Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 26, 2024; 12(18): 3340-3350
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i18.3340
Published online Jun 26, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i18.3340
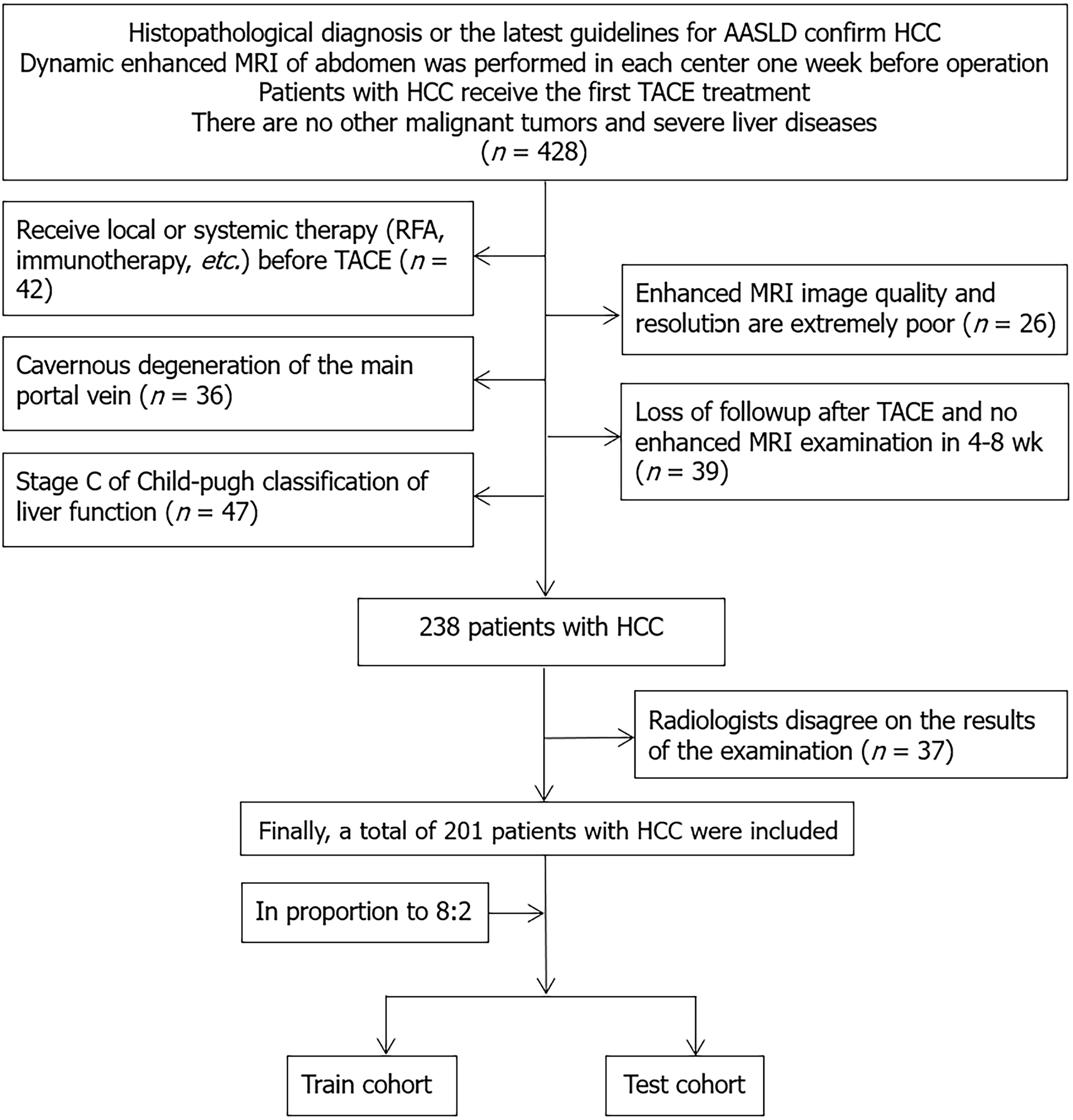
Figure 1 Flow chart of patient case screening.
HCC: Hepatocellular carcinoma; RFA: Radiofrequency ablation; TACE: Transarterial chemoembolization; MRI: Magnetic resonance imaging; AASLD: American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases.
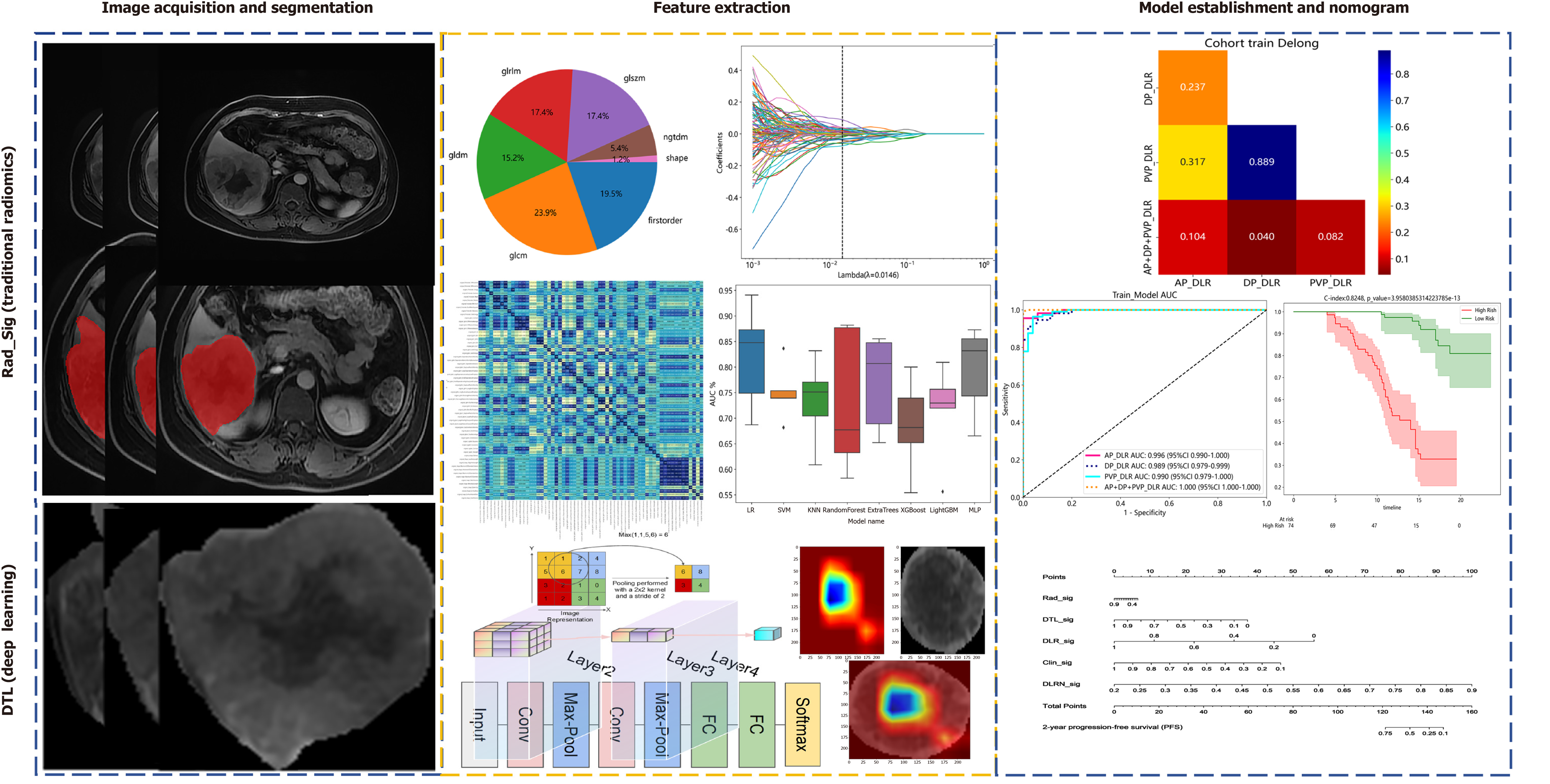
Figure 2 Workflow of radiomics and deep transfer learning.
DTL: Deep transfer learning; FC: Fully connected layer; AP: Arterial phase; DP: Delayed phase; PVP: Portal venous phase; DLR: Deep learning radiomics; SVM: Support vector machines; MLP: Multilayer perceptron.
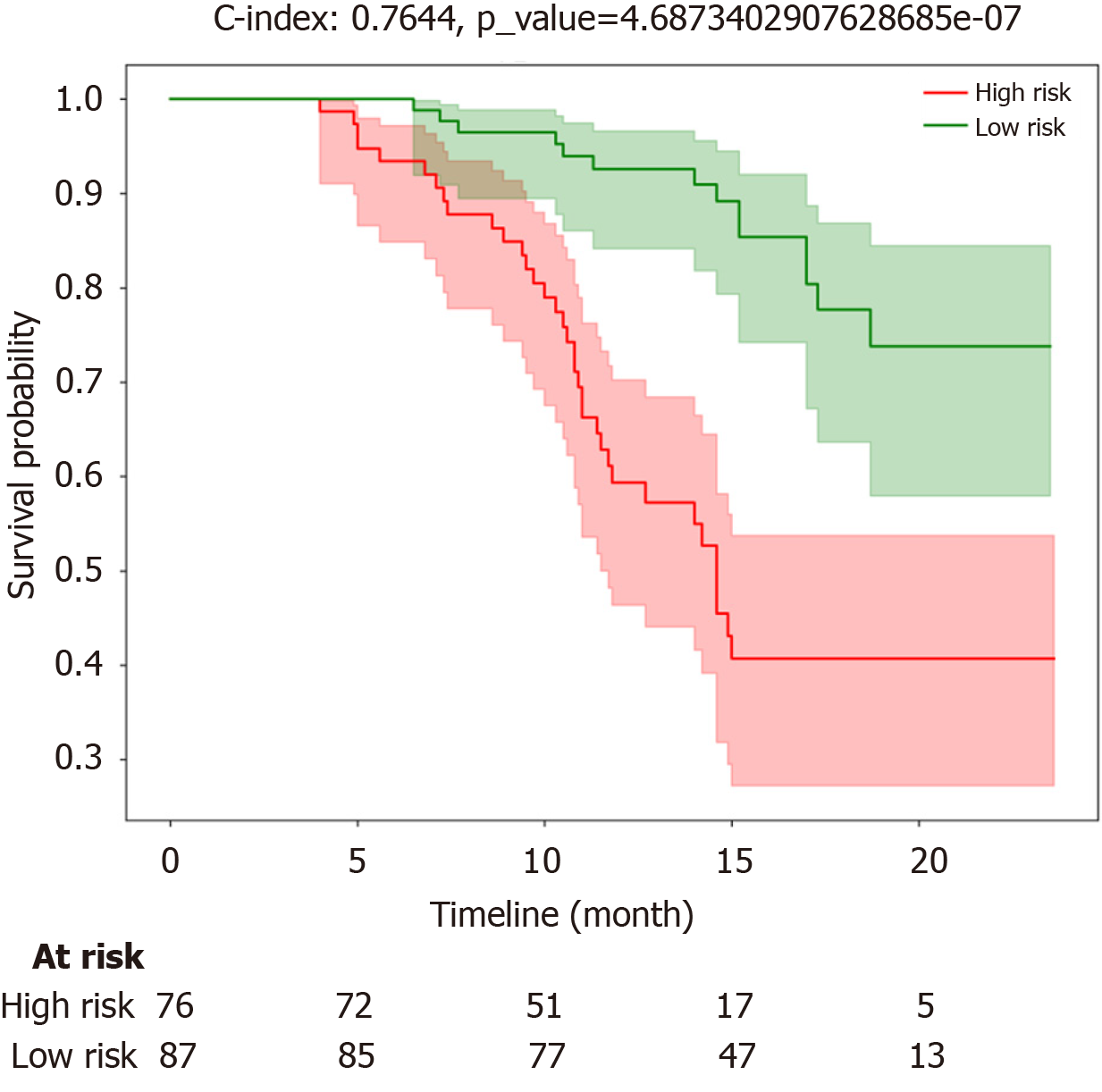
Figure 3 Progression-free survival curves for the high-risk group and low-risk group.
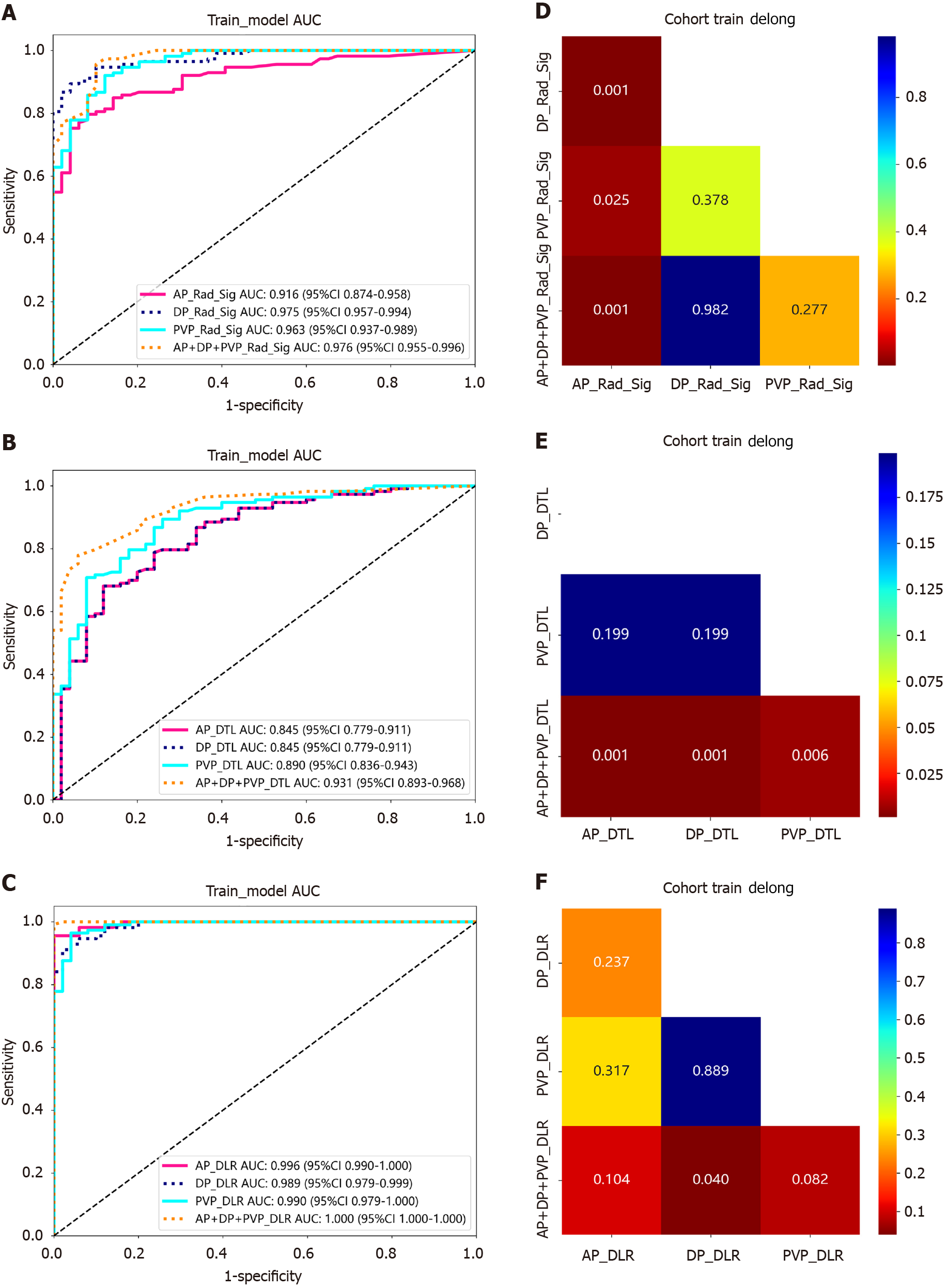
Figure 4 Performance of the models constructed with different radiomic features from various phases.
A1: Receiver operating characteristic (ROC) of traditional radiomics; B: ROC of deep transfer learning (DTL); C: ROC of deep learning radiomics (DLR; traditional radiomics +DTL); D: Delong test of traditional radiomics; E: Delong test of deep DTL; F: Delong test of DLR (traditional radiomics +DTL). DTL: Deep transfer learning; AP: Arterial phase; DP: Delayed phase; PVP: Portal venous phase; DLR: Deep learning radiomics; AUC: Area under the curve.
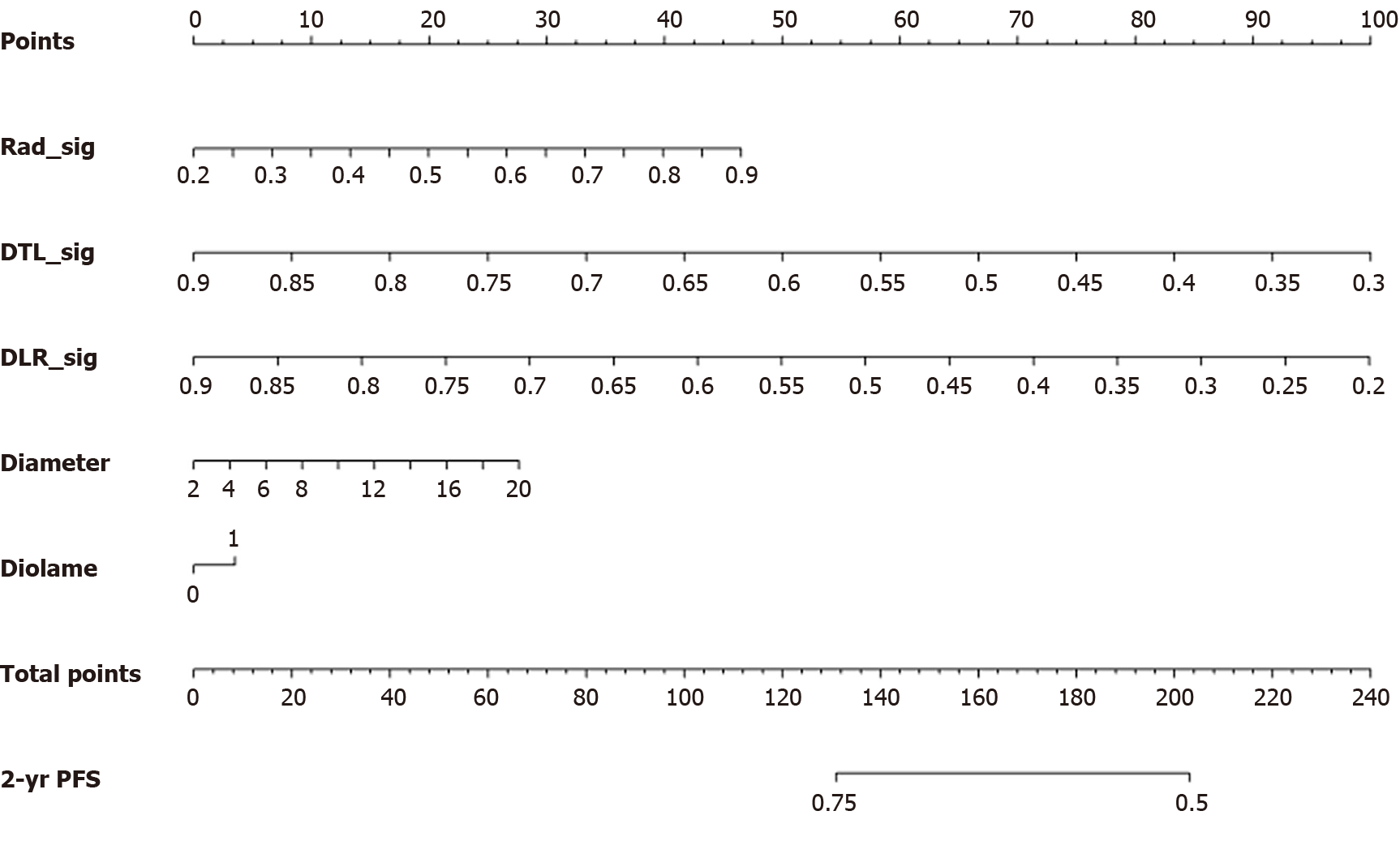
Figure 5 Line charts illustrating predictions of patients' 2-year progression-free survival probabilities using different multiphase radiomic features and multifactorial regression models.
DTL: Deep transfer learning; DLR: Deep learning radiomics; PFS: Progression-free survival.
- Citation: Guan QL, Zhang HX, Gu JP, Cao GF, Ren WX. Omics-imaging signature-based nomogram to predict the progression-free survival of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(18): 3340-3350
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i18/3340.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i18.3340