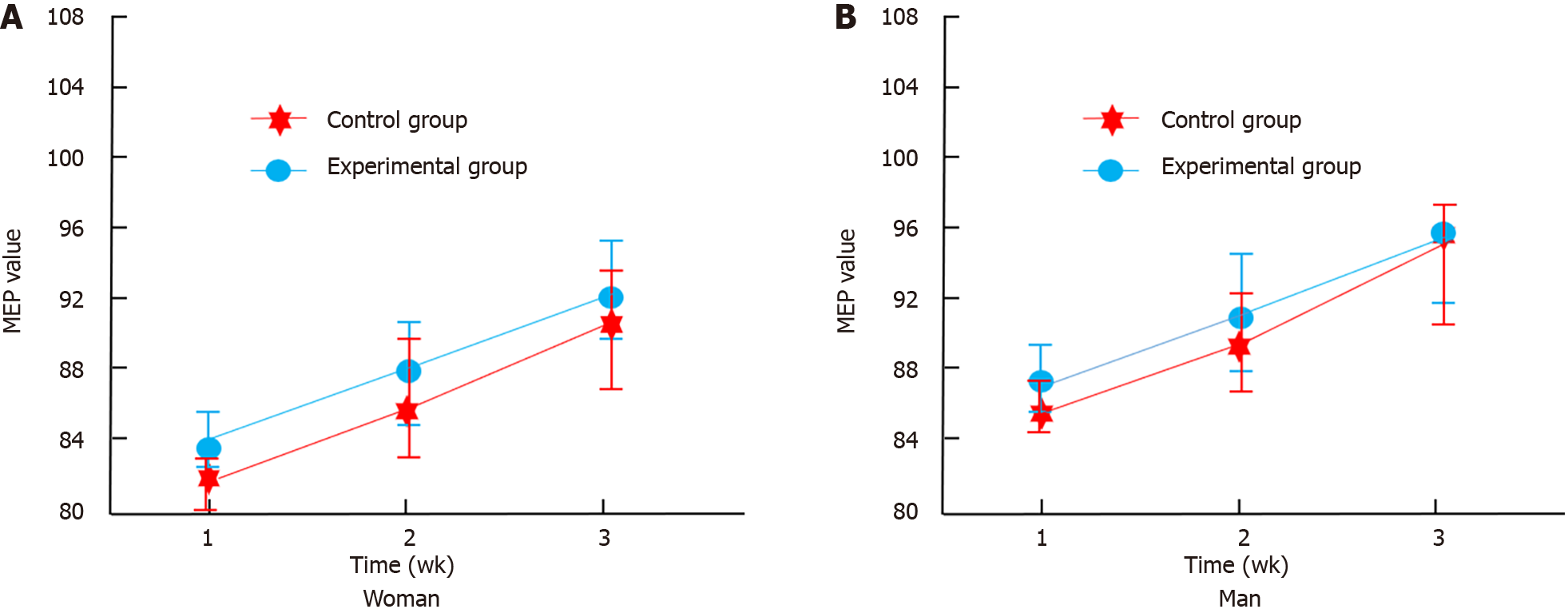
Figure 5 Changes in patient motor evoked potential values.
A: The changes in motor evoked potential (MEP) values of female patients during treatment; B: The changes in MEP values of male patients during treatment. MEP: Motor evoked potential.
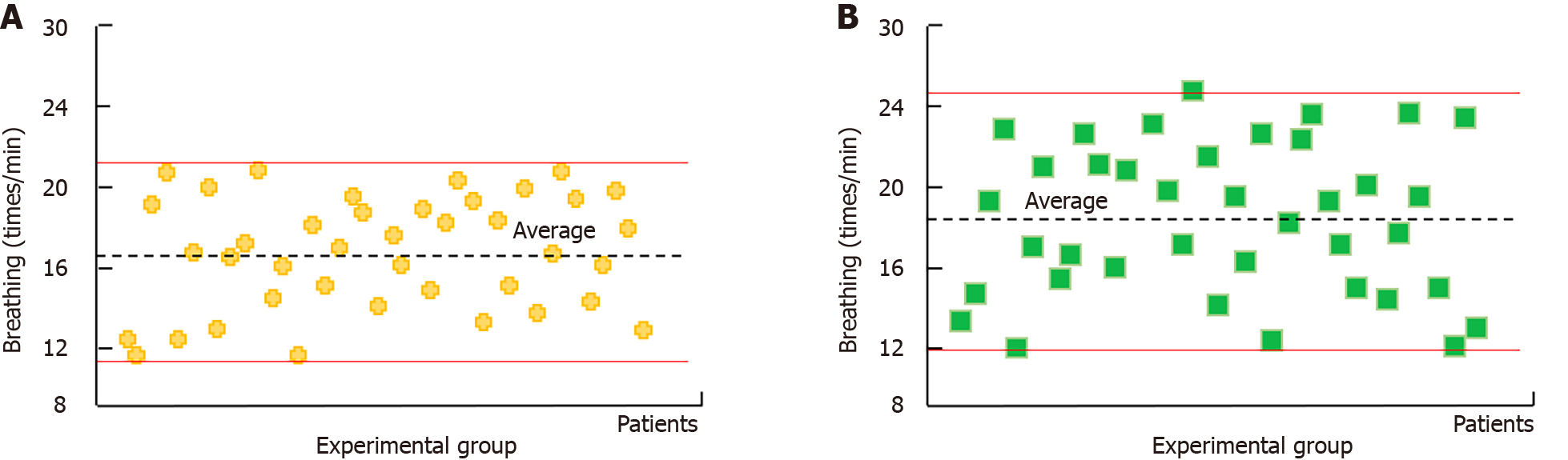
Figure 6 Patient’s average number of breaths per minute.
A: The average number of breaths per minute after surgery for patients in the experimental group; B: The average number of breaths per minute in the control group patients after surgery.
- Citation: Wang QL, Wang ZB, Zhu JF. Operation room nursing based on humanized nursing mode combined with nitric oxide on rehabilitation effect after lung surgery. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(18): 3368-3377
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i18/3368.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i18.3368