Copyright
©The Author(s) 2024.
World J Clin Cases. Jun 16, 2024; 12(17): 3130-3137
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3130
Published online Jun 16, 2024. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3130
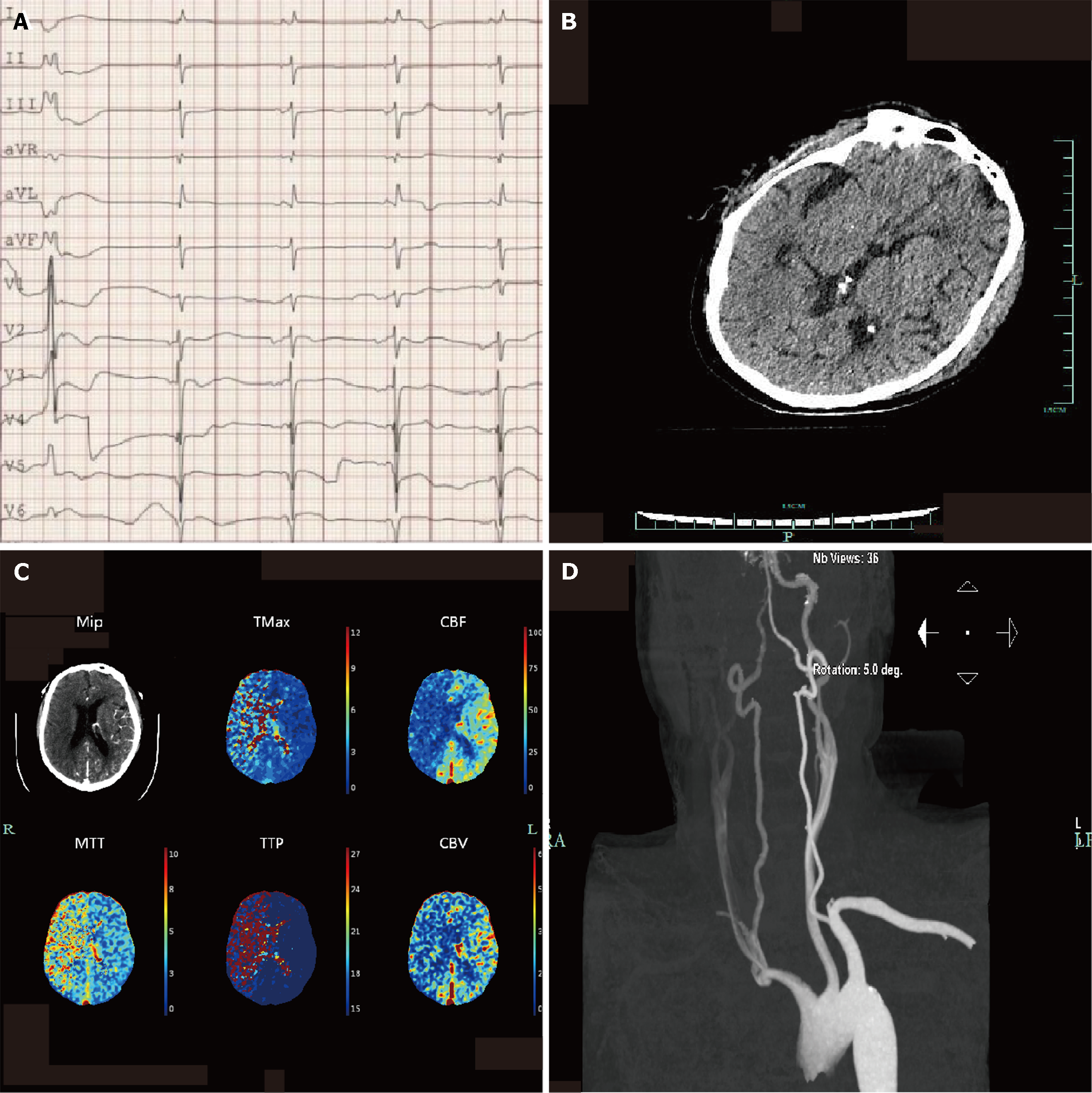
Figure 1 The initial neurological assessment on the day of admission could not confirm the patient's mental state.
After the administration of naloxone and flumazenil, the Glasgow Coma Scale score was 2 + endotracheal tube + 3, and we completed further imaging examination. A: Electrocardiogram showing sinus rhythm, atrial rhythm, premature ventricular beats, occasional junctional rhythm, acute anterior wall and anterior wall myocardial infarction, and atrioventricular block; B: Head computed tomography images showing no obvious signs of stroke; C: Computed tomography perfusion indicating cerebral infarction and poor compensatory blood flow and ischemic hypoperfusion in the right large frontoparietal and temporal lobe; D: Carotid artery computed tomography angiography image showing sparse blood flow in the right common carotid artery, M1 segment of the right middle cerebral artery, and vertebral artery blood.
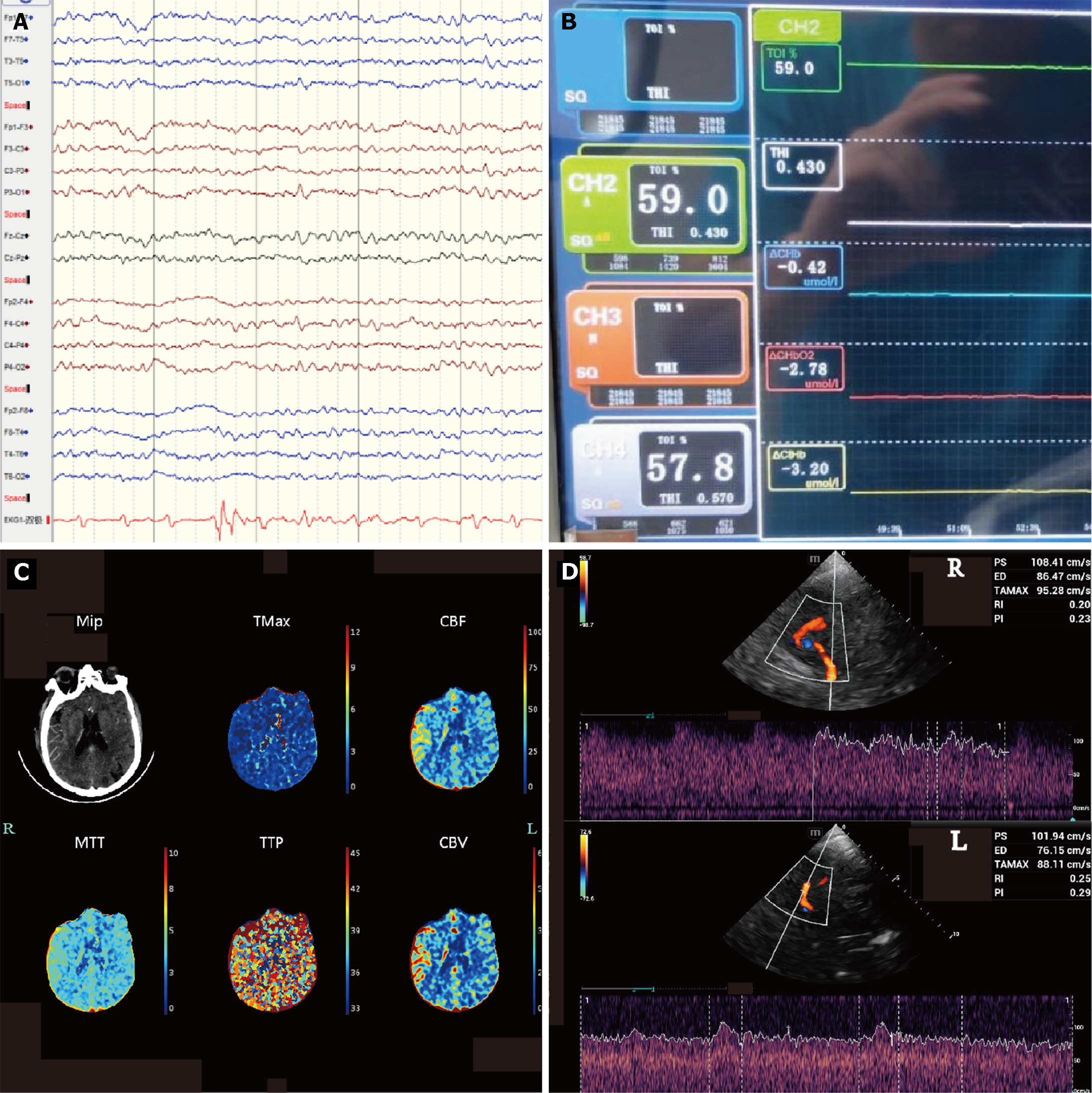
Figure 2 To identify cerebral pseudoinfarction, we used other tests for validation.
A: Continuous electroencephalogram showing no significant abnormality of the bilateral cerebral cortex; B: Near-infrared spectroscopy indicating no significant change in the oxygen value on both sides of the brain tissue. CH2 (left forehead): The value is 59.0%. CH4 (right forehead): the value is 57.8%; C: Computed tomography perfusion (CTP) (repeated) image showing that the perfusion of both cerebral hemispheres and the cerebellum on both sides was symmetrical. After a decrease of extracorporeal membrane oxygenation flow to 2 L/min, the CTP was reviewed again; D: Bedside transcranial Doppler images indicating pulsatile flow in the right middle cerebral artery and advection in the left middle cerebral artery with similar flow rates. The left middle cerebral artery exhibited advection, with a peak systolic (PS) velocity of 101.94 cm/s, end-diastolic (ED) velocity of 76.15 cm/s, time average maximum velocity (TAMAX) velocity of 88.11 cm/s, resistive index (RI) of 0.25, and pulsative index (PI) of 0.29. The right middle cerebral artery demonstrated beat flow, with PS at 108.41 cm/s, ED at 86.47 cm/s, TAMAX at 95.28 cm/s, RI at 0.20, and PI at 0.23.
- Citation: Xu M, Yan JY, Jin JJ, Li T. Cerebral pseudoinfarction due to venoarterial extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: A case report. World J Clin Cases 2024; 12(17): 3130-3137
- URL: https://www.wjgnet.com/2307-8960/full/v12/i17/3130.htm
- DOI: https://dx.doi.org/10.12998/wjcc.v12.i17.3130